Abstract
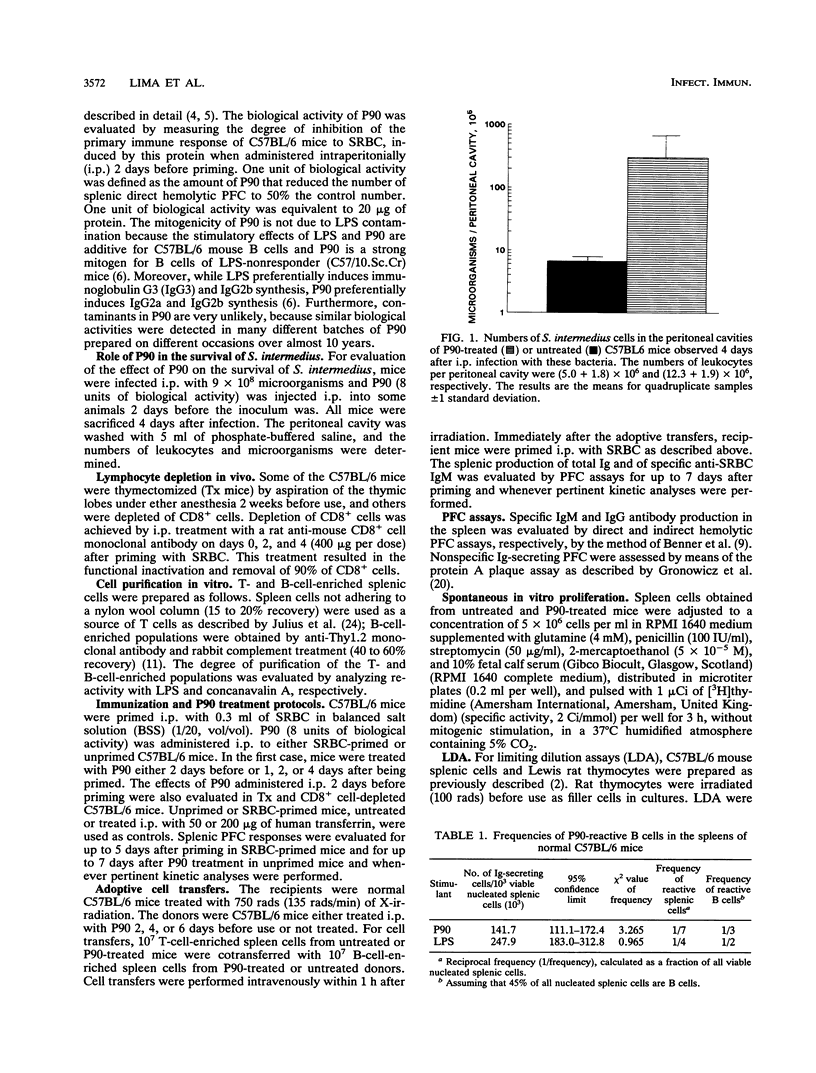
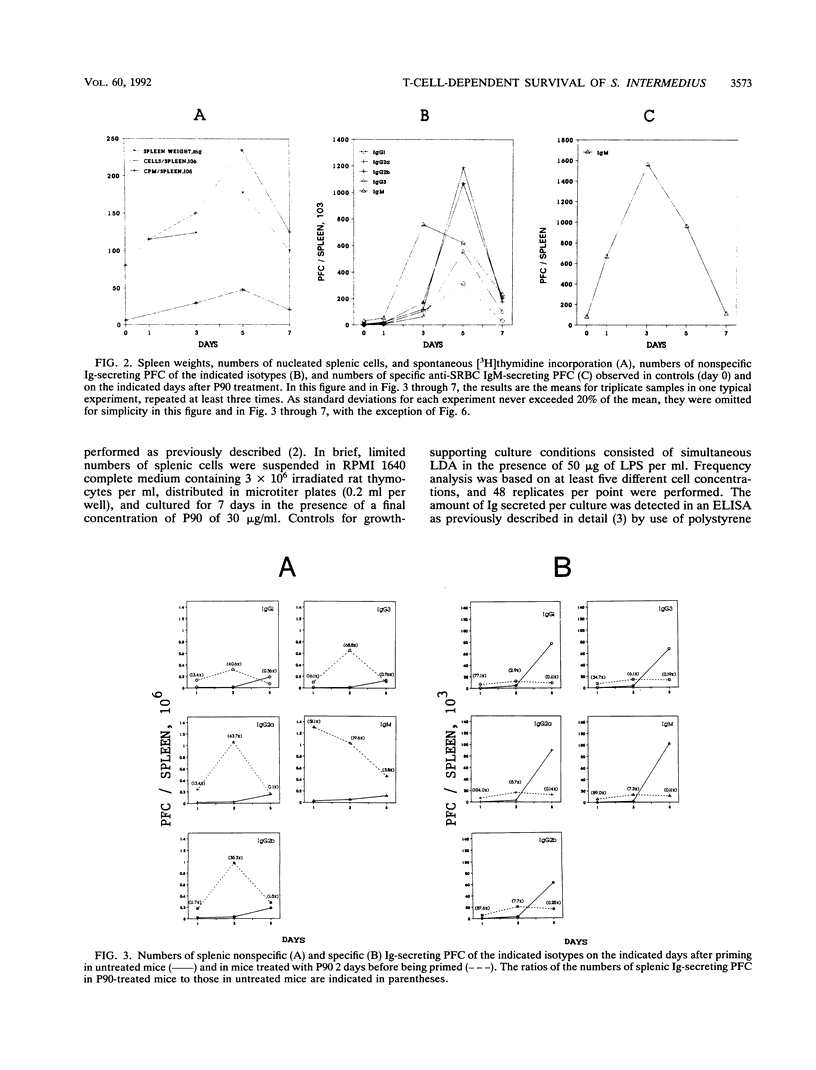
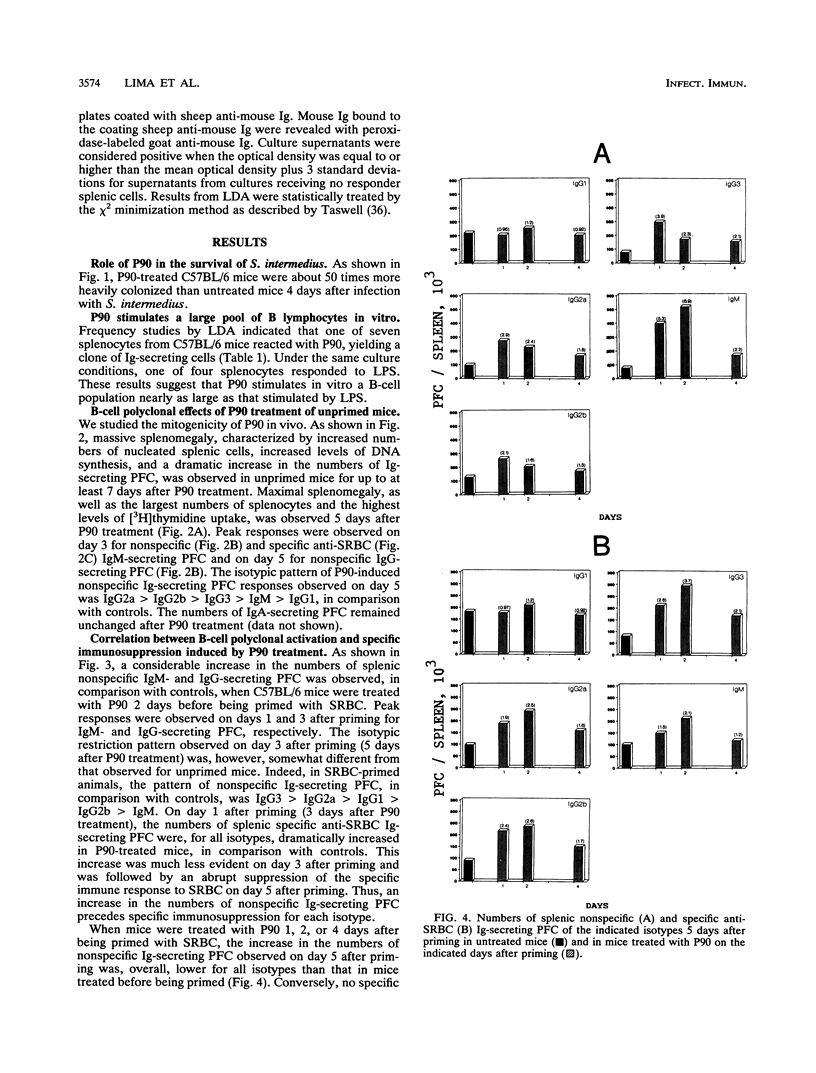
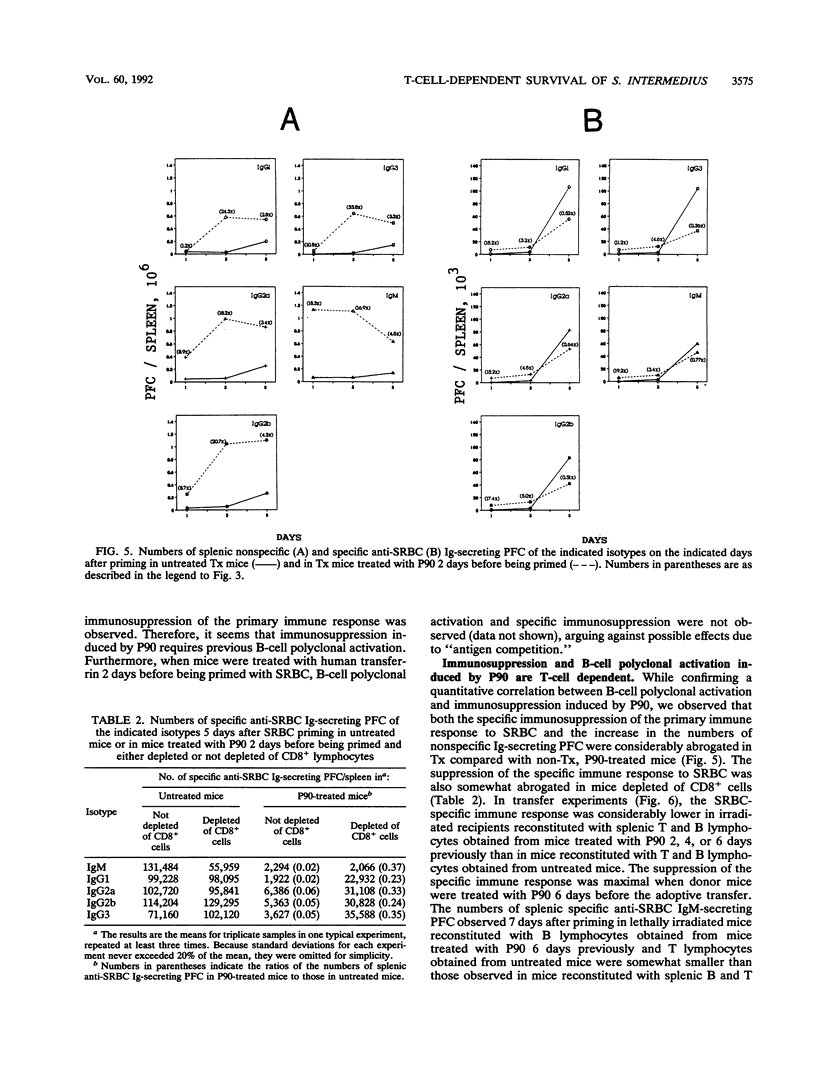
The role of a previously described bacterial protein (F3'EP-Si), now designated P90, in the survival of Streptococcus intermedius in the host was investigated, and the immunosuppressive and B-cell-mitogenic effects of this protein were further characterized. C57BL6 mice treated with P90 were about 50 times more susceptible to infection with this bacterium than untreated mice. One of seven splenocytes of C57BL/6 mice were activated by P90. Marked splenomegaly was observed in mice treated with P90, with increased numbers of splenic mononuclear cells and polyclonal immunoglobulin-secreting plaque-forming cells. Peak responses were seen on day 3 for immunoglobulin M (IgM) and on day 5 for IgG, with an isotypic pattern consisting predominantly of IgG2a and IgG2b. When mice were treated with P90 before being primed with sheep erythrocytes, polyclonal immunoglobulin synthesis was accompanied by an ephemeral stimulation of the specific immune response against sheep erythrocytes that was quickly replaced by a dramatic immunosuppression. In contrast, when mice were treated with P90 after being primed, the polyclonal activation was comparatively much less evident and there was no suppression of the specific immune response. Immunosuppression was considerably reduced in mice thymectomized as adults or depleted of CD8+ cells. Adoptive transfer experiments showed that B cells obtained from P90-treated mice were less able to respond to an antigenic challenge, even in the presence of normal T cells, and that T cells obtained from