Abstract
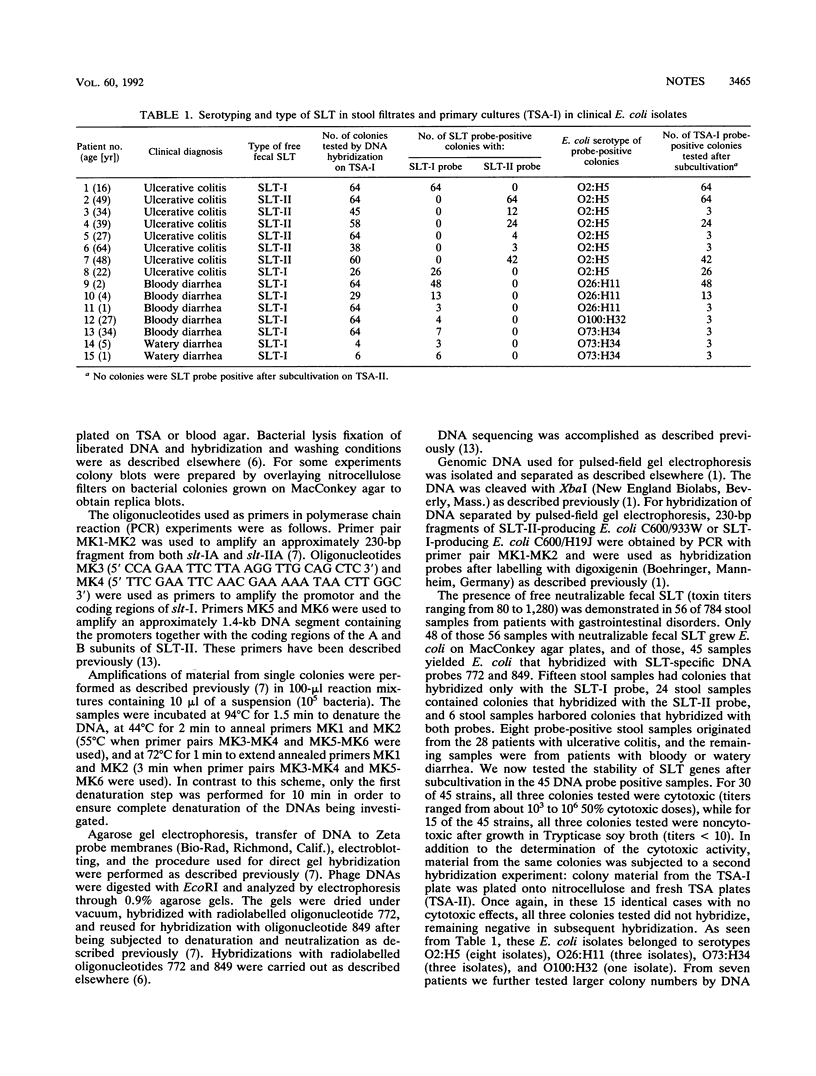
Forty-five consecutive patients with various gastrointestinal disorders were identified as having Shiga-like toxin (SLT)-producing Escherichia coli infections. This was shown by the cytotoxic effect of stool extracts in Vero cell cultures which was neutralizable by antibodies to SLTs and by isolation of E. coli that hybridized with DNA probes complementary to SLT-I and SLT-II sequences. When we tested the same strains for SLT genes after subcultivation, the isolates from 15 patients became negative by colony hybridization and polymerase chain reaction and failed to produce SLTs. The instability of SLT genes warrants direct screening methods for clinical material and the development of new culture methods to prevent the loss of SLT genes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Böhm H., Karch H. DNA fingerprinting of Escherichia coli O157:H7 strains by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):2169–2172. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.2169-2172.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hii J. H., Gyles C., Morooka T., Karmali M. A., Clarke R., De Grandis S., Brunton J. L. Development of verotoxin 2- and verotoxin 2 variant (VT2v)-specific oligonucleotide probes on the basis of the nucleotide sequence of the B cistron of VT2v from Escherichia coli E32511 and B2F1. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2704–2709. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2704-2709.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Bitzan M., Pietsch R., Stenger K. O., von Wulffen H., Heesemann J., Düsing R. Purified verotoxins of Escherichia coli O157:H7 decrease prostacyclin synthesis by endothelial cells. Microb Pathog. 1988 Sep;5(3):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Bitzan M. Purification and characterization of a phage-encoded cytotoxin from an Escherichia coli O111 strain associated with hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Nov;270(1-2):41–51. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Heesemann J., Laufs R. Phage-associated cytotoxin production by and enteroadhesiveness of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from infants with diarrhea in West Germany. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):707–715. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Meyer T. Evaluation of oligonucleotide probes for identification of shiga-like-toxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1180–1186. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1180-1186.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Meyer T. Single primer pair for amplifying segments of distinct Shiga-like-toxin genes by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2751–2757. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2751-2757.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A. Infection by verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):15–38. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Fleming P. C., Arbus G. S., Lior H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Speirs J. I., Stavric S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.775-779.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Karch H. Genes coding for Shiga-like toxin and heat-stabile enterotoxin in porcine strains of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Mar;49(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90353-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Karch H., Hacker J., Bocklage H., Heesemann J. Cloning and sequencing of a Shiga-like toxin II-related gene from Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain 7279. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1992 Jan;276(2):176–188. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland J. W., Neill R. J. DNA probes for Shiga-like toxins I and II and for toxin-converting bacteriophages. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1292–1297. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1292-1297.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Newland J. W., Miller S. F., Holmes R. K., Smith H. W., Formal S. B. Shiga-like toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli strains that cause hemorrhagic colitis or infantile diarrhea. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):694–696. doi: 10.1126/science.6387911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt C. K., McKee M. L., O'Brien A. D. Two copies of Shiga-like toxin II-related genes common in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli strains are responsible for the antigenic heterogeneity of the O157:H- strain E32511. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1065–1073. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1065-1073.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotland S. M., Smith H. R., Willshaw G. A., Rowe B. Vero cytotoxin production in strain of Escherichia coli is determined by genes carried on bacteriophage. Lancet. 1983 Jul 23;2(8343):216–216. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. R., Day N. P., Scotland S. M., Gross R. J., Rowe B. Phage-determined production of vero cytotoxin in strains of Escherichia coli serogroup O157. Lancet. 1984 Jun 2;1(8388):1242–1243. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91729-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Green P., Parsell Z. Vero cell toxins in Escherichia coli and related bacteria: transfer by phage and conjugation and toxic action in laboratory animals, chickens and pigs. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Oct;129(10):3121–3137. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-10-3121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Shiga-like toxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):695–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.695-700.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Newland J. W., Smith H. W., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Two toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain 933 encode antigenically distinct toxins with similar biologic activities. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.135-140.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. L., Jackson M. P., Samuel J. E., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Cloning and sequencing of a Shiga-like toxin type II variant from Escherichia coli strain responsible for edema disease of swine. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4223–4230. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4223-4230.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]