Abstract
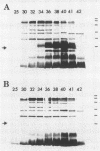
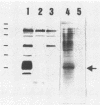
Virulent Rhodococcus equi showing 15- to 17-kDa antigens, which is virulent in mice, was found to harbor an 85-kbp plasmid, and the 15- to 17-kDa antigens were found to be associated with possession of the 85-kbp plasmid of R. equi (S. Takai, T. Sekizaki, T. Ozawa, T. Sugawara, Y. Watanabe, and S. Tsubaki, Infect. Immun. 59:4056-4060, 1991). The expression of these antigens was temperature regulated: when cells were grown at a low temperature (25 to 32 degrees C), they did not express them, whereas they expressed them in large amounts when the cells were grown at a higher temperature (34 to 41 degrees C). The antigens were expressed on the cell surface, as evidenced by their susceptibility to proteolysis by a trypsin and by the biotin-avidin protein-blotting technique.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bortolussi R., Ferrieri P., Quie P. G. Influence of growth temperature of Escherichia coli on K1 capsular antigen production and resistance to opsonization. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1136–1141. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1136-1141.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. Hemagglutination of human group A erythrocytes by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea: correlation with colonization factor. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):330–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.330-337.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Richardson L. A. The attachment to, and invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: the contribution of mannose-sensitive and mannose-resistant haemagglutinating activities. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):361–370. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Blackmon B., Curtiss R., 3rd Temperature-dependent expression of virulence genes in Shigella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):195–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.195-201.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T. Temperature regulation of virulence genes in pathogenic bacteria: a general strategy for human pathogens? Microb Pathog. 1989 Jul;7(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa M., Haritani M., Sugimoto C., Isayama Y. Virulence of Rhodococcus equi for mice. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1983 Oct;45(5):679–682. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.45.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F. Capsular serotypes of Corynebacterium equi. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Apr;45(2):130–134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F. Rhodococcus equi: an animal and human pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jan;4(1):20–34. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Travers M., Yager-Johnson J. A. Epidemiological survey of Corynebacterium equi infections on five Ontario horse farms. Can J Comp Med. 1984 Jan;48(1):10–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Koike K., Ohbushi S., Izumi C., Tsubaki S. Identification of 15- to 17-kilodalton antigens associated with virulent Rhodococcus equi. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):439–443. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.439-443.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Michizoe T., Matsumura K., Nagai M., Sato H., Tsubaki S. Correlation of in vitro properties of Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi with virulence for mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1985;29(12):1175–1184. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1985.tb00907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Ohkura H., Watanabe Y., Tsubaki S. Quantitative aspects of fecal Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi in foals. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):794–796. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.794-796.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Sekizaki T., Ozawa T., Sugawara T., Watanabe Y., Tsubaki S. Association between a large plasmid and 15- to 17-kilodalton antigens in virulent Rhodococcus equi. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4056–4060. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4056-4060.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkachuk-Saad O., Prescott J. Rhodococcus equi plasmids: isolation and partial characterization. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2696–2700. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2696-2700.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yager J. A. The pathogenesis of Rhodococcus equi pneumonia in foals. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Aug;14(3):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagawa R., Honda E. Presence of pili in species of human and animal parasites and pathogens of the genuscorynebacterium. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1293–1295. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1293-1295.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yother J., Chamness T. W., Goguen J. D. Temperature-controlled plasmid regulon associated with low calcium response in Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):443–447. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.443-447.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Wientjes F. B., Klaasen-Boor P. Production of K99 antigen by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains of antigen groups o8, o9, o20, and o101 grown at different conditions. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):216–221. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.216-221.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]