Abstract
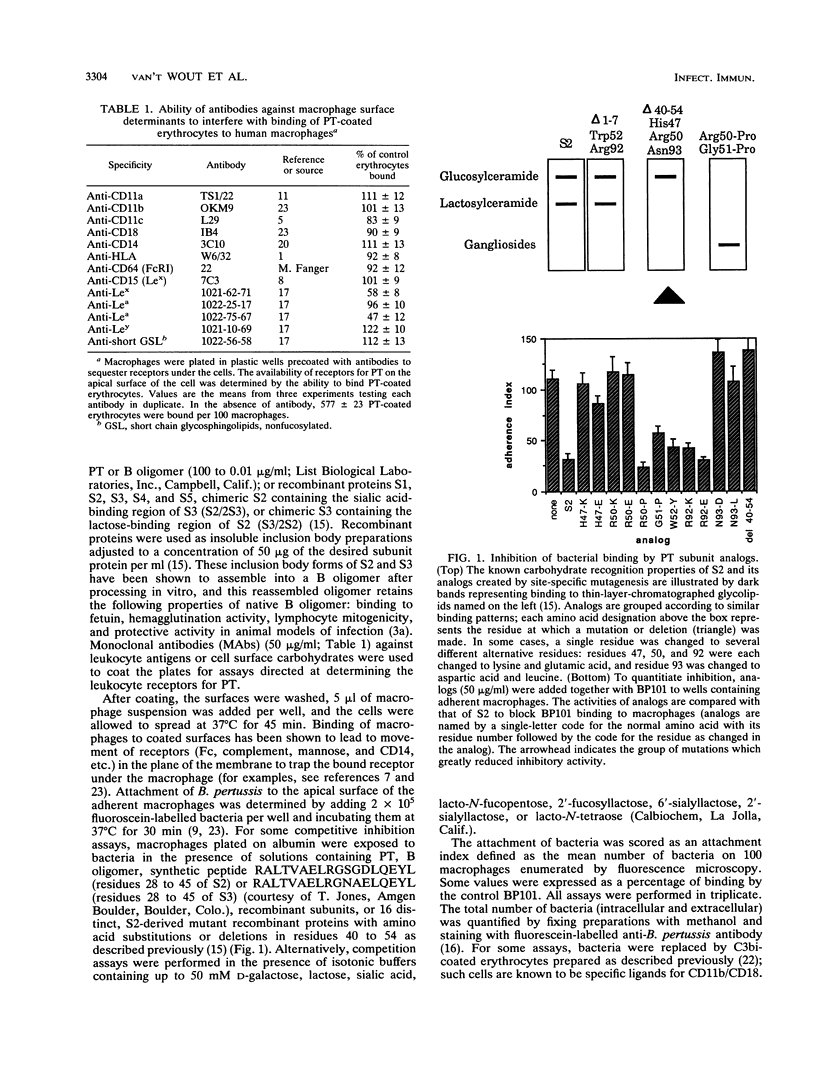
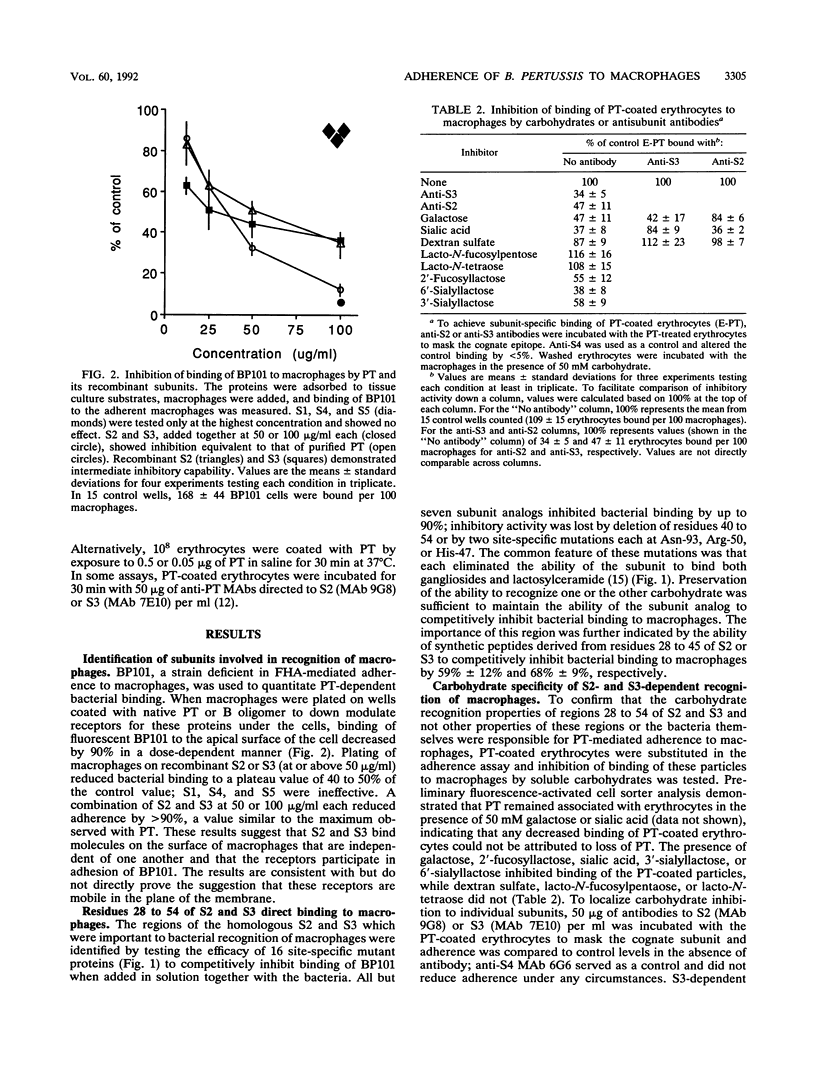
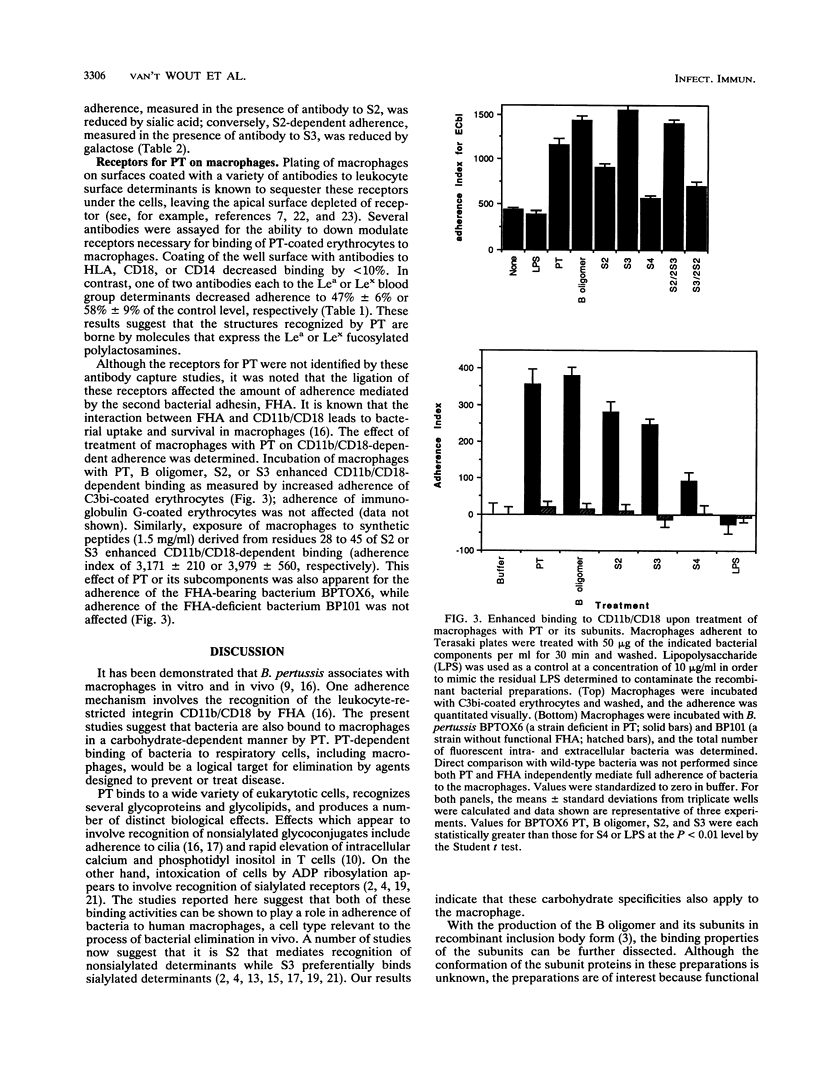
Pertussis toxin (PT) and filamentous hemagglutinin can each mediate the association of Bordetella pertussis with human macrophages. Adherence via filamentous hemagglutinin leads to integrin-mediated entry and survival of the bacteria within the human cell. We determined the contribution of PT to bacterial adherence to human macrophages. Plating macrophages on wells coated with recombinant PT subunit 2 (S2) or S3 decreased PT-dependent bacterial binding by greater than 60%; S1, S4, and S5 were ineffective. S3-dependent adherence was reduced 63% +/- 8% by sialic acid, while S2-dependent adherence was reduced 53% +/- 11% by galactose. Loss of the carbohydrate recognition properties of S2 by deletion of residues 40 to 54 or site-specific mutations at Asn-93, His-47, or Arg-50 eliminated the ability of the subunit protein to competitively inhibit bacterial binding. Peptides corresponding to residues 28 to 45 of S2 and S3 competitively inhibited adherence. Treatment of macrophages with antibodies to Le(a) or Le(x) but not CD14, CD15, CD18, or HLA interfered with PT-mediated binding. Exposure of the macrophages to the B oligomer, S2, or S3 increased binding to the CD11b/CD18 integrin. These results indicate that the carbohydrate recognition domains of both S2 and S3 participate in adherence of B. pertussis to human macrophages. The PT receptor(s), as yet unidentified, appears to carry the Le(a) or Le(x) determinants and is functionally capable of modulating integrin-mediated binding to the macrophage.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. J., David J. L., Kenimer J. G., Manclark C. R. Lectin-like binding of pertussis toxin to a 165-kilodalton Chinese hamster ovary cell glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4895–4899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. G., Armstrong G. D. Lymphocyte receptors for pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3840–3846. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3840-3846.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Arnaout M. A., Schwarting R., Warner N. L., Ross G. D. p150/95, Third member of the LFA-1/CR3 polypeptide family identified by anti-Leu M5 monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jul;15(7):713–718. