Abstract
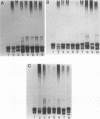
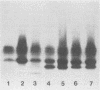
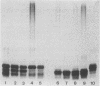
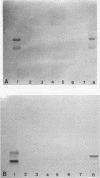
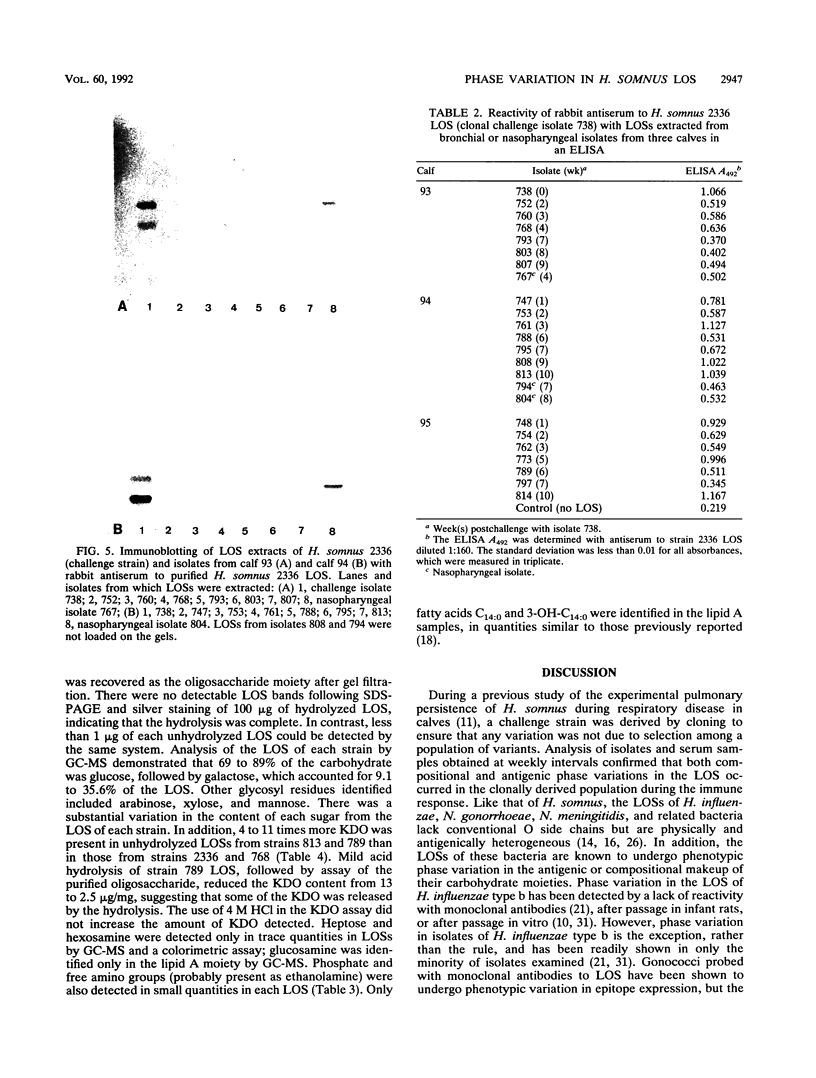
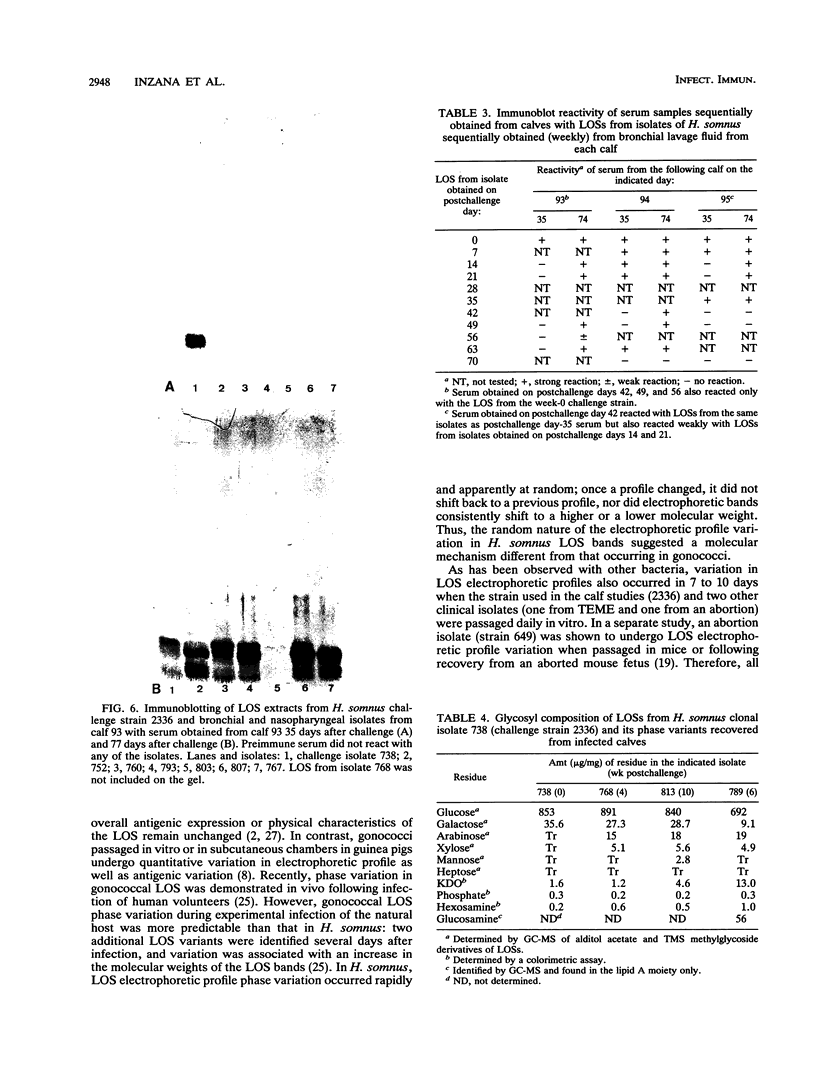
A high rate of phenotypic variation in the lipooligosaccharide (LOS) electrophoretic profile of Haemophilus somnus occurred in most isolates obtained at approximately weekly intervals from three calves intrabronchially challenged with a cloned isolate of H. somnus 2336. Daily subculturing for 2 weeks resulted in at least one major alteration in the LOS electrophoretic profiles for strain 2336 and both additional disease isolates examined, but no change occurred in the LOS electrophoretic profiles for any of three commensal isolates examined. None of the LOSs from any of the postchallenge intrabronchial isolates reacted with rabbit antiserum to the challenge strain LOS in immunoblotting, but LOSs from two nasopharyngeal isolates did. Antigenic variation in the extracted LOSs of most of the isolates was supported by the results of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Preimmune serum from each of the calves did not react with any of the isolates or the challenge strain, whereas sera obtained 35 days after challenge reacted with the challenge strain and zero to five additional isolates and sera obtained 74 days after challenge reacted with two to six additional isolates. Recognition of LOSs from isolates obtained near the end of the 70-day experiment by day-74 sera was related to clearance of the bacteria from the lungs. Isolates demonstrating major electrophoretic changes showed variations in the composition of the oligosaccharide, but not lipid A, moiety of their LOSs. The oligosaccharide of the LOS of each isolate was composed predominantly of glucose but varied substantially in the contents of galactose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, and 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid. Therefore, the LOS of H. somnus is capable of undergoing compositional and antigenic variations, which may act as an important virulence mechanism for evading host immune defense mechanisms.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A., Shero M., Jarvis G. A., Griffiss J. M., Mandrell R. E., Schneider H. Phenotypic variation in epitope expression of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharide. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1755–1761. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1755-1761.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aydintug M. K., Inzana T. J., Letonja T., Davis W. C., Corbeil L. B. Cross-reactivity of monoclonal antibodies to Escherichia coli J5 with heterologous gram-negative bacteria and extracted lipopolysaccharides. J Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;160(5):846–857. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.5.846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly M. C., Allen P. Z. Antigenic specificity and heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides from pyocin-sensitive and -resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1046–1055. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1046-1055.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Blau K., Prieur D. J., Ward A. C. Serum susceptibility of Haemophilus somnus from bovine clinical cases and carriers. