Abstract
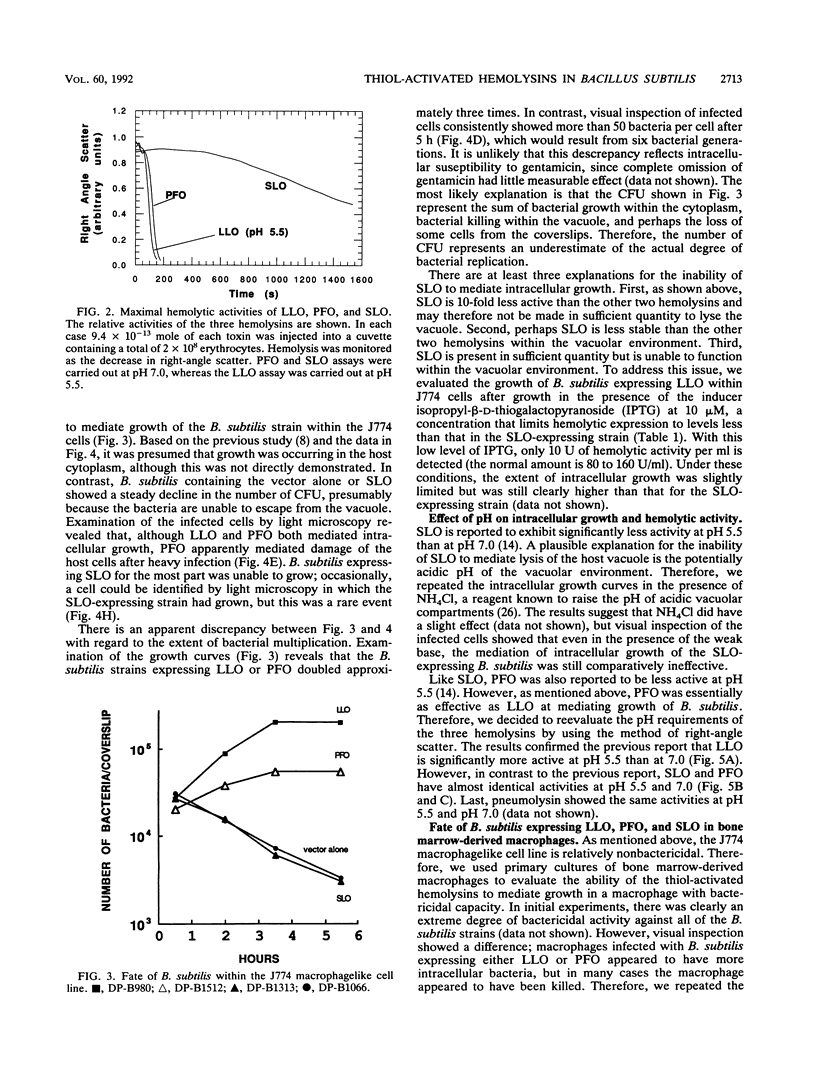
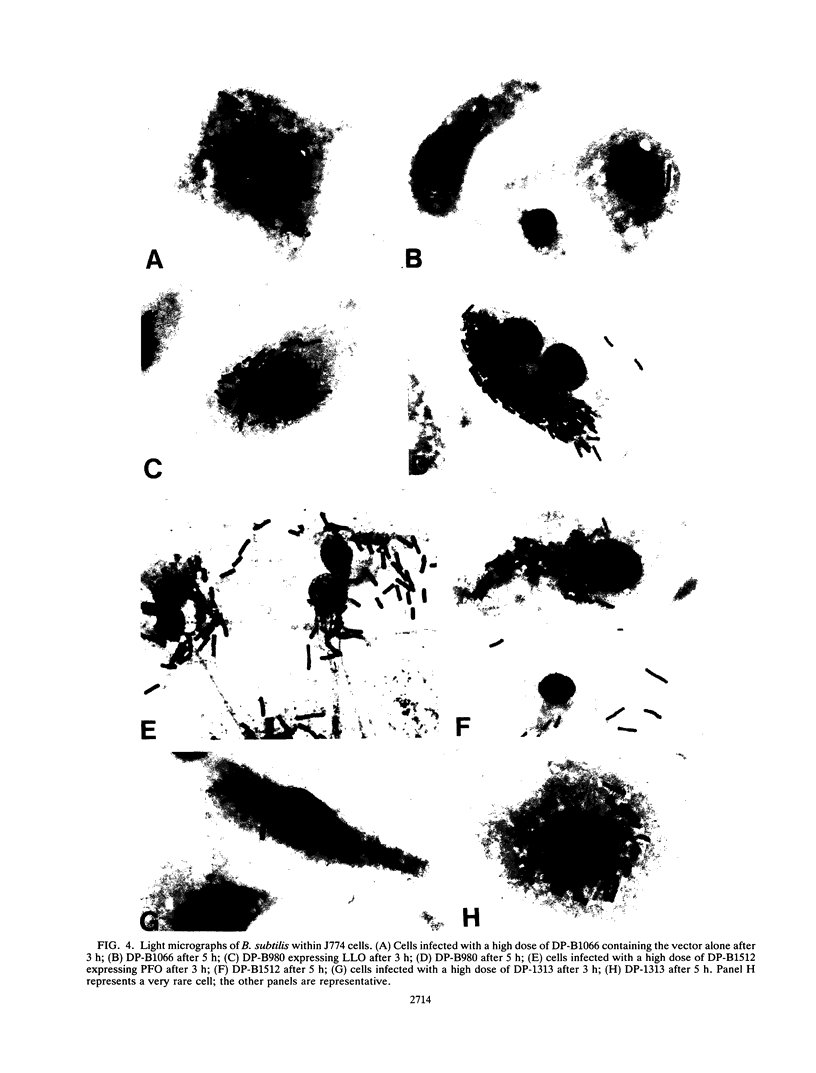
The Listeria monocytogenes hemolysin listeriolysin O (LLO) plays a major role in mediating the escape of L. monocytogenes from a vacuolar compartment. In a previous report, it was shown that Bacillus subtilis expressing LLO could escape from a host vacuolar compartment and grow in the cytoplasm (J. Bielecki, P. Youngman, P. Connelly, and D. A. Portnoy, Nature [London] 345:175-176, 1990). In the present study, two related thiol-activated hemolysins, streptolysin O (SLO) and perfringolysin O (PFO), were expressed in B. subtilis and their ability to mediate intracellular growth was monitored by visual inspection and by assaying for CFU. Like LLO, PFO was active within the vacuolar environment, whereas SLO showed negligible activity. However, expression of PFO seemed to damage the host cells. The pH of the vacuole probably had little to do with these results, since all three hemolysins showed full or enhanced activity at pH 5.5, although LLO showed greatly reduced activity at pH 7. In addition, neutralization of the pH within host vacuoles by using weak bases had little effect on the lysis of the vacuole. The lack of SLO activity is probably caused by its lower specific activity; the purified protein had 10-fold less activity on a molar basis. These results suggest that LLO is not unique in its capacity to mediate intracellular growth of B. subtilis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. W., Abrams C. K., Slatin S. L., Griffiths G. A T. cruzi-secreted protein immunologically related to the complement component C9: evidence for membrane pore-forming activity at low pH. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1277–1287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90692-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barclay R., Threlfall D. R., Leighton I. Haemolysins and extracellular enzymes of Listeria monocytogenes and L. ivanovii. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Oct;30(2):111–118. doi: 10.1099/00222615-30-2-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini M. L., Mounier J., d'Hauteville H., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Identification of icsA, a plasmid locus of Shigella flexneri that governs bacterial intra- and intercellular spread through interaction with F-actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3867–3871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry A. M., Yother J., Briles D. E., Hansman D., Paton J. C. Reduced virulence of a defined pneumolysin-negative mutant of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2037–2042. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2037-2042.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Roth M., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J. Isolation and identification of two hemolytic forms of streptolysin-O. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):394–400. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.394-400.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Membrane damage by pore-forming bacterial cytolysins. Microb Pathog. 1986 Feb;1(1):5–14. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielecki J., Youngman P., Connelly P., Portnoy D. A. Bacillus subtilis expressing a haemolysin gene from Listeria monocytogenes can grow in mammalian cells. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):175–176. doi: 10.1038/345175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulnois G. J., Paton J. C., Mitchell T. J., Andrew P. W. Structure and function of pneumolysin, the multifunctional, thiol-activated toxin of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2611–2616. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilli A., Goldfine H., Portnoy D. A. Listeria monocytogenes mutants lacking phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C are avirulent. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):751–754. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Vicente M. F., Mengaud J., Baquero F., Perez-Diaz J. C., Berche P. Listeriolysin O is essential for virulence of Listeria monocytogenes: direct evidence obtained by gene complementation. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3629–3636. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3629-3636.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Sansonetti P. Transposon mutagenesis as a tool to study the role of hemolysin in the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.50-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy C., Gaillard J. L., Alouf J. E., Berche P. Purification, characterization, and toxicity of the sulfhydryl-activated hemolysin listeriolysin O from Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1641–1646. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1641-1646.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. W., Sims P. J., Tweten R. K. Evidence that Clostridium perfringens theta-toxin induces colloid-osmotic lysis of erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2499–2501. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2499-2501.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. W., Sims P. J., Tweten R. K. Kinetic aspects of the aggregation of Clostridium perfringens theta-toxin on erythrocyte membranes. A fluorescence energy transfer study. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6936–6941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Synthesis and secretion of interferon by murine fibroblasts in response to intracellular Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):787–792. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.787-792.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kathariou S., Metz P., Hof H., Goebel W. Tn916-induced mutations in the hemolysin determinant affecting virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1291–1297. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1291-1297.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M. A., Miller L., Walker J. A., Boulnois G. J. Nucleotide sequence of the streptolysin O (SLO) gene: structural homologies between SLO and other membrane-damaging, thiol-activated toxins. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3228–3232. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3228-3232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M., Timmis K. N. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the streptolysin O determinant from Streptococcus pyogenes: characterization of the cloned streptolysin O determinant and demonstration of the absence of substantial homology with determinants of other thiol-activated toxins. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):804–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.804-810.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney T. J., Moran C. P., Jr Organization and regulation of an operon that encodes a sporulation-essential sigma factor in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3329–3339. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3329-3339.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Kathariou S., Goebel W. Hemolysin supports survival but not entry of the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):79–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.79-82.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Domann E., Chakraborty T. Detection of a gene encoding a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C that is co-ordinately expressed with listeriolysin in Listeria monocytogenes. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):361–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Sasakawa C., Kamata K., Kurata T., Yoshikawa M. A genetic determinant required for continuous reinfection of adjacent cells on large plasmid in S. flexneri 2a. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90880-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R. Weak bases and ionophores rapidly and reversibly raise the pH of endocytic vesicles in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):676–681. