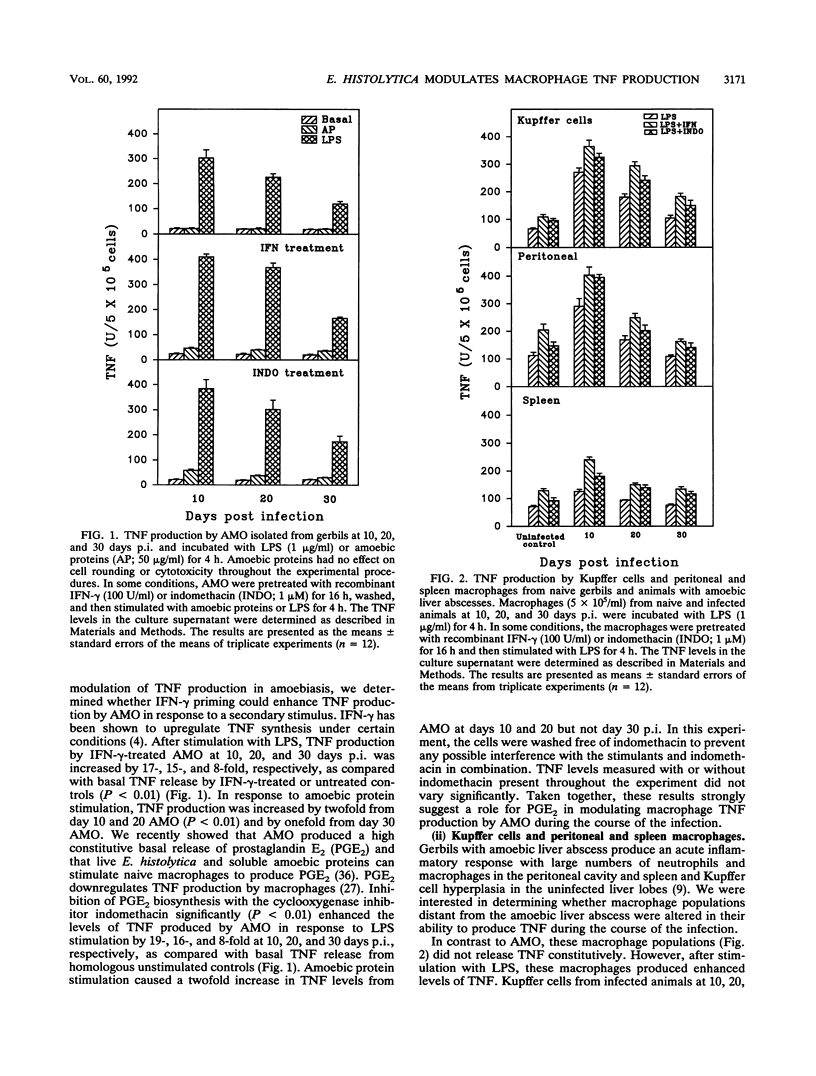
Abstract
The macrophage-derived mediator tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) is a cytokine with pleiotropic effects. TNF exhibits potent immunologic and inflammatory properties in parasitic diseases. The present study examined the production of TNF by macrophages isolated from gerbils infected with Entamoeba histolytica and by naive macrophages in response to amoebae in vitro. Amoebic liver abscess-derived macrophages produced low constitutive basal levels of TNF; in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation, TNF production was enhanced by 14-, 11-, and 6-fold at 10, 20, and 30 days postinfection, respectively. Amoebic liver abscess-derived macrophages pretreated with either recombinant gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) or the cyclooxygenase inhibitor indomethacin augmented TNF production in response to soluble amoebic proteins and LPS. Kupffer cells and peritoneal and spleen macrophages from infected animals did not release TNF constitutively in vitro. However, TNF production in response to LPS stimulation was significantly higher at 10 and 20 days postinfection. Macrophages from infected and naive animals pretreated with recombinant IFN-gamma or indomethacin produced increased amounts of TNF in response to LPS but not in response to soluble amoebic protein stimulation. Pretreatment of naive macrophages with amoebic proteins inhibited LPS-induced TNF production by 69 to 79%; the effect of the amoebic proteins was partially reversed by indomethacin pretreatment. In contrast, IFN-gamma- and LPS-activated naive macrophages produced enhanced levels of TNF in response to live amoebae and soluble amoebic proteins. Our results demonstrate that TNF production by macrophages is altered during E. histolytica infection and in response to amoebae and suggest a role for IFN-gamma and prostaglandin E2 in regulating TNF production during the infection.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bate C. A., Taverne J., Playfair J. H. Soluble malarial antigens are toxic and induce the production of tumour necrosis factor in vivo. Immunology. 1989 Apr;66(4):600–605. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boraschi D., Censini S., Bartalini M., Tagliabue A. Regulation of arachidonic acid metabolism in macrophages by immune and nonimmune interferons. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):502–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchett S. K., Weaver W. M., Westall J. A., Larsen A., Kronheim S., Wilson C. B. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin and IL-1 secretion in human mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3473–3481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadee K., Meerovitch E. Entamoeba histolytica: diffuse liver inflammation in gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus) with experimentally induced amebic liver abscess. J Protozool. 1989 Mar-Apr;36(2):154–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1989.tb01064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadee K., Meerovitch E. The Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus) as an experimental host for Entamoeba histolytica. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Jan;33(1):47–54. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadee K., Meerovitch E. The pathogenesis of experimentally induced amebic liver abscess in the gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). Am J Pathol. 1984 Oct;117(1):71–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Otterness I. G., Higashi G. I., Forsch C. S., Kunkel S. L. Monokine production by hypersensitivity (Schistosoma mansoni egg) and foreign body (Sephadex bead)-type granuloma macrophages. Evidence for sequential production of IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1281–1286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Cowden W. B., Butcher G. A., Hunt N. H. Possible roles of tumor necrosis factor in the pathology of malaria. Am J Pathol. 1987 Oct;129(1):192–199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Hunt N. H., Butcher G. A., Cowden W. B. Inhibition of murine malaria (Plasmodium chabaudi) in vivo by recombinant interferon-gamma or tumor necrosis factor, and its enhancement by butylated hydroxyanisole. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3493–3496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Belin D., Vassalli J. D., de Kossodo S., Vassalli P. Gamma interferon enhances macrophage transcription of the tumor necrosis factor/cachectin, interleukin 1, and urokinase genes, which are controlled by short-lived repressors. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):2113–2118. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Chadee K. Cytokine activation of murine macrophages for in vitro killing of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1750–1756. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1750-1756.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Chadee K. Human neutrophils activated by interferon-gamma and tumour necrosis factor-alpha kill Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites in vitro. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Sep;46(3):270–274. doi: 10.1002/jlb.46.3.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Chadee K. In vitro and in vivo studies of macrophage functions in amebiasis. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3126–3131. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3126-3131.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Keller K., Chadee K. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin and amebic liver abscess. Am J Med. 1990 Jan;88(1):84–85. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Staugas R. E., Rowan-Kelly B., Bresatz S., Kumaratilake L. M., Rzepczyk C. M., Adolf G. R. Production of tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta by human mononuclear leukocytes stimulated with mitogens, bacteria, and malarial parasites. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3996–4003. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3996-4003.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton R. Y., Golenbock D. T., Raetz C. R. Lipid A binding sites in membranes of macrophage tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14802–14807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katakami Y., Nakao Y., Koizumi T., Katakami N., Ogawa R., Fujita T. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor production by mouse peritoneal macrophages: the role of cellular cyclic AMP. Immunology. 1988 Aug;64(4):719–724. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A., Harlan J. M., Sparks L. H., Gamble J. R., Agosti J. M., Waltersdorph A. M. Stimulation of neutrophils by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4220–4225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W., Phan S. H. Prostaglandins as endogenous mediators of interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Wiggins R. C., Chensue S. W., Larrick J. Regulation of macrophage tumor necrosis factor production by prostaglandin E2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 29;137(1):404–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll H., Binöder K., Bogdan C., Solbach W., Röllinghoff M. Production of tumour necrosis factor during murine cutaneous leishmaniasis. Parasite Immunol. 1990 Sep;12(5):483–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1990.tb00983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picot S., Peyron F., Vuillez J. P., Barbe G., Marsh K., Ambroise-Thomas P. Tumor necrosis factor production by human macrophages stimulated in vitro by Plasmodium falciparum. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):214–216. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.214-216.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salata R. A., Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Ravdin J. I. The role of gamma interferon in the generation of human macrophages cytotoxic for Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Jul;37(1):72–78. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.37.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scuderi P., Sterling K. E., Lam K. S., Finley P. R., Ryan K. J., Ray C. G., Petersen E., Slymen D. J., Salmon S. E. Raised serum levels of tumour necrosis factor in parasitic infections. Lancet. 1986 Dec 13;2(8520):1364–1365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solis-Herruzo J. A., Brenner D. A., Chojkier M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits collagen gene transcription and collagen synthesis in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5841–5845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Palombella V. J., Henriksen-DeStefano D., Swenson C., Feinman R., Hirai M., Tsujimoto M. Fibroblast growth enhancing activity of tumor necrosis factor and its relationship to other polypeptide growth factors. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):632–643. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth J. J., Kierszenbaum F. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor enhances macrophage destruction of Trypanosoma cruzi in the presence of bacterial endotoxin. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):286–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


