Abstract
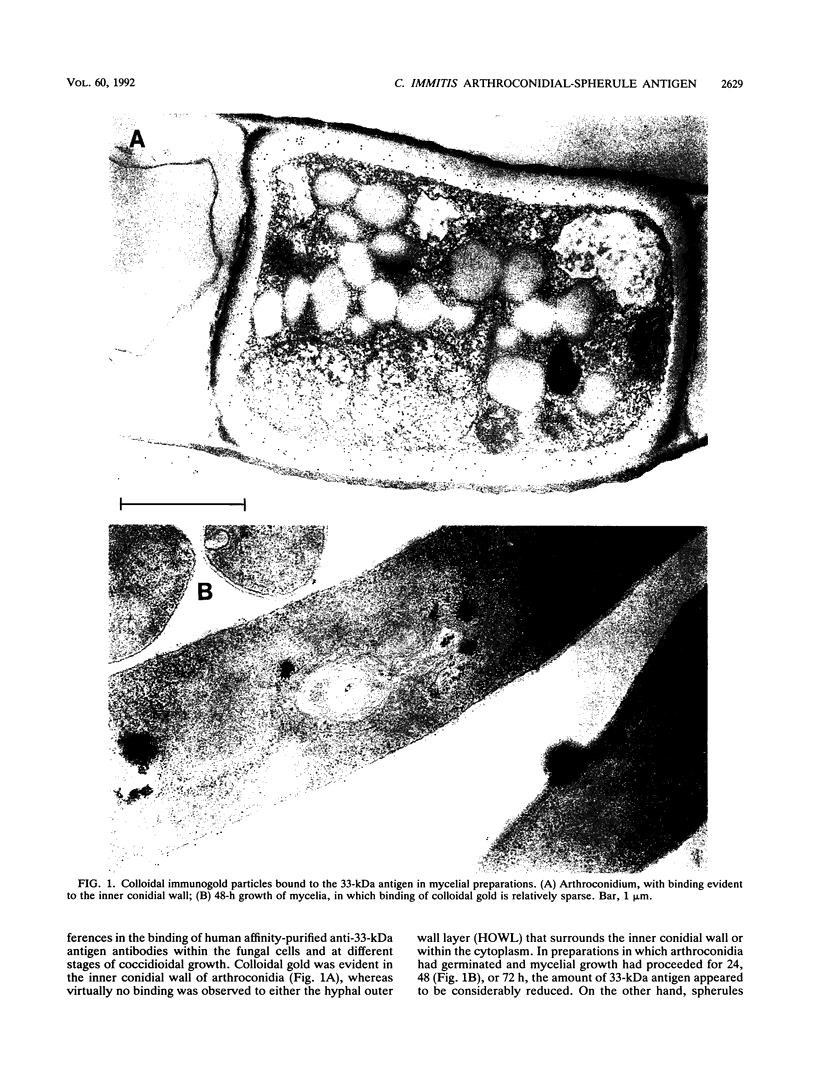
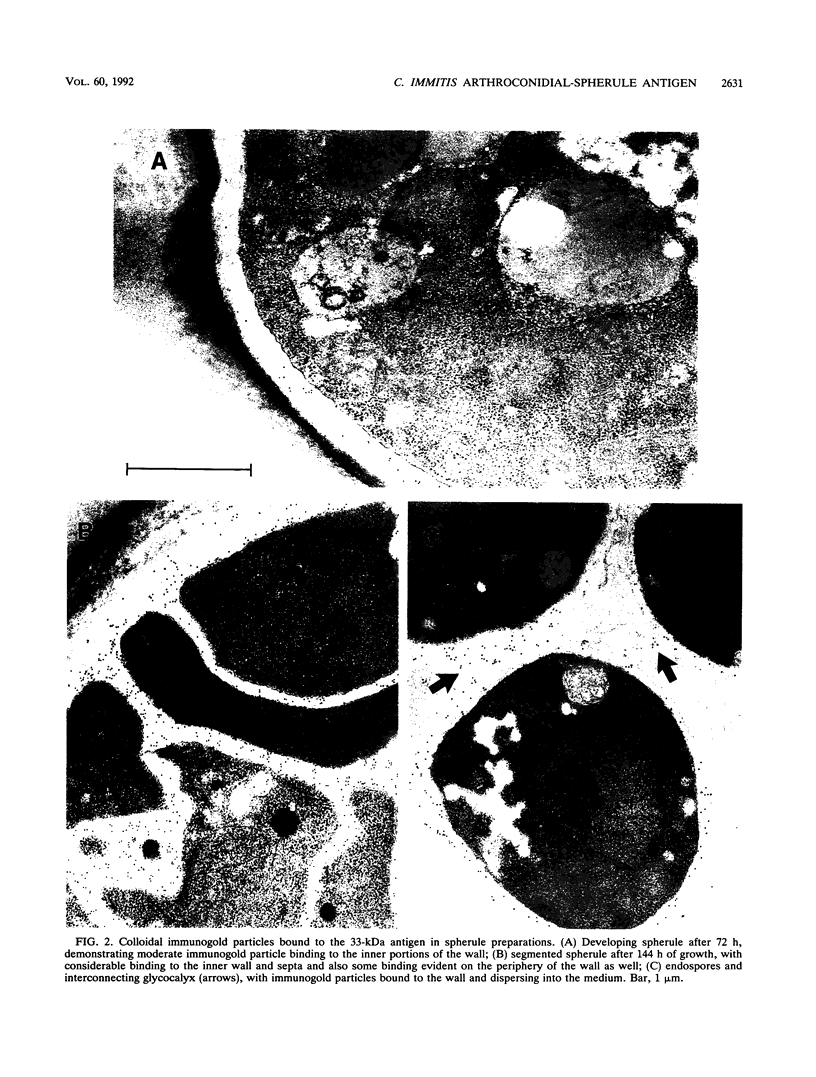
A 33-kDa protein antigen purified from spherules of Coccidioides immitis was analyzed for ultrastructural localization and for binding to serum antibodies from infected or immunized humans. By using colloidal gold detection of affinity-purified anti-33-kDa protein antibodies, electron photomicrographs showed binding to the inner cell wall of arthroconidia and spherules and to the septa and glycocalyx surrounding endospores. Enzyme immunoassay measurements also demonstrated that the antigen was most abundant in mature spherules. Of 37 patients with coccidioidomycosis but without concurrent human immunodeficiency virus infections, all but 2 demonstrated immunoglobulin M (IgM) (usually with early infection) or IgG antibodies for the 33-kDa antigen. In contrast, only one of four HIV-infected patients with active coccidioidal infections demonstrated antibody. On the other hand, 107 of 108 patients without evident coccidioidomycosis and 15 of 16 patients with histoplasmosis did not have similar antibodies, indicating a high degree of specificity. Immunization of humans with a spherule vaccine produced IgM responses to this antigen that were not evident in placebo recipients.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaman L. V., Pappagianis D., Benjamini E. Mechanisms of resistance to infection with Coccidioides immitis in mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):681–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.681-685.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Pappagianis D., Benjamini E. Significance of T cells in resistance to experimental murine coccidioidomycosis. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):580–585. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.580-585.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun D. L., Osir E. O., Dugger K. O., Galgiani J. N., Law J. H. Humoral antibody responses to specific antigens of Coccidioides immitis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):265–272. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coalson J. J., Winter V. T., Martin H. M., King R. J. Colloidal gold immunoultrastructural localization of rat surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Feb;133(2):230–237. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. M., Galgiani J. N., Potter D., Ogden D. A. Coccidioidomycosis in renal replacement therapy. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Mar;142(3):489–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kirkland T. N., Franco M., Zhu S., Yuan L., Sun S. H., Hearn V. M. Immunoreactivity of a surface wall fraction produced by spherules of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2695–2701. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2695-2701.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kruse D., Seshan K. R. Antigen complex of Coccidioides immitis which elicits a precipitin antibody response in patients. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2434–2446. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2434-2446.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kruse D., Zhu S. W., Seshan K. R., Wheat R. W. Composition, serologic reactivity, and immunolocalization of a 120-kilodalton tube precipitin antigen of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):179–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.179-188.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Seshan K. R., Franco M., Bukownik E., Sun S. H., Hearn V. M. Isolation and morphology of an immunoreactive outer wall fraction produced by spherules of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2686–2694. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2686-2694.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Britt L. A. Antigenic identity of biologically active antigens in coccidioidin and spherulin. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2590–2596. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2590-2596.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Britt L. A., Michael R. A. Isolation of Coccidioides immitis F antigen by immunoaffinity chromatography with monospecific antiserum. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):227–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.227-232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan M. J., Cox R. A. Production and characterization of a monoclonal antibody to the complement fixation antigen of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2175–2180. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2175-2180.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan M. J., Cox R. A., Williams V., Woolley S. Development and characterization of a monoclonal antibody against the tube precipitin antigen of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1035–1039. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1035-1039.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J., Huppert M. Coccidioidomycosis: factors affecting the host-parasite interaction. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):372–390. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugger K. O., Galgiani J. N., Ampel N. M., Sun S. H., Magee D. M., Harrison J., Law J. H. An immunoreactive apoglycoprotein purified from Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2245–2251. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2245-2251.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes D. M., Templeton J. W., Hunter D. M., Adams L. G. Production and use of murine monoclonal antibodies reactive with bovine IgM isotype and IgG subisotypes (IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b) in assessing immunoglobulin levels in serum of cattle. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 May;25(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(90)90110-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish D. G., Ampel N. M., Galgiani J. N., Dols C. L., Kelly P. C., Johnson C. H., Pappagianis D., Edwards J. E., Wasserman R. B., Clark R. J. Coccidioidomycosis during human immunodeficiency virus infection. A review of 77 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1990 Nov;69(6):384–391. doi: 10.1097/00005792-199011000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Dugger K. O., Ampel N. M., Sun S. H., Law J. H. Extraction of serologic and delayed hypersensitivity antigens from spherules of Coccidioides immitis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;11(2):65–80. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(88)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Grace G. M., Lundergan L. L. New serologic tests for early detection of coccidioidomycosis. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):671–674. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. E., Goodman N. L. Variation in complement fixation test results with three Histoplasma capsulatum yeast phase antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):1066–1067. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.1066-1067.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse D., Cole G. T. Isolation of tube precipitin antibody-reactive fractions of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):169–178. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.169-178.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE H. B., COBB J. M., SMITH C. E. Immunogenicity of spherule-endospore vaccines of Coccidioides immitis for mice. J Immunol. 1961 Aug;87:218–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE H. B., KONG Y. C., SMITH C. IMMUNIZATION OF MICE TO COCCIDIOIDES IMMITIS: DOSE, REGIMEN AND SPHERULATION STAGE OF KILLED SPHERULE VACCINES. J Immunol. 