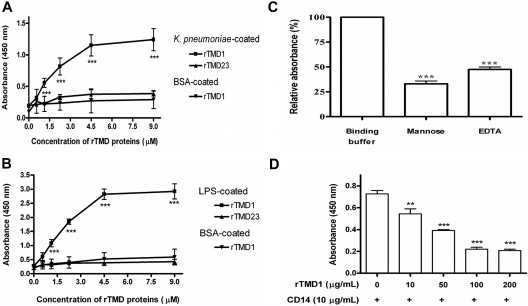
Figure 4.
Binding of rTMD proteins with K pneumoniae and LPS, and the blocking effect of rTMD1 on the binding of CD14 to LPS. (A) K pneumoniae or BSA. (B) E coli O111:B4 LPS or BSA. (A,B) K pneumoniae, LPS, or BSA was coated onto wells. Equimolar amounts of rTMD proteins were added to each well. The binding of rTMD proteins was detected. Values are the mean plus or minus SD (n = 6). ***P < .001 compared with the rTMD23-added group and BSA-coated group. (C) LPS was coated onto wells and incubated with rTMD1 (50 μg/mL) in binding buffer containing CaCl2 in the absence and presence of 0.2 M mannose or 5 mM EDTA. The results are expressed as the percentage of relative absorbance normalized with binding buffer group (100%). Values are the mean plus or minus SD (n = 6). ***P < .001 compared with the binding buffer group. The results shown are typical of those obtained in at least 3 independent experiments. (D) rTMD1 blockage of the binding of CD14 to LPS. LPS was coated onto wells and incubated with indicated concentrations of rTMD1 and CD14. The binding of CD14 to LPS was detected using CD14 antibody (M-305, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA). Values are the mean plus or minus SD (n = 4), **P < .01 and ***P < .001 compared with the group that received only CD14. Similar results were obtained in 3 independent experiments.