Abstract
The complete Shiga toxin B subunit and two N-terminal segments of the B subunit have been inserted into a cell surface exposed loop of the LamB protein, and expression of the hybrid proteins from three different promoter systems, i.e., (i) an in vitro-inducible tac promoter that provides high-level expression, (ii) the iron-regulated aerobactin promoter presumably induced in vivo under the iron-limiting conditions of the intestinal mucosal environment, and (iii) a synthetic, modified beta-lactamase promoter providing moderate level constitutive expression, has been analyzed in Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, and attenuated antigen carrier strains of S. typhimurium (aroA mutants). The hybrid vaccine strains were used to immunize mice by the oral and intraperitoneal routes. S. typhimurium aroA mutants apparently have a membrane export defect which prevents the transport of LamB and its derivatives across the cytoplasmic membrane. High-level expression of hybrid proteins through use of the tac promoter proved deleterious to the vaccine strains and prevented the production of viable cells at reasonable cell densities. The lower levels of gene expression observed with the beta-lactamase and aerobactin promoters did not have this effect. Immunization of mice with S. typhimurium aroA strains carrying the hybrid genes expressed from these two promoters resulted in significant B subunit-specific mucosal and serum antibody responses. This suggests that such expression systems may be useful when incorporated into candidate antidysentery live oral vaccines for inducing protection against the effect of Shiga toxin in infections caused by Shigella dysenteriae 1 and other Shiga toxin-or Shiga-like toxin-producing pathogens.
Full text
PDF




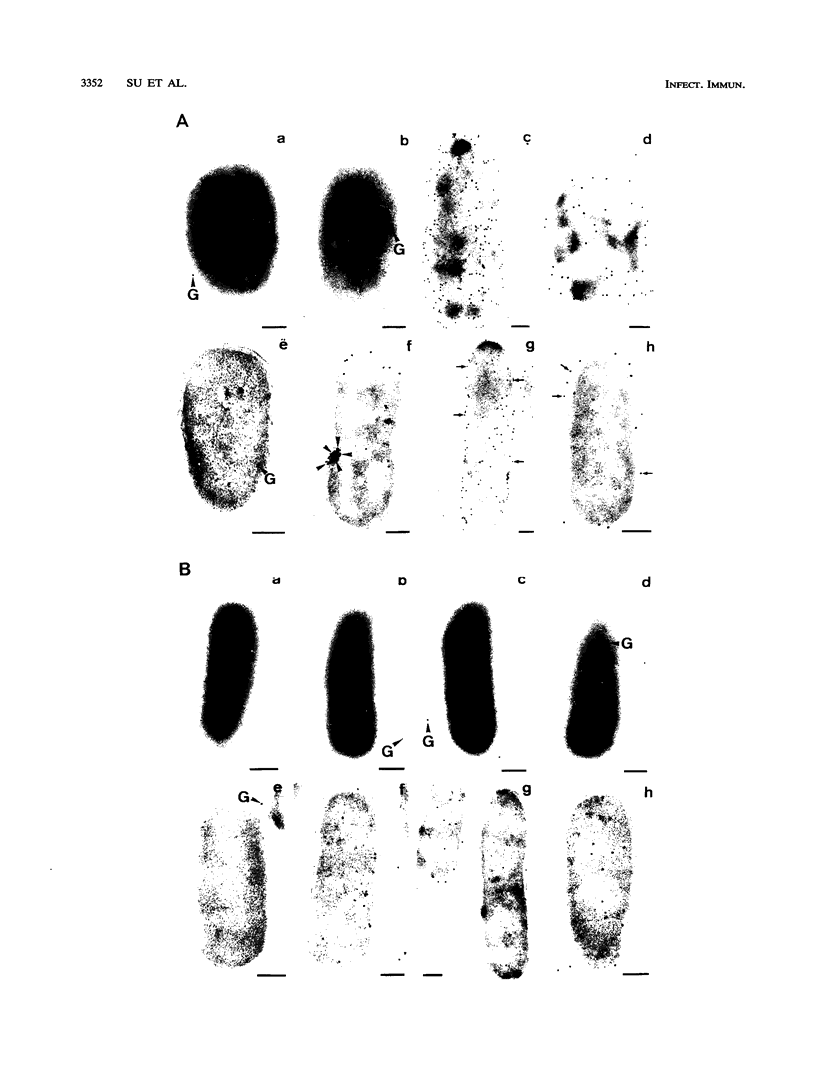




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassford P., Beckwith J., Ito K., Kumamoto C., Mizushima S., Oliver D., Randall L., Silhavy T., Tai P. C., Wickner B. The primary pathway of protein export in E. coli. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):367–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch M. A., Desaymard C. Antigenic polymorphism of the LamB protein among members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):106–110. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.106-110.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulain J. C., Charbit A., Hofnung M. Mutagenesis by random linker insertion into the lamB gene of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Nov;205(2):339–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00430448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brazil G. M., Clayton C. L., Sekizaki T., Timmis K. N. Development of DNA probes for cytotoxin and enterotoxin genes in enteric bacteria. Experientia. 1988 Oct 15;44(10):848–853. doi: 10.1007/BF01941182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R. Shiga toxin--an expanding role in the pathogenesis of infectious diseases. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):766–771. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbit A., Boulain J. C., Ryter A., Hofnung M. Probing the topology of a bacterial membrane protein by genetic insertion of a foreign epitope; expression at the cell surface. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3029–3037. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04602.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbit A., Hofnung M. Isolation of different bacteriophages using the LamB protein for adsorption on Escherichia coli K-12. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):667–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.667-671.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbit A., Molla A., Saurin W., Hofnung M. Versatility of a vector for expressing foreign polypeptides at the surface of gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Lyon F. L., Lowe K. L., Farrand A. L., el-Morshidy S. Oral immunization of mice with attenuated Salmonella enteritidis containing a recombinant plasmid which codes for production of the B subunit of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):685–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.685-692.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Edson C., Thorley-Lawson D., Jacewicz M. Pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. IX. Simplified high yield purification of Shigella toxin and characterization of subunit composition and function by the use of subunit-specific monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1767–1781. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K., Yutsudo T., Takeda Y., Ogasawara T., Igarashi K. Site of action of a Vero toxin (VT2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and of Shiga toxin on eukaryotic ribosomes. RNA N-glycosidase activity of the toxins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine A., Arondel J., Sansonetti P. J. Construction and evaluation of live attenuated vaccine strains of Shigella flexneri and Shigella dysenteriae 1. Res Microbiol. 1990 Sep-Oct;141(7-8):907–912. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90129-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine A., Arondel J., Sansonetti P. J. Role of Shiga toxin in the pathogenesis of bacillary dysentery, studied by using a Tox- mutant of Shigella dysenteriae 1. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3099–3109. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3099-3109.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harari I., Arnon R. Carboxy-terminal peptides from the B subunit of Shiga toxin induce a local and parenteral protective effect. Mol Immunol. 1990 Jul;27(7):613–621. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90003-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harari I., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G., Arnon R. Synthetic peptides of Shiga toxin B subunit induce antibodies which neutralize its biological activity. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1618–1624. