Abstract
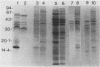
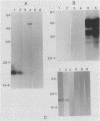
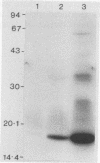
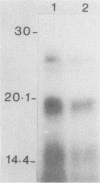
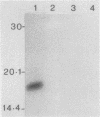
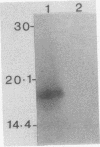
Serpulina (Treponema) hyodysenteriae P18A and VS1 were extracted by using the detergent Triton X-114 and separated into detergent and aqueous phases. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Western immunoblot analysis confirmed that a membrane-associated 16-kDa antigen was hydrophobic, since it was found in the detergent phase. A 45-kDa antigen partitioned into the aqueous phase, suggesting that it was hydrophilic and may be of periplasmic origin. When spirochetes were grown in the presence of [3H]palmitic acid, a predominant 16-kDa antigen was labeled; from the results of immunoprecipitation experiments, this antigen appeared to be the same as that recognized by both polyclonal and monoclonal antisera to a previously described 16-kDa antigen. This antigen was proteinase K sensitive and was not a component of the lipopolysaccharide, which, although [3H]palmitate labeled, was resistant to proteinase K digestion. The most probable explanation is that the 16-kDa antigen is a membrane-associated, surface-exposed, immunodominant lipoprotein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Hayes S. F. Variation in a major surface protein of Lyme disease spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.94-100.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Todd W. J. Lyme disease spirochetes and ixodid tick spirochetes share a common surface antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):795–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.795-804.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt M. E., Riley B. S., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Immunogenic integral membrane proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi are lipoproteins. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):983–991. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.983-991.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain N. R., Brandt M. E., Erwin A. L., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Major integral membrane protein immunogens of Treponema pallidum are proteolipids. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2872–2877. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2872-2877.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain N. R., DeOgny L., Slaughter C., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Acylation of the 47-kilodalton major membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum determines its hydrophobicity. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2878–2885. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2878-2885.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemetson K. J., Bienz D., Zahno M. L., Lüscher E. F. Distribution of platelet glycoproteins and phosphoproteins in hydrophobic and hydrophilic phases in Triton X-114 phase partition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 19;778(3):463–469. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90395-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. L., Chang P., McDowall A. W., Radolf J. D. The outer membrane, not a coat of host proteins, limits antigenicity of virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1076–1083. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1076-1083.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham T. M., Walker E. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Selective release of the Treponema pallidum outer membrane and associated polypeptides with Triton X-114. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5789–5796. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5789-5796.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan I. T., Harris D. L., Joens L. A. Comparison of the microtitration agglutination test and the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of herds affected with swine dysentery. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Jul;44(7):1323–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halter M. R., Joens L. A. Lipooligosaccharides from Treponema hyodysenteriae and Treponema innocens. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3152–3156. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3152-3156.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantke K., Braun V. Covalent binding of lipid to protein. Diglyceride and amide-linked fatty acid at the N-terminal end of the murein-lipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr;34(2):284–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Alexander T. J., Whipp S. C., Robinson I. M., Glock R. D., Matthews P. J. Swine dysentery: studies of gnotobiotic pigs inoculated with Treponema hyodysenteriae, Bacteroides vulgatus, and Fusobacterium necrophorum. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Feb 15;172(4):468–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Glock R. D., Christensen C. R., Kinyon J. M. Inoculation of pigs with Treponema hyodysenteriae (new species) and reproduction f the disease. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1972 Jan;67(1):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Wu H. C. Lipoproteins in bacteria. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Jun;22(3):451–471. doi: 10.1007/BF00763177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joens L. A., Harris D. L., Baum D. H. Immunity to Swine dysentery in recovered pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Oct;40(10):1352–1354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joens L. A., Marquez R. B. Molecular characterization of proteins from porcine spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):893–896. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.893-896.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent K. A., Lemcke R. M., Lysons R. J. Production, purification and molecular weight determination of the haemolysin of Treponema hyodysenteriae. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Nov;27(3):215–224. doi: 10.1099/00222615-27-3-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent K. A., Sellwood R., Lemcke R. M., Burrows M. R., Lysons R. J. Analysis of the axial filaments of Treponema hyodysenteriae by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jun;135(6):1625–1632. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-6-1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A., Singer S. J. Anomalous interaction of the acetylcholine receptor protein with the nonionic detergent Triton X-114. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):958–962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson L. D. Clinical and pathological observations on the experimental passage of swine dysentery. Can J Comp Med. 1974 Jan;38(1):7–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell B. K., Swancutt M. A., Radolf J. D. Lipid modification of the 15 kiloDalton major membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1371–1379. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees A. S., Lysons R. J., Stokes C. R., Bourne F. J. Antibody production by the pig colon during infection with Treponema hyodysenteriae. Res Vet Sci. 1989 Sep;47(2):263–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schouls L. M., Mout R., Dekker J., van Embden J. D. Characterization of lipid-modified immunogenic proteins of Treponema pallidum expressed in Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1989 Sep;7(3):175–188. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellwood R., Kent K. A., Burrows M. R., Lysons R. J., Bland A. P. Antibodies to a common outer envelope antigen of Treponema hyodysenteriae with antibacterial activity. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Aug;135(8):2249–2257. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-8-2249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton T. B., Jensen N. S., Casey T. A., Tordoff L. A., Dewhirst F. E., Paster B. J. Reclassification of Treponema hyodysenteriae and Treponema innocens in a new genus, Serpula gen. nov., as Serpula hyodysenteriae comb. nov. and Serpula innocens comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;41(1):50–58. doi: 10.1099/00207713-41-1-50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton T. B. Proposal to change the genus designation Serpula to Serpulina gen. nov. containing the species Serpulina hyodysenteriae comb. nov. and Serpulina innocens comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;42(1):189–190. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-1-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swancutt M. A., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. The 34-kilodalton membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum is a lipoprotein. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):384–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.384-392.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W., Sellwood R. Monoclonal antibodies to a 16-kDa antigen of Serpulina (Treponema) hyodysenteriae. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Sep;37(3):214–220. doi: 10.1099/00222615-37-3-214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemuehler M. J., Hubbard R. D., Greer J. M. Characterization of the major outer membrane antigens of Treponema hyodysenteriae. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3032–3039. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3032-3039.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]