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. K., Lee S., Ramos R. A., Lobb R., Rosa M., Chi-Rosso G., Wright S. D. Endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 stimulates the adhesive activity of leukocyte integrin CR3 (CD11b/CD18, Mac-1, alpha m beta 2) on human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1493–1500. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauseef W. M., Root R. K., Newman S. L., Malech H. L. Inhibition of zymosan activation of human neutrophil oxidative metabolism by a mouse monoclonal antibody. Blood. 1983 Sep;62(3):635–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D., Tuomanen E., Falkow S., Golenbock D. T., Saukkonen K., Wright S. D. Recognition of a bacterial adhesion by an integrin: macrophage CR3 (alpha M beta 2, CD11b/CD18) binds filamentous hemagglutinin of Bordetella pertussis. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1375–1382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90701-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers T. S., Corey S. J., Rosoff P. M. Identification of a 43-kilodalton human T lymphocyte membrane protein as a receptor for pertussis toxin. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):678–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Madrid F., Krensky A. M., Ware C. F., Robbins E., Strominger J. L., Burakoff S. J., Springer T. A. Three distinct antigens associated with human T-lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis: LFA-1, LFA-2, and LFA-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7489–7493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Sato Y., Ito A., Ohishi I. Effect of monoclonal antibody to pertussis toxin on toxin activity. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):909–915. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.909-915.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen K., Burnette W. N., Mar V. L., Masure H. R., Tuomanen E. I. Pertussis toxin has eukaryotic-like carbohydrate recognition domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):118–122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen K., Cabellos C., Burroughs M., Prasad S., Tuomanen E. Integrin-mediated localization of Bordetella pertussis within macrophages: role in pulmonary colonization. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1143–1149. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. A., Schmidt W. Inhibition of pertussis toxin binding to model receptors by antipeptide antibodies directed at an antigenic domain of the S2 subunit. