Abstract
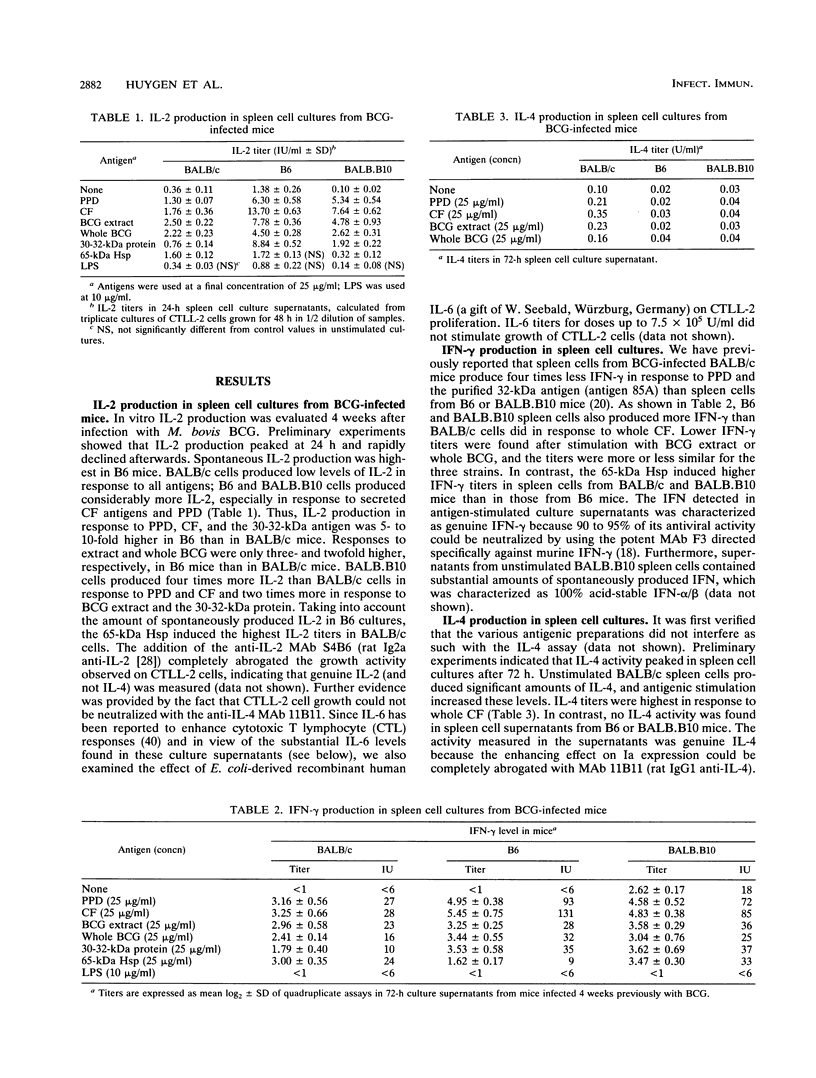
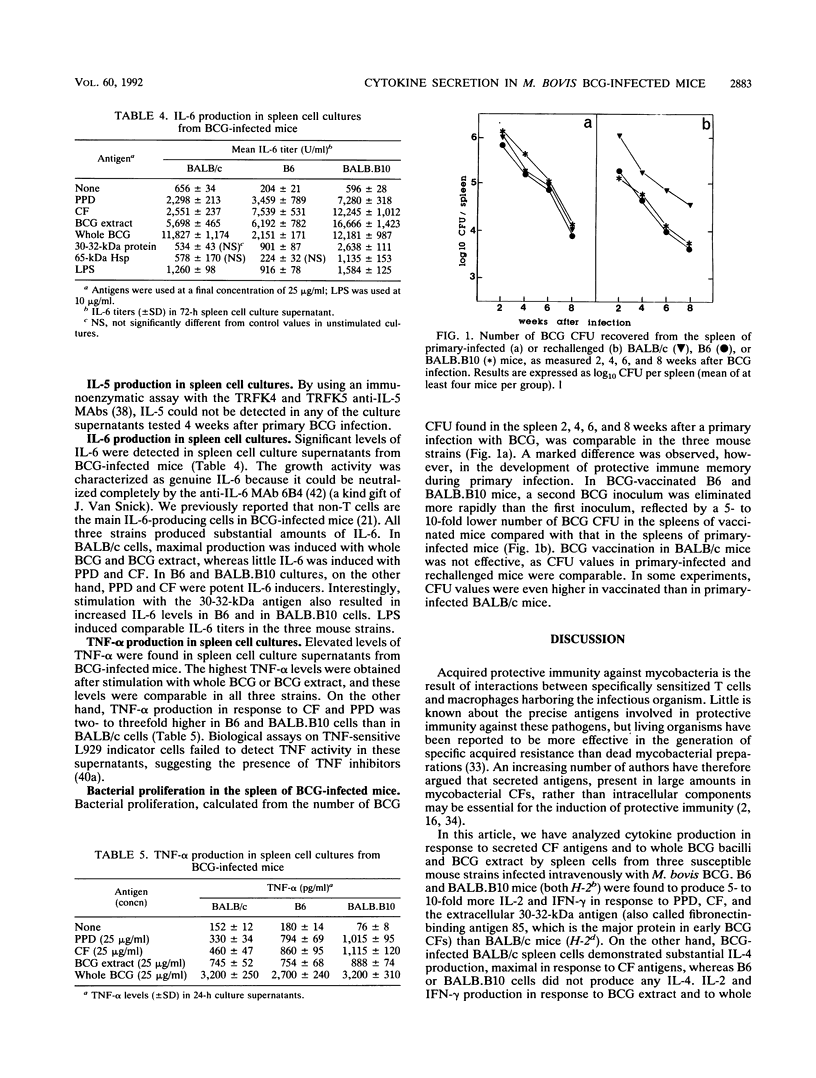
Three susceptible mouse strains, i.e., BALB/c (H-2d), C57BL/6 (H-2b), and major histocompatibility complex-congenic BALB.B10 (H-2b), were infected intravenously with 4 x 10(6) CFU of live Mycobacterium bovis BCG and analyzed 4 weeks later for in vitro spleen cell cytokine secretion in response to purified protein derivative (PPD), BCG culture filtrate (CF), BCG cellular extract, total BCG, the purified extracellular 30-32-kDa antigen (the fibronectin-binding antigen 85), or the intracellular 65-kDa heat shock protein. C57BL/6 and BALB.B10 mice produced 5- to 10-fold more gamma interferon and interleukin-2 (IL-2) when stimulated with CF, PPD, and antigen 85 than BALB/c mice did. When stimulated with BCG extract and whole BCG, gamma interferon and IL-2 levels were generally lower and comparable in the three strains. IL-4 was detected in spleen cell culture supernatants from infected BALB/c mice but not from C57BL/6 or BALB.B10 mice. IL-5 could not be detected. C57BL/6 and BALB.B10 spleen cells also produced more tumor necrosis factor alpha and IL-6 after stimulation with PPD and CF than BALB/c cells did. Finally, BCG vaccination generated efficient protective immunity in C57BL/6 and BALB.B10 mice but not in BALB/c mice. These data suggest that secreted mycobacterial CF antigens selectively induce a strong TH1 response in BCG-infected C57BL/6 and BALB.B10 mice, whereas in BALB/c mice this response is partly counterbalanced by TH2 cells.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramowicz D., Doutrelepont J. M., Lambert P., Van der Vorst P., Bruyns C., Goldman M. Increased expression of Ia antigens on B cells after neonatal induction of lymphoid chimerism in mice: role of interleukin 4. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Mar;20(3):469–476. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Askgaard D., Ljungqvist L., Bentzon M. W., Heron I. T-cell proliferative response to antigens secreted by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1558–1563. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1558-1563.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom W. H., Liebster L., Abbas A. K., Titus R. G. Patterns of cytokine secretion in murine leishmaniasis: correlation with disease progression or resolution. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3863–3870. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3863-3870.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett S. J., Ivanyi J. Genetic influences on the immune repertoire following tuberculous infection in mice. Immunology. 1990 Sep;71(1):113–119. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Closs O., Løvik M., Wigzell H., Taylor B. A. H-2-linked gene(s) influence the granulomatous reaction to viable Mycobacterium lepraemurium in the mouse. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Jul;18(1):59–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00836.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruyn J., Bosmans R., Turneer M., Weckx M., Nyabenda J., Van Vooren J. P., Falmagne P., Wiker H. G., Harboe M. Purification, partial characterization, and identification of a skin-reactive protein antigen of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):245–252. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.245-252.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruyn J., Huygen K., Bosmans R., Fauville M., Lippens R., Van Vooren J. P., Falmagne P., Weckx M., Wiker H. G., Harboe M. Purification, characterization and identification of a 32 kDa protein antigen of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Microb Pathog. 1987 May;2(5):351–366. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Gregg E. O. Modulation of Mycobacterium avium growth in murine macrophages: reversal of unresponsiveness to interferon-gamma by indomethacin or interleukin-4. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Jan;49(1):65–72. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douvas G. S., Looker D. L., Vatter A. E., Crowle A. J. Gamma interferon activates human macrophages to become tumoricidal and leishmanicidal but enhances replication of macrophage-associated mycobacteria. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.1-8.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Activation of tuberculostatic macrophage functions by gamma interferon, interleukin-4, and tumor necrosis factor. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2675–2677. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2675-2677.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Stimulation of antibacterial macrophage activities by B-cell stimulatory factor 2 (interleukin-6). Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):269–271. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.269-271.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajewski T. F., Pinnas M., Wong T., Fitch F. W. Murine Th1 and Th2 clones proliferate optimally in response to distinct antigen-presenting cell populations. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 15;146(6):1750–1758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haanen J. B., de Waal Malefijt R., Res P. C., Kraakman E. M., Ottenhoff T. H., de Vries R. R., Spits H. Selection of a human T helper type 1-like T cell subset by mycobacteria. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):583–592. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havlir D. V., Wallis R. S., Boom W. H., Daniel T. M., Chervenak K., Ellner J. J. Human immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):665–670. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.665-670.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P., Sadick M. D., Holaday B. J., Coffman R. L., Locksley R. M. Reciprocal expression of interferon gamma or interleukin 4 during the resolution or progression of murine leishmaniasis. Evidence for expansion of distinct helper T cell subsets. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):59–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heremans H., Dijkmans R., Sobis H., Vandekerckhove F., Billiau A. Regulation by interferons of the local inflammatory response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4175–4179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huygen K., Ljungqvist L., ten Berg R., Van Vooren J. P. Repertoires of antibodies to culture filtrate antigens in different mouse strains infected with Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2192–2197. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2192-2197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huygen K., Palfliet K., Jurion F., Hilgers J., ten Berg R., Van Vooren J. P., De Bruyn J. H-2-linked control of in vitro gamma interferon production in response to a 32-kilodalton antigen (P32) of Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3196–3200. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3196-3200.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huygen K., Vandenbussche P., Heremans H. Interleukin-6 production in Mycobacterium bovis BCG-infected mice. Cell Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;137(1):224–231. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90071-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi J., Sharp K. Control by H-2 genes of murine antibody responses to protein antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Immunology. 1986 Nov;59(3):329–332. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locksley R. M., Scott P. Helper T-cell subsets in mouse leishmaniasis: induction, expansion and effector function. Immunol Today. 1991 Mar;12(3):A58–A61. doi: 10.1016/S0167-5699(05)80017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInnes A., Rennick D. M. Interleukin 4 induces cultured monocytes/macrophages to form giant multinucleated cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):598–611. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond J. J., Carman J., Sarma C., Ohara J., Finkelman F. D. Interferon-gamma suppresses B cell stimulation factor (BSF-1) induction of class II MHC determinants on B cells. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3534–3537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Moore K. W. The role of IL-10 in crossregulation of TH1 and TH2 responses. Immunol Today. 