1965 Jan;94:132–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine H. B., Cobb J. M., Scalarone G. M. Spherule coccidioidin in delayed dermal sensitivity reactions of experimental animals. Sabouraudia. 1969 Feb;7(1):20–32. doi: 10.1080/00362177085190051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort A. J., Lamport D. T. Anhydrous hydrogen fluoride deglycosylates glycoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):289–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPAGIANIS D., SMITH C. E., KOBAYASHI G. S., SAITO M. T. Studies of antigens from young mycelia of Coccidioides immitis. J Infect Dis. 1961 Jan-Feb;108:35–44. doi: 10.1093/infdis/108.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappagianis D., Zimmer B. L. Serology of coccidioidomycosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jul;3(3):247–268. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.3.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick S., Zimmer B., Pappagianis D., Eakin A., McKerrow J. Purification and amino-terminal sequence analysis of the complement-fixing and precipitin antigens from Coccidioides immitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):385–388. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.385-388.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalarone G. M., Levine H. B., Pappagianis D., Chaparas S. D. Spherulin as a complement-fixing antigen in human coccidioidomycosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Sep;110(3):324–328. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.3.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. P., Remington J. S. Comparison of methods for quantitating antigen-specific immunoglobulin M antibody with a reverse enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):63–70. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.63-70.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wack E. E., Dugger K. O., Galgiani J. N. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antigens of Coccidioides immitis: human sera interference corrected by acidification-heat extraction. J Lab Clin Med. 1988 May;111(5):560–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagh P. V., Bahl O. P. Sugar residues on proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1981;10(4):307–377. doi: 10.3109/10409238109113602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieden M. A., Galgiani J. N., Pappagianis D. Comparison of immunodiffusion techniques with standard complement fixation assay for quantitation of coccidioidal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):529–534. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.529-534.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L., Cole G. T., Sun S. H. Possible role of a proteinase in endosporulation of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1551–1559. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1551-1559.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer B. L., Pappagianis D. Characterization of a soluble protein of Coccidiodes immitis with activity as an immunodiffusion-complement fixation antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2250–2256. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2250-2256.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer B. L., Pappagianis D. Comparison of immunoblot analyses of spherule-endospore-phase extracellular protein and mycelial-phase antigen of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):64–70. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.64-70.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer B. L., Pappagianis D. Immunoaffinity isolation and partial characterization of the Coccidioides immitis antigen detected by the tube precipitin and immunodiffusion-tube precipitin tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1759–1766. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1759-1766.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]