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Braun-Breton C., Cossart P. Identification of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity in Listeria monocytogenes: a novel type of virulence factor? Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Vicente M. F., Chenevert J., Pereira J. M., Geoffroy C., Gicquel-Sanzey B., Baquero F., Perez-Diaz J. C., Cossart P. Expression in Escherichia coli and sequence analysis of the listeriolysin O determinant of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):766–772. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.766-772.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier J., Ryter A., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular and cell-to-cell spread of Listeria monocytogenes involves interaction with F-actin in the enterocytelike cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1048–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1048-1058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkney M., Beachey E., Kehoe M. The thiol-activated toxin streptolysin O does not require a thiol group for cytolytic activity. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2553–2558. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2553-2558.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pál T., Newland J. W., Tall B. D., Formal S. B., Hale T. L. Intracellular spread of Shigella flexneri associated with the kcpA locus and a 140-kilodalton protein. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):477–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.477-486.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Ryter A., Clerc P., Maurelli A. T., Mounier J. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri within HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):461–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.461-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz I. Permeabilizing cells: some methods and applications for the study of intracellular processes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;192:280–300. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)92077-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L., Mitten J., Henry C. Effects of alpha and theta toxins from Clostridium perfringens on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Infect Dis. 1987 Aug;156(2):324–333. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.2.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweten R. K. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the perfringolysin O (theta-toxin) gene from Clostridium perfringens and characterization of the gene product. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3228–3234. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3228-3234.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweten R. K. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for perfringolysin O (theta-toxin) from Clostridium perfringens: significant homology with the genes for streptolysin O and pneumolysin. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3235–3240. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3235-3240.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Andersen B. R. Streptolysin O inhibition of neutrophil chemotaxis and mobility: nonimmune phenomenon with species specificity. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):27–33. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.27-33.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A. Pore-forming cytolysins of gram-negative bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):521–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Rickettsia species (as organisms). Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:131–153. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Losick R. Role of AbrB in Spo0A- and Spo0B-dependent utilization of a sporulation promoter in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2223–2230. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2223-2230.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]