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):192–198. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.192-198.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Widders P. R., Gogolewski R., Arthur J., Inzana T. J., Ward A. C. Haemophilus somnus: Bovine Reproductive and Respiratory Disease. Can Vet J. 1986 Feb;27(2):90–93. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demarco de Hormaeche R., Jessop H., Senior K. Gonococcal variants selected by growth in vivo or in vitro have antigenically different LPS. Microb Pathog. 1988 Apr;4(4):289–297. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilsdorf J. R., Ferrieri P. Susceptibility of phenotypic variants of Haemophilus influenzae type b to serum bactericidal activity: relation to surface lipopolysaccharide. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):223–231. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Kania S. A., Inzana T. J., Widders P. R., Liggitt H. D., Corbeil L. B. Protective ability and specificity of convalescent serum from calves with Haemophilus somnus pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1403–1411. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1403-1411.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Leathers C. W., Liggitt H. D., Corbeil L. B. Experimental Haemophilus somnus pneumonia in calves and immunoperoxidase localization of bacteria. Vet Pathol. 1987 May;24(3):250–256. doi: 10.1177/030098588702400309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Schaefer D. C., Wasson S. K., Corbeil R. R., Corbeil L. B. Pulmonary persistence of Haemophilus somnus in the presence of specific antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1767–1774. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1767-1774.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Leive L., Mäkelä P. H., Rietschel E. T., Strittmatter W., Morrison D. C. Lipopolysaccharide nomenclature--past, present, and future. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):699–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.699-705.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman J. K., Dintzis H. M. The derivatization of cross-linked polyacrylamide beads. Controlled introduction of functional groups for the preparation of special-purpose, biochemical adsorbents. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):4074–4082. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J., Corbeil L. B. Development of a defined medium for Haemophilus somnus isolated from cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Mar;48(3):366–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J. Electrophoretic heterogeneity and interstrain variation of the lipopolysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):492–499. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J., Iritani B., Gogolewski R. P., Kania S. A., Corbeil L. B. Purification and characterization of lipooligosaccharides from four strains of "Haemophilus somnus". Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2830–2837. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2830-2837.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Jackson J. J., Carlo D. J. A new and improved microassay to determine 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate in lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Hansen E. J. Antigenic and phenotypic variations of Haemophilus influenzae type b lipopolysaccharide and their relationship to virulence. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):69–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.69-79.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Apicella M. A. Isolation of a lipopolysaccharide mutant of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: an analysis of the antigenic and biologic difference. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):206–216. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppler M. S. Two physically and serologically distinct lipopolysaccharide profiles in strains of Bordetella pertussis and their phenotype variants. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):224–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.224-232.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Griffiss J. M., Boslego J. W., Hitchcock P. J., Zahos K. M., Apicella M. A. Expression of paragloboside-like lipooligosaccharides may be a necessary component of gonococcal pathogenesis in men. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1601–1605. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Hale T. L., Zollinger W. D., Seid R. C., Jr, Hammack C. A., Griffiss J. M. Heterogeneity of molecular size and antigenic expression within lipooligosaccharides of individual strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):544–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.544-549.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Hammack C. A., Apicella M. A., Griffiss J. M. Instability of expression of lipooligosaccharides and their epitopes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):942–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.942-946.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Gilkerson E. Quantitation of glycosaminoglycan hexosamine using 3-methyl-2-benzothiazolone hydrazone hydrochloride. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):478–480. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinola S. M., Kwaik Y. A., Lesse A. J., Campagnari A. A., Apicella M. A. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a Haemophilus influenzae type b lipooligosaccharide synthesis gene(s) that encodes a 2-keto-3-deoxyoctulosonic acid epitope. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1558–1564. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1558-1564.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Boykins R., Frasch C. E. Heterogeneity and variation among Neisseria meningitidis lipopolysaccharides. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):498–504. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.498-504.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
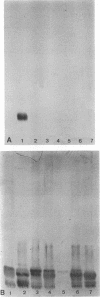
- Wright B. G., Rebers P. A. Procedure for determining heptose and hexose in lipopolysaccharides. Modification of the cysteine-sulfuric acid method. Anal Biochem. 1972 Oct;49(2):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90433-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarnall M., Gogolewski R. P., Corbeil L. B. Characterization of two Haemophilus somnus Fc receptors. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jul;134(7):1993–1999. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-7-1993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]