Abstract
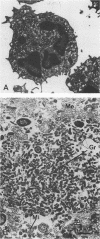
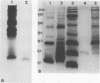
Endogenous, cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptides known as defensins are prominent components of human, rabbit, and rat neutrophils, yet little is known about their occurrence in other mammalian species. Although we did not detect mature (i.e., processed) defensins in equine neutrophil granules, we found that these granules contained small amounts of other cysteine-rich peptides with antimicrobial activity. One of these, eNAP-1, was purified by a combination of gel permeation and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography from acid extracts prepared from the cytoplasmic granules of equine neutrophils. The molecular mass of eNAP-1 was approximately 7.2 kDa, as determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis. Amino acid analysis revealed that eNAP-1 had an unusually high cysteine content and that it was relatively enriched in alanine, glycine, lysine, and proline residues. The partial (N-terminal) amino acid sequence of eNAP-1 was DVQCGEGHFCHDXQTCCRASQGGXACCPYSQGVCCADQRHCCPVGF. Thirty-six of these residues (78.3%) were identical to those of a recently cloned human neutrophil peptide of unknown function and belonging to the granulin family. Homologous peptides have also been noted in rat bone marrow cells and rat kidney epithelins. We tested the ability of eNAP-1 to kill several equine uterine pathogens. Streptococcus zooepidemicus was killed most effectively, sustaining a greater than 99.8% decrease in CFU per milliliter after a 2-h exposure to 100 micrograms of eNAP-1 per ml (approximately 15 microM). Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa were somewhat less susceptible, manifesting 87.0 and 87.1% mean decreases in CFU per milliliter, respectively, after incubation for 2 h with 200 micrograms of eNAP-1 per ml. Klebsiella pneumoniae numbers were not significantly reduced after exposure to eNAP-1. These antimicrobial properties suggest that eNAP-1 may contribute to phagocyte-mediated host defense against equine infections.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bateman A., Belcourt D., Bennett H., Lazure C., Solomon S. Granulins, a novel class of peptide from leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1161–1168. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80908-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidlingmeyer B. A., Cohen S. A., Tarvin T. L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 7;336(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond G., Zasloff M., Eck H., Brasseur M., Maloy W. L., Bevins C. L. Tracheal antimicrobial peptide, a cysteine-rich peptide from mammalian tracheal mucosa: peptide isolation and cloning of a cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly C. B., Gilchrist J. E., Peeler J. T., Campbell J. E. Spiral plate count method for the examination of raw and pasteurized milk. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):21–27. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.21-27.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhauer P. B., Harwig S. S., Szklarek D., Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. Purification and antimicrobial properties of three defensins from rat neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2021–2027. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2021-2027.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Harwig S. S., Daher K., Bainton D. F., Lehrer R. I. Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1427–1435. doi: 10.1172/JCI112120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwig S. S., Park A. S., Lehrer R. I. Characterization of defensin precursors in mature human neutrophils. Blood. 1992 Mar 15;79(6):1532–1537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson R. L., Meredith S. C. Amino acid analysis by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography: precolumn derivatization with phenylisothiocyanate. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Babior B. M., Curnutte J. T. Neutrophils and host defense. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Jul 15;109(2):127–142. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-2-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Brown D. M., DeLange R. J., Harwig S. S., Lehrer R. I. Primary structures of six antimicrobial peptides of rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4579–4584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Harwig S. S., Ganz T., Schilling J. W., Lehrer R. I. Primary structures of three human neutrophil defensins. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1436–1439. doi: 10.1172/JCI112121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Harwig S. S. Purification, primary structure, and antimicrobial activities of a guinea pig neutrophil defensin. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2281–2286. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2281-2286.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Lehrer R. I. Purification and antibacterial activity of antimicrobial peptides of rabbit granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):150–154. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.150-154.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoyab M., McDonald V. L., Byles C., Todaro G. J., Plowman G. D. Epithelins 1 and 2: isolation and characterization of two cysteine-rich growth-modulating proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7912–7916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]