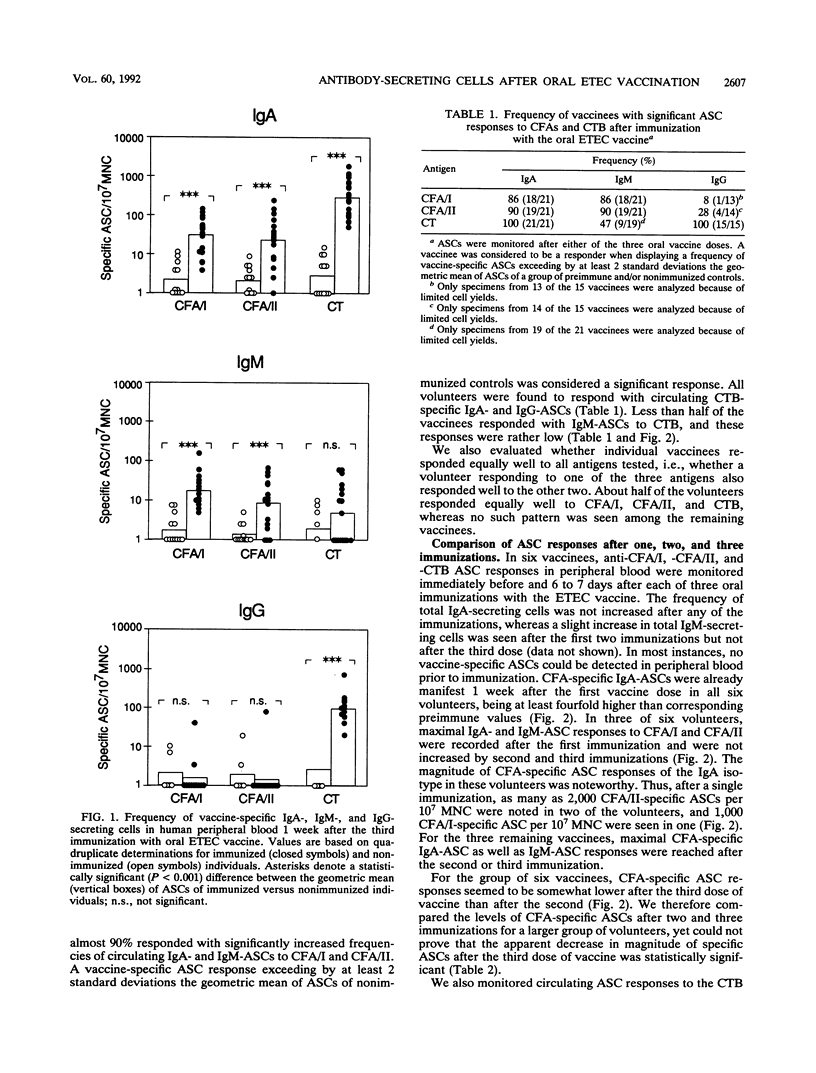
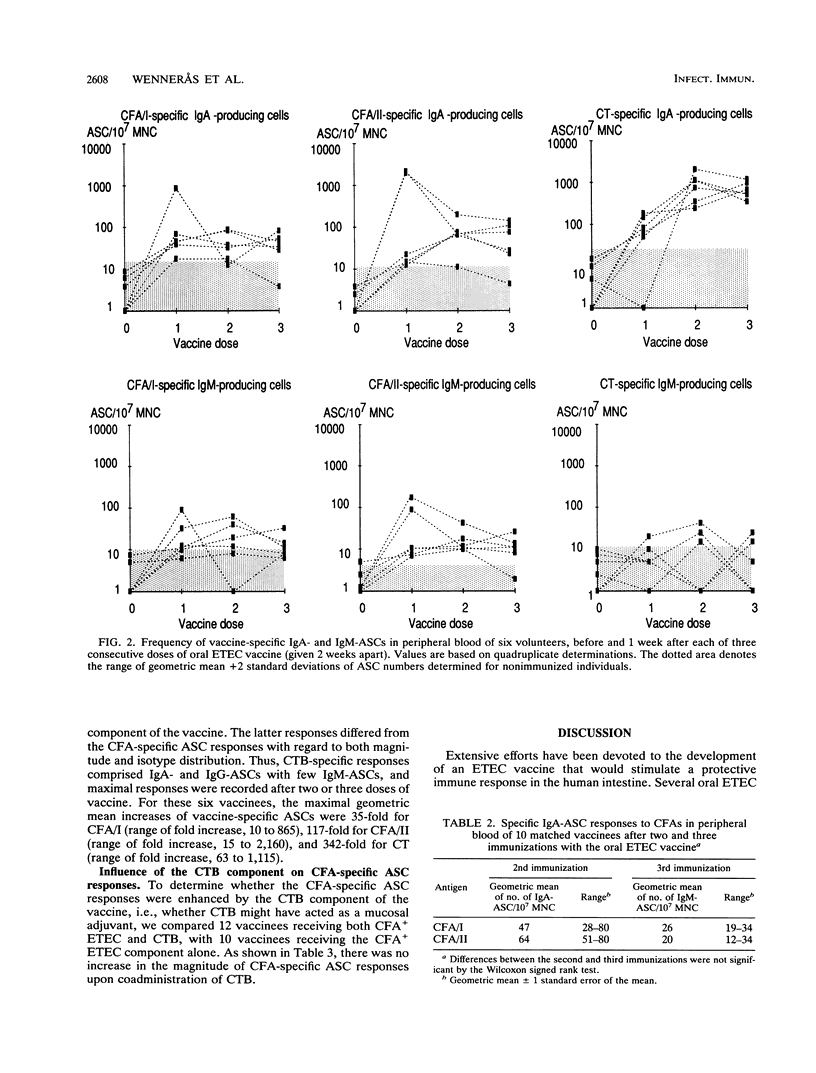
Abstract
Vaccine antigen-specific antibody-secreting cell (ASC) responses in peripheral blood of healthy adult volunteers were studied after oral immunization with a prototype enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) vaccine by means of the enzyme-linked immunospot technique. Three doses of vaccine consisting of formalin-killed ETEC bacteria expressing fimbrial colonization factor antigens I and II (CFA/I and CFA/II) in combination with purified cholera toxin B subunit (CTB) were given 2 weeks apart. The ASC responses were detected 7 days after each immunization. Immunoglobulin A (IgA) was the predominant isotype produced by CFA/I- as well as CFA/II-specific ASCs. Moderate CFA/I- and CFA/II-specific IgM-secreting ASC (IgM-ASC) responses were also seen, whereas IgG-ASC responses to either of the CFAs were negligible. The ASC responses to CTB, on the other hand, comprised both IgA- and IgG-ASCs, with few if any specific IgM-ASCs. Almost 90% of the volunteers developed CFA-specific ASC responses after vaccination. Maximal CFA-specific ASC responses were usually observed after a single dose or two doses of vaccine. A third dose of vaccine did not result in increased but rather resulted in decreased magnitudes of CFA-specific ASC responses. Furthermore, it was found that CTB did not function as a mucosal adjuvant, since CFA-specific ASC responses were not enhanced by the simultaneous administration of CTB. These results suggest that two oral doses of ETEC vaccine induce a strong mucosal immune response, as reflected by the presence of large numbers of antigen-specific mucosal B cell immunoblasts in the blood.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clancy R. L., Cripps A. W., Husband A. J., Buckley D. Specific immune response in the respiratory tract after administration of an oral polyvalent bacterial vaccine. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):491–496. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.491-496.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens J. D., Sack D. A., Harris J. R., Chakraborty J., Khan M. R., Stanton B. F., Kay B. A., Khan M. U., Yunus M., Atkinson W. Field trial of oral cholera vaccines in Bangladesh. Lancet. 1986 Jul 19;2(8499):124–127. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91944-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens J. D., Sack D. A., Harris J. R., Chakraborty J., Neogy P. K., Stanton B., Huda N., Khan M. U., Kay B. A., Khan M. R. Cross-protection by B subunit-whole cell cholera vaccine against diarrhea associated with heat-labile toxin-producing enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: results of a large-scale field trial. J Infect Dis. 1988 Aug;158(2):372–377. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.2.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C. C., Nilsson L. A., Nygren H., Ouchterlony O., Tarkowski A. A solid-phase enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay for enumeration of specific antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C., Moldoveanu Z., Mestecky J., Nilsson L. A., Ouchterlony O. A novel two colour ELISPOT assay. I. Simultaneous detection of distinct types of antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Nov 25;115(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C., Prince S. J., Michalek S. M., Jackson S., Russell M. W., Moldoveanu Z., McGhee J. R., Mestecky J. IgA antibody-producing cells in peripheral blood after antigen ingestion: evidence for a common mucosal immune system in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2449–2453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C., Svennerholm A. M., Quiding M., Jonsson R., Holmgren J. Antibody-producing cells in peripheral blood and salivary glands after oral cholera vaccination of humans. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):996–1001. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.996-1001.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge J. H., Gilley R. M., Staas J. K., Moldoveanu Z., Meulbroek J. A., Tice T. R. Biodegradable microspheres: vaccine delivery system for oral immunization. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;146:59–66. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74529-4_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W. Cholera toxin feeding did not induce oral tolerance in mice and abrogated oral tolerance to an unrelated protein antigen. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):2892–2897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Clegg S., Pauley J. A. Purification and characterization of the CFA/I antigen of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):738–748. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.738-748.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Graham D. Y., Evans D. J., Jr Administration of purified colonization factor antigens (CFA/I, CFA/II) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to volunteers. Response to challenge with virulent enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):934–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest B. D. Identification of an intestinal immune response using peripheral blood lymphocytes. Lancet. 1988 Jan 16;1(8577):81–83. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90284-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis M. L., Moss J., Fitz T. A., Mond J. J. cAMP-independent effects of cholera toxin on B cell activation. I. A possible role for cell surface ganglioside GM1 in B cell activation. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3162–3169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gothefors L., Ahrén C., Stoll B., Barua D. K., Orskov F., Salek M. A., Svennerholm A. M. Presence of colonization factor antigens on fresh isolates of fecal Escherichia coli: a prospective study. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1128–1133. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson H. A., Holmgren J., Svennerholm L. Ultrastructural localization of cell membrane GM1 ganglioside by cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3782–3786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husband A. J., Gowans J. L. The origin and antigen-dependent distribution of IgA-containing cells in the intestine. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1146–1160. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantele A., Arvilommi H., Jokinen I. Specific immunoglobulin-secreting human blood cells after peroral vaccination against Salmonella typhi. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1126–1131. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantele A., Kantele J. M., Arvilommi H., Mäkelä P. H. Active immunity is seen as a reduction in the cell response to oral live vaccine. Vaccine. 1991 Jun;9(6):428–431. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(91)90130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Ristaino P., Marley G., Smyth C., Knutton S., Boedeker E., Black R., Young C., Clements M. L., Cheney C. Coli surface antigens 1 and 3 of colonization factor antigen II-positive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: morphology, purification, and immune responses in humans. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):409–420. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.409-420.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Vidal Y., Svennerholm A. M. Monoclonal antibodies against the different subcomponents of colonization factor antigen II of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1906–1912. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1906-1912.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N., Strober W. Cholera toxin promotes B cell isotype differentiation. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3781–3787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M. R., Bienenstock J. Evidence for a common mucosal immunologic system. I. Migration of B immunoblasts into intestinal, respiratory, and genital tissues. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1892–1898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio A. M., Schwarting G. A., Robbins P. W. Glycolipids of the mouse peritoneal macrophage. Alterations in amount and surface exposure of specific glycolipid species occur in response to inflammation and tumoricidal activation. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1114–1125. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., McGhee J. R., Arnold R. R., Michalek S. M., Prince S. J., Babb J. L. Selective induction of an immune response in human external secretions by ingestion of bacterial antigen. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):731–737. doi: 10.1172/JCI108986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltola H., Siitonen A., Kyrönseppä H., Simula I., Mattila L., Oksanen P., Kataja M. J., Cadoz M. Prevention of travellers' diarrhoea by oral B-subunit/whole-cell cholera vaccine. Lancet. 1991 Nov 23;338(8778):1285–1289. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92590-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiding M., Nordström I., Kilander A., Andersson G., Hanson L. A., Holmgren J., Czerkinsky C. Intestinal immune responses in humans. Oral cholera vaccination induces strong intestinal antibody responses and interferon-gamma production and evokes local immunological memory. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):143–148. doi: 10.1172/JCI115270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J., Sack D. A. Development of oral vaccines against enterotoxinogenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea. Vaccine. 1989 Jun;7(3):196–198. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(89)90228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Jertborn M., Gothefors L., Karim A. M., Sack D. A., Holmgren J. Mucosal antitoxic and antibacterial immunity after cholera disease and after immunization with a combined B subunit-whole cell vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jun;149(6):884–893. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.6.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Wennerås C., Holmgren J., McConnell M. M., Rowe B. Roles of different coli surface antigens of colonization factor antigen II in colonization by and protective immunogenicity of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):341–346. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.341-346.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi I., Okahashi N., Matsushita K., Tokuda M., Kanamoto T., Munekata E., Russell M. W., Koga T. Immunogenicity and protective effect against oral colonization by Streptococcus mutans of synthetic peptides of a streptococcal surface protein antigen. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):332–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S., Samegai Y., Kurata H., Nagamine T., Aizawa C., Kurata T. Protection against influenza virus infection by vaccine inoculated intranasally with cholera toxin B subunit. Vaccine. 1988 Oct;6(5):409–413. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(88)90140-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Verg L., Herrington D. A., Murphy J. R., Wasserman S. S., Formal S. B., Levine M. M. Specific immunoglobulin A-secreting cells in peripheral blood of humans following oral immunization with a bivalent Salmonella typhi-Shigella sonnei vaccine or infection by pathogenic S. sonnei. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):2002–2004. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.2002-2004.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Stone J., Bergmann K. C., Khakoo R., Lazzell V., Jacknowitz A., Waldman E. R., Howard S. Secretory antibody following oral influenza immunization. Am J Med Sci. 1986 Dec;292(6):367–371. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198612000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Isselbacher K. J., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules: effect of oral immunization. Science. 1972 Aug 18;177(4049):608–610. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4049.608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarchoan R., Murphy B. R., Strober W., Clements M. L., Nelson D. L. In vitro production of anti-influenza virus antibody after intranasal inoculation with cold-adapted influenza virus. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1958–1963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



