Abstract
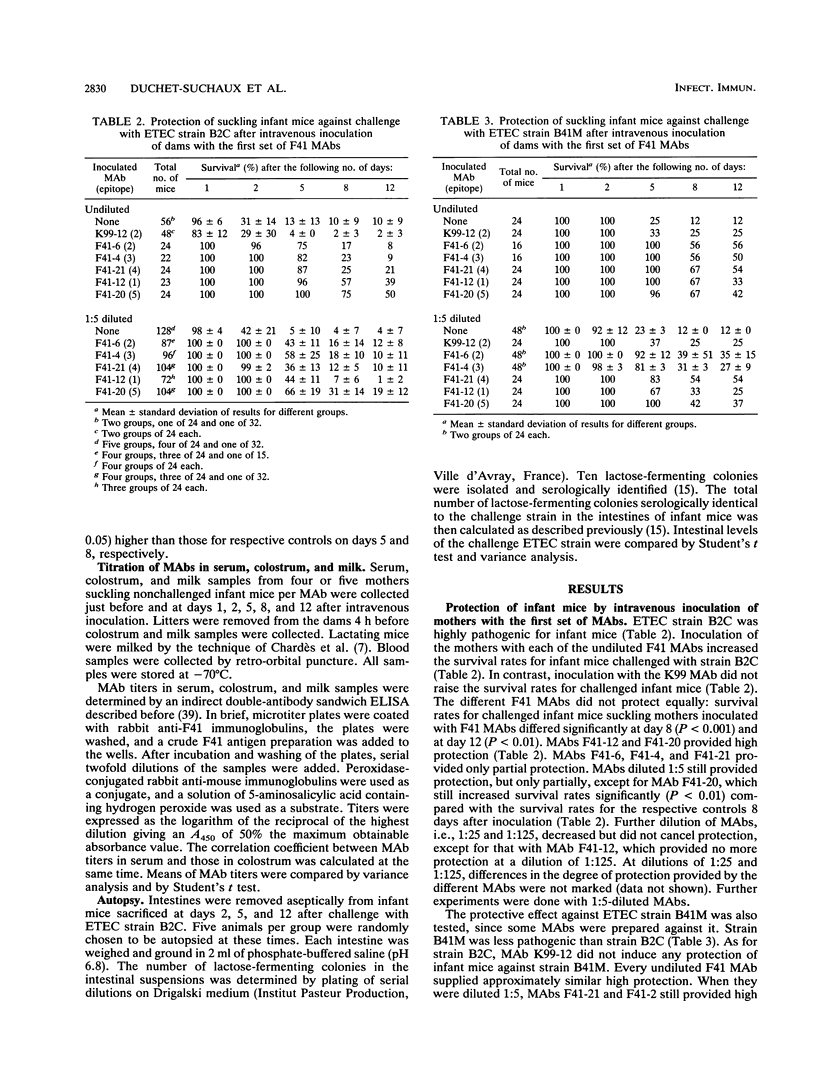
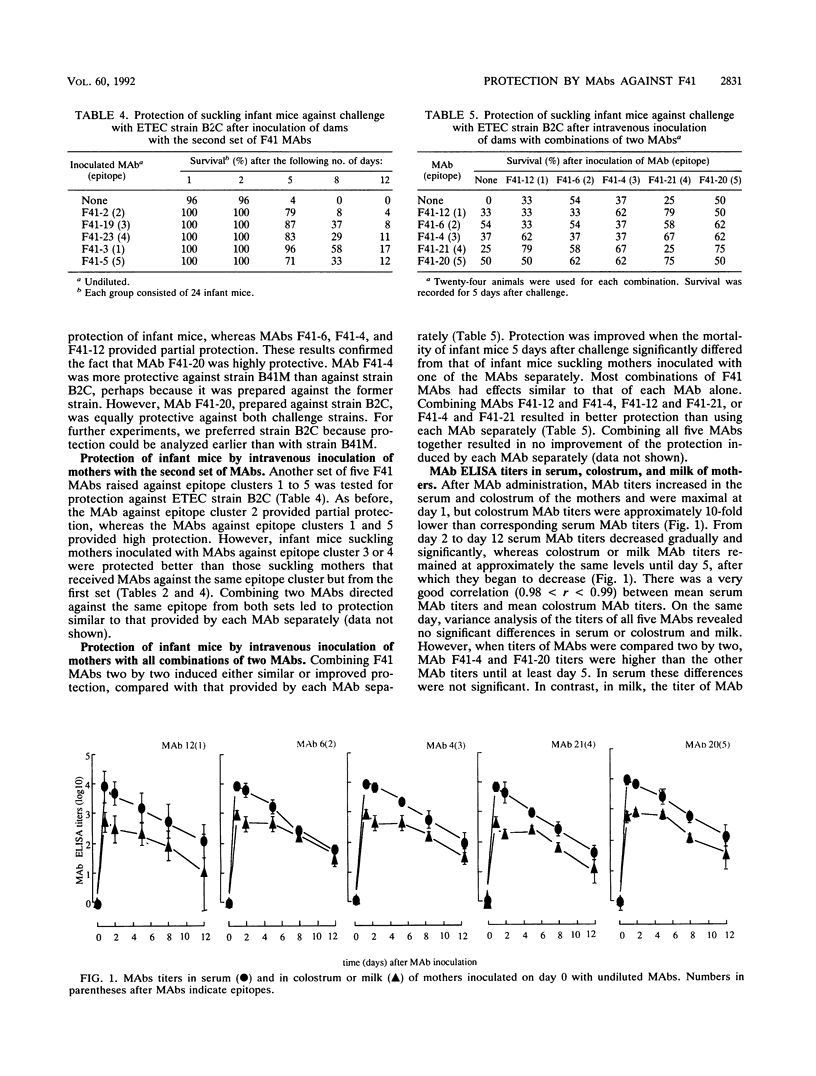
Ten monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) against five different epitope clusters of adhesion factor F41 (two MAbs per cluster) were tested for protection of infant mice against an oral challenge with F41-positive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) B2C and B41M. Infant mice suckling dams intravenously inoculated with MAbs were orally challenged, and the survival rates were measured for 12 days after inoculation and challenge. Irrespective of their epitope specificity, all F41 MAbs given in a single dose of 4 mg per dam had a protective effect against both ETEC strains. In contrast, one K99 MAb of the same isotype and given in the same dose as the F41 MAbs did not protect infant mice at all. A reduction in the dose of F41 MAbs to 0.032 mg per dam resulted in a decrease in protection. Two different MAbs against the same epitope cluster were not necessarily equally protective. Combining MAbs two by two, whether the MAbs recognized the same epitope cluster or not, resulted in protective activity essentially similar to that obtained with each MAb separately, without any improvement. Therefore, one MAb against any epitope may be sufficient for protection. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) titers of MAbs in the serum of dams were similar, irrespective of the epitope specificity of the MAbs, and gradually decreased from day 1 to day 12 after inoculation. We found a good correlation between colostrum and milk ELISA titers of MAbs and serum ELISA titers of MAbs. Colostrum and milk MAb titers were 10-fold lower than corresponding serum MAb titers and stayed high until day 5 after inoculation. The most protective MAb had the highest ELISA titers in colostrum and milk for the first 5 days after inoculation. ETEC strain B2C colonized the intestines of infant mice suckling MAb-inoculated mothers until day 12 after challenge. Intestinal levels of the challenge strain were high on day 2 but never reached the very high numbers (10(9) to 10(10)) described previously in a diarrheic infant mouse model. MAbs did not eliminate the challenge ETEC strain from the intestines of infant mice.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acres S. D., Forman A. J., Kapitany R. A. Antigen-extinction profile in pregnant cows, using a K99-containing whole-cell bacterin to induce passive protection against enterotoxigenic colibacillosis of calves. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Apr;43(4):569–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acres S. D., Isaacson R. E., Babiuk L. A., Kapitany R. A. Immunization of calves against enterotoxigenic colibacillosis by vaccinating dams with purified K99 antigen and whole cell bacterins. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):121–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.121-126.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmann K., Mukkur T. K. Passive immunisation of neonatal lambs against infection with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli via colostrum of ewes immunised with crude and purified K99 pili. Res Vet Sci. 1983 Sep;35(2):234–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertin A. F41 antigen as a virulence factor in the infant mouse model of Escherichia coli diarrhoea. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Nov;131(11):3037–3045. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-11-3037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows M. R., Sellwood R., Gibbons R. A. Haemagglutinating and adhesive properties associated with the K99 antigen of bovine strains of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Oct;96(2):269–275. doi: 10.1099/00221287-96-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey T. A., Moon H. W. Genetic characterization and virulence of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli mutants which have lost virulence genes in vivo. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):4156–4158. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.4156-4158.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardès T., Bourguin I., Mevelec M. N., Dubremetz J. F., Bout D. Antibody responses to Toxoplasma gondii in sera, intestinal secretions, and milk from orally infected mice and characterization of target antigens. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1240–1246. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1240-1246.