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1618-1624.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):238–239. doi: 10.1038/291238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. A computer program for predicting protein antigenic determinants. Mol Immunol. 1983 Apr;20(4):483–489. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacewicz M., Clausen H., Nudelman E., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea. XI. Isolation of a shigella toxin-binding glycolipid from rabbit jejunum and HeLa cells and its identification as globotriaosylceramide. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1391–1404. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. P. Structure-function analyses of Shiga toxin and the Shiga-like toxins. Microb Pathog. 1990 Apr;8(4):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90050-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A. Infection by verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):15–38. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Brown J. E., Strömberg N., Westling-Ryd M., Schultz J. E., Karlsson K. A. Identification of the carbohydrate receptor for Shiga toxin produced by Shigella dysenteriae type 1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1779–1785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills S. D., Sekizaki T., Gonzalez-Carrero M. I., Timmis K. N. Analysis and genetic manipulation of Shigella virulence determinants for vaccine development. Vaccine. 1988 Apr;6(2):116–122. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(88)80012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton D. L., Napier M. L., Myers R. M., Hardman J. K. In vitro mutagenesis and overexpression of the Escherichia coli trpA gene and the partial characterization of the resultant tryptophan synthase mutant alpha-subunits. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16604–16615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Shiga and Shiga-like toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):206–220. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.206-220.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Gaora P., Maskel D., Coleman D., Cafferkey M., Dougan G. Cloning and characterisation of the serC and aroA genes of Yersinia enterocolitica, and construction of an aroA mutant. Gene. 1989 Dec 7;84(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Reisbig R., Eiklid K. Subunit structure of Shigella cytotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8732–8738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Westermann P. Arrangement of the maltose-inducible major outer membrane proteins, the bacteriophage lambda receptor in Escherichia coli and the 44 K protein in Salmonella typhimurium. FEBS Lett. 1979 Mar 1;99(1):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80253-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson S. E., Karmali M. A., Becker L. E., Smith C. R. The histopathology of the hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli infections. Hum Pathol. 1988 Sep;19(9):1102–1108. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Bendayan M., Carlemalm E., Villiger W., Garavito M. Enhancement of structural preservation and immunocytochemical staining in low temperature embedded pancreatic tissue. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 May;29(5):663–671. doi: 10.1177/29.5.6166664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena S. K., O'Brien A. D., Ackerman E. J. Shiga toxin, Shiga-like toxin II variant, and ricin are all single-site RNA N-glycosidases of 28 S RNA when microinjected into Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):596–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauder B., Blöcker H., Frank R., McCarthy J. E. Inducible expression vectors incorporating the Escherichia coli atpE translational initiation region. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schülein K., Benz R. LamB (maltoporin) of Salmonella typhimurium: isolation, purification and comparison of sugar binding with LamB of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Apr;4(4):625–632. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekizaki T., Harayama S., Brazil G. M., Timmis K. N. Localization of stx, a determinant essential for high-level production of shiga toxin by Shigella dysenteriae serotype 1, near pyrF and generation of stx transposon mutants. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2208–2214. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2208-2214.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Jackson M. P., Sung L. M., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Cloning and sequencing of the genes for Shiga toxin from Shigella dysenteriae type 1. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1116–1122. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1116-1122.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swidersky U. E., Hoffschulte H. K., Müller M. Determinants of membrane-targeting and transmembrane translocation during bacterial protein export. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1777–1785. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08302.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmelcman S., Hofnung M. Maltose transport in Escherichia coli K-12: involvement of the bacteriophage lambda receptor. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):112–118. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.112-118.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh V. L., O'Brien A. D. The pathogenic mechanisms of Shiga toxin and the Shiga-like toxins. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1817–1822. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Wee S., Herrero M., Neilands J. B. Operator sequences of the aerobactin operon of plasmid ColV-K30 binding the ferric uptake regulation (fur) repressor. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2624–2630. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2624-2630.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]