1991 Mar;12(3):A49–A53. doi: 10.1016/S0167-5699(05)80015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. S., Madri J., Tite J., Carding S. R., Bottomly K. MHC control of CD4+ T cell subset activation. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2135–2140. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M. Characteristics and specificity of acquired immunologic memory to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3589–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M. The immune response to the cell wall of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Mar;71(3):388–393. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M. The molecular targets of T cells in acquired immunity to tuberculosis. Immunol Lett. 1991 Oct;30(2):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(91)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Mayer N., Sachs D. H. Hybridoma cell lines secreting monoclonal antibodies to mouse H-2 and Ia antigens. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):533–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roch F., Bach M. A. Strain differences in mouse cellular responses to Mycobacterium lepraemurium and BCG subcutaneous infections. II. Production of interleukins 2, 4, and 6 and of interferon-gamma by draining lymph node cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Sep;60(3):443–454. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90100-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A., Taverne J., Leveton C., Steele J. The role of gamma-interferon, vitamin D3 metabolites and tumour necrosis factor in the pathogenesis of tuberculosis. Immunology. 1987 Oct;62(2):229–234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher J. H., O'Garra A., Shrader B., van Kimmenade A., Bond M. W., Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. The characterization of four monoclonal antibodies specific for mouse IL-5 and development of mouse and human IL-5 enzyme-linked immunosorbent. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1576–1581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E. Genetic control of resistance to mycobacterial infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;124:49–66. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70986-9_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyttenhove C., Coulie P. G., Van Snick J. T cell growth and differentiation induced by interleukin-HP1/IL-6, the murine hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1417–1427. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink A., Coulie P. G., Wauters P., Nordan R. P., Van Snick J. B cell growth and differentiation activity of interleukin-HP1 and related murine plasmacytoma growth factors. Synergy with interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):607–612. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worsaae A., Ljungqvist L., Heron I. Monoclonal antibodies produced in BALB.B10 mice define new antigenic determinants in culture filtrate preparations of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2608–2614. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2608-2614.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura M., Uyemura K., Deans R. J., Weinberg K., Rea T. H., Bloom B. R., Modlin R. L. Defining protective responses to pathogens: cytokine profiles in leprosy lesions. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):277–279. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waal Malefyt R., Haanen J., Spits H., Roncarolo M. G., te Velde A., Figdor C., Johnson K., Kastelein R., Yssel H., de Vries J. E. Interleukin 10 (IL-10) and viral IL-10 strongly reduce antigen-specific human T cell proliferation by diminishing the antigen-presenting capacity of monocytes via downregulation of class II major histocompatibility complex expression. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):915–924. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Gonzalez N. M., de Vries R. R., Convit J., van Rood J. J. HLA-linked control of predisposition to lepromatous leprosy. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):9–14. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


