Abstract
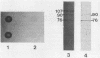
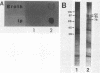
Haemophilus influenzae type b acquires transferrin-bound iron via a siderophore-independent mechanism involving direct contact between the human iron-binding glycoprotein and the bacterial cell surface. Evidence has accumulated to show that the transferrin receptor consists of at least two iron-regulated outer membrane transferrin-binding proteins (TBPs), of which one has a molecular mass of around 100 kDa (TBP1) and the other has a molecular mass of 60 to 90 kDa (TBP2). In H. influenzae type b strain Eagan, proteins of 76, 90, and 107 kDa appear to be involved in transferrin binding. To determine whether these TBPs are expressed during growth in vivo, strain Eagan was recovered without subculture from the intraperitoneal cavities of infected infant rats. By using a dot blot assay, outer membranes prepared from these in vivo-grown bacteria, unlike those grown in iron-sufficient broth, bound human transferrin and produced the 76-, 90-, and 107-kDa TBPs. Immunoblotting experiments using convalescent sera from infected rats also revealed the presence of antibodies to the 76- and 90-kDa strain Eagan TBPs. In addition, convalescent sera from three of four patients recovering from H. influenzae type b meningitis contained antibodies to the 90- and 105-kDa TBPs of the corresponding infecting strain. Furthermore, fresh clinical isolates of H. influenzae type b recovered from blood and cerebrospinal fluid showed constitutive expression of the TBPs, which became iron regulated only after prolonged in vitro subculture on iron-sufficient medium. This contrasted with the laboratory-adapted Eagan strain, in which the TBPs remained iron regulated even after animal passage. These findings indicate that the H. influenzae type b transferrin receptor is expressed during experimental animal and human infections.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ala'Aldeen D. A., Davies H. A., Wall R. A., Borriello S. P. The 70 kilodalton iron regulated protein of Neisseria meningitidis is not the human transferrin receptor. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 May;57(1-2):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90409-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Johnston R. B., Jr, Smith D. H. Human serum activities against Hemophilus influenzae, type b. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):31–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI106793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E., Stevenson P., Ray A. Antigenic and molecular heterogeneity of the transferrin-binding protein of Neisseria meningitidis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 May;57(1-2):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90408-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerina N. G., Langermann S., Schoolnik G. K., Kessler T. W., Goldmann D. A. Purification and characterization of Haemophilus influenzae pili, and their structural and serological relatedness to Escherichia coli P and mannose-sensitive pili. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):145–159. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Frisch C. F., McDade R. L., Jr, Johnston K. H. Identification of immunogenic outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b in the infant rat model system. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1084–1092. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1084-1092.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J., Towner K. J., Williams P. Isolation and characterisation of Haemophilus influenzae type b mutants defective in transferrin-binding and iron assimilation. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jan 15;61(2-3):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90566-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J., Towner K. J., Williams P. Tn916 insertion mutagenesis in Escherichia coli and Haemophilus influenzae type b following conjugative transfer. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Mar;138(3):509–515. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-3-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israels L. G., Yoda B., Schacter B. A. Heme binding and its possible significance in heme movement and availability in the cell. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Apr 15;244:651–661. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb41559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Hansen E. J. Antigenic and phenotypic variations of Haemophilus influenzae type b lipopolysaccharide and their relationship to virulence. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):69–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.69-79.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. S., Moxon E. R. Genetic and phenotypic variation in the capsulation and virulence of culture collection strains of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Microb Pathog. 1989 Dec;7(6):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford P. R., Williams A. E., Moxon E. R. Immunogenic outer-membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b in infection. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jan;138(1):155–159. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-1-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from transferrin and iron compounds. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):555–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.555-564.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. J., Williams P. Siderophore-independent acquisition of transferrin-bound iron by Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 May;136(5):927–933. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-5-927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. J., Williams P. Utilization of transferrin-bound iron by Haemophilus species of human and porcine origins. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Nov;53(1-2):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90378-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Smith A. L., Averill D. R., Smith D. H. Haemophilus influenzae meningitis in infant rats after intranasal inoculation. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):154–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Vaughn K. A. The type b capsular polysaccharide as a virulence determinant of Haemophilus influenzae: studies using clinical isolates and laboratory transformants. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):517–524. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller-Eberhard U. Hemopexin. N Engl J Med. 1970 Nov 12;283(20):1090–1094. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197011122832007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padda J. S., Schryvers A. B. N-linked oligosaccharides of human transferrin are not required for binding to bacterial transferrin receptors. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2972–2976. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2972-2976.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M. Iron and virulence in the family Enterobacteriaceae. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1988;16(2):81–111. doi: 10.3109/10408418809104468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pidcock K. A., Wooten J. A., Daley B. A., Stull T. L. Iron acquisition by Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):721–725. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.721-725.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, Triton X-100, and lysozyme on the morphology and chemical composition of isolate cell walls of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):553–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.553-563.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B. Characterization of the human transferrin and lactoferrin receptors in Haemophilus influenzae. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jul;2(4):467–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B. Identification of the transferrin- and lactoferrin-binding proteins in Haemophilus influenzae. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jun;29(2):121–130. doi: 10.1099/00222615-29-2-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Morris L. J. Identification and characterization of the transferrin receptor from Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):281–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson C., Brener D., DeVoe I. W. Expression of a high-affinity mechanism for acquisition of transferrin iron by Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.107-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Smith D. H., Averill D. R., Jr, Marino J., Moxon E. R. Production of Haemophilus influenzae b meningitis in infant rats by intraperitoneal inoculation. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):278–290. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.278-290.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson P., Williams P., Griffiths E. Common antigenic domains in transferrin-binding protein 2 of Neisseria meningitidis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2391–2396. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2391-2396.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoscheck C. M. Increased uniformity in the response of the coomassie blue G protein assay to different proteins. Anal Biochem. 1990 Jan;184(1):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90021-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J., Dyer D. W., Sparling P. F. Loss of transferrin receptor activity in Neisseria meningitidis correlates with inability to use transferrin as an iron source. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3132–3138. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3132-3138.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C., GRANICK S. HEMIN BIOSYNTHESIS IN HAEMOPHILUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Apr;85:842–850. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.4.842-850.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser J. N., Love J. M., Moxon E. R. The molecular mechanism of phase variation of H. influenzae lipopolysaccharide. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):657–665. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser J. N., Maskell D. J., Butler P. D., Lindberg A. A., Moxon E. R. Characterization of repetitive sequences controlling phase variation of Haemophilus influenzae lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3304–3309. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3304-3309.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. Role of the cell envelope in bacterial adaptation to growth in vivo in infections. Biochimie. 1988 Aug;70(8):987–1011. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90263-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwahlen A., Rubin L. G., Moxon E. R. Contribution of lipopolysaccharide to pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae: comparative virulence of genetically-related strains in rats. Microb Pathog. 1986 Oct;1(5):465–473. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Alphen L., Geelen-van den Broek L., van Ham M. In vivo and in vitro expression of outer membrane components of Haemophilus influenzae. Microb Pathog. 1990 Apr;8(4):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90053-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]