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3828–3833. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3828-3833.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W., Schmidt M. A. Mapping of linear B-cell epitopes of the S2 subunit of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):438–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.438-445.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Towbin H., Rosenfelder G., Braun D., Larson G., Hansson G. C., Hill R. Receptor analogs and monoclonal antibodies that inhibit adherence of Bordetella pertussis to human ciliated respiratory epithelial cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):267–277. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Weiss A. Characterization of two adhesins of Bordetella pertussis for human ciliated respiratory-epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):118–125. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell G. J., Peppler M. S., Bonnah R. A., Clark C. G., Chong P., Armstrong G. D. Lectinlike properties of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1854–1857. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1854-1857.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Voorhis W. C., Steinman R. M., Hair L. S., Luban J., Witmer M. D., Koide S., Cohn Z. A. Specific antimononuclear phagocyte monoclonal antibodies. Application to the purification of dendritic cells and the tissue localization of macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):126–145. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witvliet M. H., Burns D. L., Brennan M. J., Poolman J. T., Manclark C. R. Binding of pertussis toxin to eucaryotic cells and glycoproteins. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3324–3330. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3324-3330.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Rao P. E., Van Voorhis W. C., Craigmyle L. S., Iida K., Talle M. A., Westberg E. F., Goldstein G., Silverstein S. C. Identification of the C3bi receptor of human monocytes and macrophages by using monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5699–5703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Silverstein S. C. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters stimulate C3b and C3b' receptor-mediated phagocytosis in cultured human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1149–1164. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



