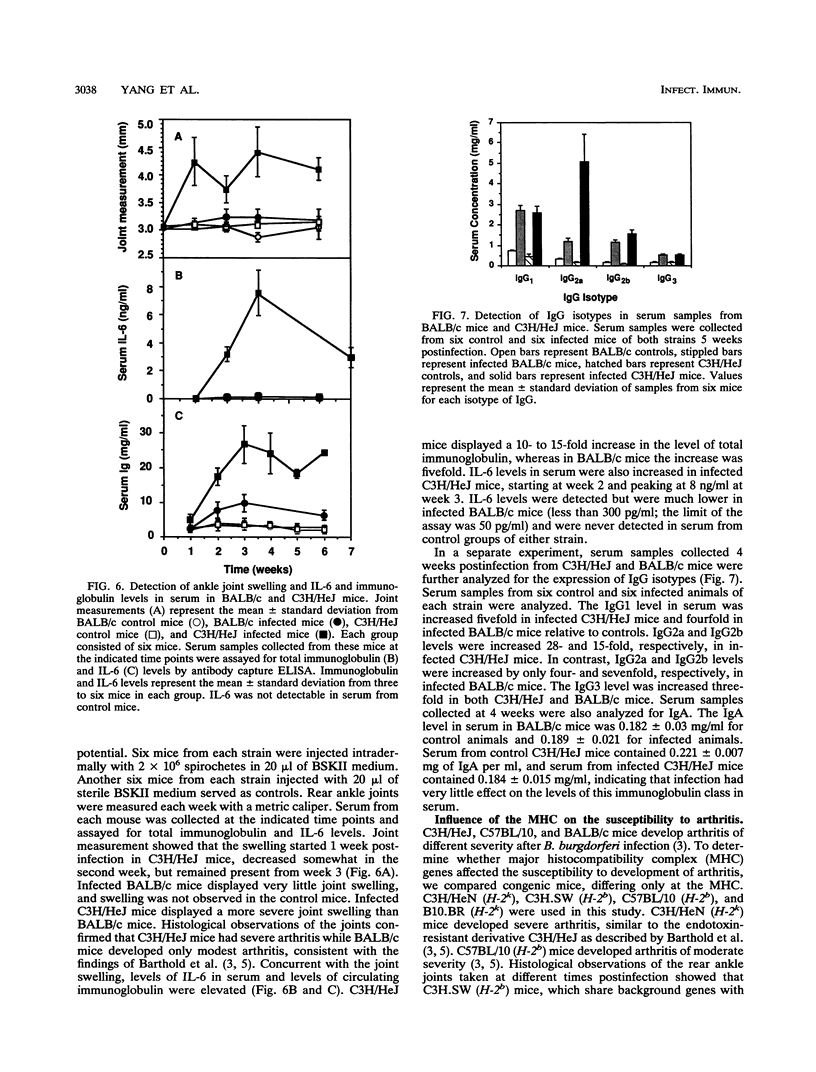
Abstract
Borrelia burgdorferi produces a mitogen for murine B lymphocytes which can be measured in vitro by polyclonal stimulation of proliferation and immunoglobulin production (R. Schoenfeld, B. Araneo, Y. Ma, L. Yang, and J. J. Weis, Infect. Immun. 60:455-464, 1992). Sonicated B. burgdorferi cells also stimulated IL-6 production by splenocyte cultures. We have used the murine model for Lyme disease described by Barthold et al. (S. W. Barthold, D. S. Beck, G. M. Hansen, G. A. Terwilliger, and K. D. Moody, J. Infect. Dis. 162:133-138, 1990) to determine whether the B. burgdorferi B-cell mitogen is expressed during active infection. To correlate arthritic changes with immune events, we have studied two strains of mice injected with B. burgdorferi; one of them, C3H/HeJ, developed severe disease, and the other, BALB/c, developed only mild disease. C3H/HeJ mice displayed a persistent 10-fold increase in circulating immunoglobulin G (IgG) levels, a 2-fold increase in IgM levels, and a 15-fold increase in peripheral lymph node B-cell numbers, providing evidence of mitogenic activity. Infected BALB/c mice also had evidence for mitogen activity, since the IgG level in serum increased three- to fourfold. The bulk of the increase in circulating IgG levels was not directed against B. burgdorferi antigens, supporting the occurrence of polyclonal B-cell activation. Analysis of IgG isotypes pointed out a contrast between C3H/HeJ and BALB/c mice in that levels of all isotypes were elevated somewhat in both strains of infected mice but IgG2a levels were much more dramatically increased in the C3H/HeJ mice (28-fold) than in the BALB/c mice (4-fold). In this study, interleukin-6 levels were found to be persistently elevated in the serum of infected C3H/HeJ mice. Interestingly, interleukin-6 levels in serum were much lower in the infected BALB/c mice. These findings indicate that the B. burgdorferi mitogen is active in infected animals and may contribute to the inflammatory and immune response to infection.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barthold S. W., Beck D. S., Hansen G. M., Terwilliger G. A., Moody K. D. Lyme borreliosis in selected strains and ages of laboratory mice. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):133–138. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W. Infectivity of Borrelia burgdorferi relative to route of inoculation and genotype in laboratory mice. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):419–420. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Moody K. D., Terwilliger G. A., Duray P. H., Jacoby R. O., Steere A. C. Experimental Lyme arthritis in rats infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):842–846. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Persing D. H., Armstrong A. L., Peeples R. A. Kinetics of Borrelia burgdorferi dissemination and evolution of disease after intradermal inoculation of mice. Am J Pathol. 1991 Aug;139(2):263–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck G., Habicht G. S., Benach J. L., Coleman J. L. Chemical and biologic characterization of a lipopolysaccharide extracted from the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi). J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):108–117. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casali P., Notkins A. L. CD5+ B lymphocytes, polyreactive antibodies and the human B-cell repertoire. Immunol Today. 1989 Nov;10(11):364–368. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comstock L. E., Thomas D. D. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi invasion of cultured endothelial cells. Microb Pathog. 1991 Feb;10(2):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90074-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comstock L. E., Thomas D. D. Penetration of endothelial cell monolayers by Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1626–1628. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1626-1628.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattwyler R. J., Volkman D. J., Luft B. J., Halperin J. J., Thomas J., Golightly M. G. Seronegative Lyme disease. Dissociation of specific T- and B-lymphocyte responses to Borrelia burgdorferi. N Engl J Med. 1988 Dec 1;319(22):1441–1446. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198812013192203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Pierres A., Wall K. A., Havran W., Otten G., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Kappler J. Characterization of the murine antigenic determinant, designated L3T4a, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: expression of L3T4a by functional T cell clones appears to correlate primarily with class II MHC antigen-reactivity. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:29–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser C., Radbruch A. Immunoglobulin class switching: molecular and cellular analysis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:717–735. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelman F. D., Holmes J., Katona I. M., Urban J. F., Jr, Beckmann M. P., Park L. S., Schooley K. A., Coffman R. L., Mosmann T. R., Paul W. E. Lymphokine control of in vivo immunoglobulin isotype selection. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:303–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Monco J. C., Villar B. F., Alen J. C., Benach J. L. Borrelia burgdorferi in the central nervous system: experimental and clinical evidence for early invasion. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1187–1193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golightly M., Thomas J., Volkman D., Dattwyler R. Modulation of natural killer cell activity by Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths M. M., DeWitt C. W. Genetic control of collagen-induced arthritis in rats: the immune response to type II collagen among susceptible and resistant strains and evidence for multiple gene control. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2830–2836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habicht G. S., Beck G., Benach J. L., Coleman J. L., Leichtling K. D. Lyme disease spirochetes induce human and murine interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3147–3154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habicht G. S., Katona L. I., Benach J. L. Cytokines and the pathogenesis of neuroborreliosis: Borrelia burgdorferi induces glioma cells to secrete interleukin-6. J Infect Dis. 1991 Sep;164(3):568–574. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.3.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Hayakawa K. Development and physiology of Ly-1 B and its human homolog, Leu-1 B. Immunol Rev. 1986 Oct;93:53–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haughton G., Arnold L. W., Bishop G. A., Mercolino T. J. The CH series of murine B cell lymphomas: neoplastic analogues of Ly-1+ normal B cells. Immunol Rev. 1986 Oct;93:35–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Y., Sturrock A., Weis J. J. Intracellular localization of Borrelia burgdorferi within human endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):671–678. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.671-678.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaka N., Sato K., Hashimoto J., Kohsaka H., Yamamoto K., Goto M., Inoue K., Matsuda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Constitutive production of interleukin 6/B cell stimulatory factor-2 from inflammatory synovium. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Aug;52(2):238–247. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawata Y., Eugui E. M., Lee S. W., Allison A. C. IL-6 is the principal factor produced by synovia of patients with rheumatoid arthritis that induces B-lymphocytes to secrete immunoglobulins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;557:230-8, discussion 239. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Wallich R., Tran T., Simon M. M. Experimental Borrelia burgdorferi infection in inbred mouse strains: antibody response and association of H-2 genes with resistance and susceptibility to development of arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2397–2405. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfeld R., Araneo B., Ma Y., Yang L. M., Weis J. J. Demonstration of a B-lymphocyte mitogen produced by the Lyme disease pathogen, Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):455–464. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.455-464.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinmei M., Masuda K., Kikuchi T., Shimomura Y., Okada Y. Production of cytokines by chondrocytes and its role in proteoglycan degradation. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1991 Feb;27:89–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal L. H. Lyme disease, 1988: immunologic manifestations and possible immunopathogenetic mechanisms. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Feb;18(3):151–167. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(89)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal L. H., Steere A. C., Dwyer J. M. In vivo and in vitro evidence of B cell hyperactivity during Lyme disease. J Rheumatol. 1988 Apr;15(4):648–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnes H. F., Jr, Pearce M. K., Tewari A., Yim J. H., Zou J. C., Abrams J. S. Anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibodies protect against lethal Escherichia coli infection and lethal tumor necrosis factor-alpha challenge in mice. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4185–4191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczepanski A., Furie M. B., Benach J. L., Lane B. P., Fleit H. B. Interaction between Borrelia burgdorferi and endothelium in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1637–1647. doi: 10.1172/JCI114615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawara T., Shingu M., Nobunaga M., Naono T. Effects of recombinant human IL-1 beta on production of prostaglandin E2, leukotriene B4, NAG, and superoxide by human synovial cells and chondrocytes. Inflammation. 1991 Apr;15(2):145–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00917509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:253–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Luthra H. S., Griffiths M. M., Stuart J. M., Huse A., David C. S. Type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. IV. Variations in immunogenetic regulation provide evidence for multiple arthritogenic epitopes on the collagen molecule. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2443–2451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yssel H., Shanafelt M. C., Soderberg C., Schneider P. V., Anzola J., Peltz G. Borrelia burgdorferi activates a T helper type 1-like T cell subset in Lyme arthritis. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):593–601. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoschke D. C., Skemp A. A., Defosse D. L. Lymphoproliferative responses to Borrelia burgdorferi in Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Feb 15;114(4):285–289. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-4-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]