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contrepois M., Girardeau J. P., Dubourguier H. C., Gouet P., Levieux D. Specific protection by colostrum from cows vaccinated with the K 99 antigen in newborn calves experimentally infected with E. coli Ent+ K99+. Ann Rech Vet. 1978;9(2):385–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchet-Suchaux M., Bertin A., Dubray G. Morphological description of surface structures on strain B41 of bovine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli bearing both K99 and F41 antigens. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Apr;134(4):983–995. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-4-983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchet-Suchaux M., Le Maitre C., Bertin A. Differences in susceptibility of inbred and outbred infant mice to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of bovine, porcine and human origin. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Mar;31(3):185–190. doi: 10.1099/00222615-31-3-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchet-Suchaux M. Le souriceau, modèle d'étude de la diarrhée colibacillaire. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1980 Nov-Dec;131B(3):239–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchet-Suchaux M. Protective antigens against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli O101:K99,F41 in the infant mouse diarrhea model. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1364–1370. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1364-1370.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory D. W., Cardella M. A., Myers L. L. Lamb model in the study of immunity to enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infections. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Nov;44(11):2073–2077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Role of the K88 antigen in the pathogenesis of neonatal diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli in piglets. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):918–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.918-927.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainil J. G., Sadowski P. L., Tarsio M., Moon H. W. In vivo emergence of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli variants lacking genes for K99 fimbriae and heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3111–3116. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3111-3116.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W. Colonization factor antigens of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in animals. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;151:147–165. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74703-8_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Nagy B., Isaacson R. E., Orskov I. Occurrence of K99 antigen on Escherichia coli isolated from pigs and colonization of pig ileum by K99+ enterotoxigenic E. coli from calves and pigs. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):614–620. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.614-620.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W. Protection against enteric colibacillosis in pigs suckling orally vaccinated dams: evidence for pili as protective antigens. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Feb;42(2):173–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau M. C., Raibaud P., Muller M. C. Relation entre le développement du système immunitaire intestinal à IgA et l'établissement de la flore microbienne dans le tube digestif du souriceau holoxénique. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1982 Jul-Aug;133D(1):29–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. L., Isaacson R. E., Moon H. W., Brinton C. C., To C. C. Immunization of suckling pigs against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-induced diarrheal disease by vaccinating dams with purified 987 or K99 pili: protection correlates with pilus homology of vaccine and challenge. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):771–777. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.771-777.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. A., Thorns C. J., Wells G. A., Scott A. C., Sojka W. J. The production of F41 fimbriae by piglet strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli that lack K88, K99 and 987P fimbriae. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2753–2759. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. A., Thorns C., Scott A. C., Sojka W. J., Wells G. A. Adhesion in vitro and in vivo associated with an adhesive antigen (F41) produced by a K99 mutant of the reference strain Escherichia coli B41. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1146–1153. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1146-1153.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. A., Wray C., Sojka W. J. Passive protection of lambs against enteropathogenic Escherichia coli: role of antibodies in serum and colostrum of dams vaccinated with K99 antigen. J Med Microbiol. 1980 May;13(2):265–271. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L. Enteric colibacillosis in calves: immunogenicity and antigenicity of Escherichia coli antigens. Am J Vet Res. 1978 May;39(5):761–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L. Passive protection of calves against experimentally induced and naturally occurring enteric colibacillosis. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Dec;41(12):1952–1956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B. Vaccination of cows with a K99 extract to protect newborn calves against experimental enterotoxic colibacillosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):21–24. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.21-24.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsome P. M., Burgess M. N., Burgess M. R., Coney K. A., Goddard M. E., Morris J. A. A model of acute infectious neonatal diarrhoea. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Feb;23(1):19–28. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Smith H. W., Sojka W. J. The establishment of K99, a thermolabile, transmissible escherichia coli K antigen, previously called "Kco", possessed by calf and lamb enteropathogenic strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Feb;83(1):31–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runnels P. L., Moseley S. L., Moon H. W. F41 pili as protective antigens of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli that produce F41, K99, or both pilus antigens. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):555–558. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.555-558.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter J. M., Jones G. W. Protection against enteric disease caused by Escherichia coli--a model for vaccination with a virulence determinant? Nature. 1973 Apr 20;242(5399):531–532. doi: 10.1038/242531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman D. M., Acres S. D., Sadowski P. L., Springer J. A., Bray B., Raybould T. J., Muscoplat C. C. Protection of calves against fatal enteric colibacillosis by orally administered Escherichia coli K99-specific monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):653–658. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.653-658.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Nagy L. K., Sherwood D., Campbell I. Passive immunity in calf diarrhea: vaccination with K99 antigen of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and rotavirus. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):586–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.586-591.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sojka W. J., Wray C., Morris J. A. Passive protection of lambs against experimental enteric colibacillosis by colostral transfer of antibodies from K99-vaccinated ewes. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Nov;11(4):493–499. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-4-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. R., Hohmann A. W. Immunity to Escherichia coli in pigs: adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to isolated intestinal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):776–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.776-782.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Roorda I. Production, purification, and characterization of the fimbrial adhesive antigen F41 isolated from calf enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strain B41M. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):751–758. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.751-758.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Wientjes F. B., Klaasen-Boor P. Production of K99 antigen by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains of antigen groups o8, o9, o20, and o101 grown at different conditions. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):216–221. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.216-221.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zijderveld F. G., Westenbrink F., Anakotta J., Brouwers R. A., van Zijderveld A. M. Characterization of the F41 fimbrial antigen of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1192–1199. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1192-1199.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