P90-treated mice could actively suppress the specific immune response of normal B cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Coutinho A., Lernhardt W., Melchers F. Clonal growth and maturation to immunoglobulin secretion in vitro of every growth-inducible B lymphocyte. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Coutinho A., Melchers F. Frequencies of mitogen-reactive B cells in the mouse. II. Frequencies of B cells producing antibodies which lyse sheep or horse erythrocytes, and trinitrophenylated or nitroiodophenylated sheep erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1977 Jun 1;145(6):1520–1530. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.6.1520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arala-Chaves M. P., Higerd T. B., Porto M. T., Munoz J., Goust J. M., Fudenberg H. H., Loadholt C. B. Evidence for the synthesis and release of strongly immunosuppressive, noncytotoxic substances by Streptococcus intermedius. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):871–883. doi: 10.1172/JCI109553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arala-Chaves M. P., Porto M. T., Arnaud P., Saraiva M. J., Geada H., Patrick C. C., Fudenberg H. H. Fractionation and characterization of the immunosuppressive substance in crude extracellular products released by Streptococcus intermedius. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):294–302. doi: 10.1172/JCI110247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arala-Chaves M. P., Ribeiro A. S., Santarém M. M., Coutinho A. Strong mitogenic effect for murine B lymphocytes of an immunosuppressor substance released by Streptococcus intermedius. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):543–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.543-548.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arala-Chaves M. P., Ribeiro A. dos S., Vilanova M., Porto M. T., Santarem M. G., Lima M. Correlation between B-cell mitogenicity and immunosuppressor effects of a protein released by porcine monocytes infected with African swine fever virus. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Nov;49(11):1955–1961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arala-Chaves M. P., Santarém M. M., Azevedo C., Soares J. O., Granjo E. Evidence for the generation of specific T suppressor lymphocytes by Streptococcus intermedius. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1983 Mar-Apr;19(2):89–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner R., Meima F., van der Meulen G. M., van Muiswinkel W. B. Antibody formation in mouse bone marrow. I. Evidence for the development of plaque-forming cells in situ. Immunology. 1974 Feb;26(2):247–255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björklund M., Beretta A., Coutinho A., Gullberg M. Effector functions and specificities of normal murine T cells stimulated by syngeneic blasts. Eur J Immunol. 1986 May;16(5):471–477. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce J., Symington F. W., McKearn T. J., Sprent J. A monoclonal antibody discriminating between subsets of T and B cells. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2496–2501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutelier J. P., Van Snick J. Isotypically restricted activation of B lymphocytes by lactic dehydrogenase virus. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Mar;15(3):250–255. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Imperio Lima M. R., Joskowicz M., Coutinho A., Kipnis T., Eisen H. Very large and isotypically atypical polyclonal plaque-forming cell responses in mice infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Feb;15(2):201–203. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dammacco F., Iodice G., Campobasso N. Treatment of adult patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura with intravenous immunoglobulin: effects on circulating T cell subsets and PWM-induced antibody synthesis in vitro. Br J Haematol. 1986 Jan;62(1):125–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1986.tb02908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delfraissy J. F., Tchernia G., Laurian Y., Wallon C., Galanaud P., Dormont J. Suppressor cell function after intravenous gammaglobulin treatment in adult chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 1985 Jun;60(2):315–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb07417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidinger D., Khan S. A., Millar K. G. The effect of antigenic competition on various manifestations of humoral antibody formation and cellular immunity. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):1183–1200. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falanga P. B., D'Imperio Lima M. R., Coutinho A., Pereira da Silva L. Isotypic pattern of the polyclonal B cell response during primary infection by Plasmodium chabaudi and in immune-protected mice. Eur J Immunol. 1987 May;17(5):599–603. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira P., Soares R., Ribeiro A., Arala-Chaves M. Correlation between specific immunosuppression and polyclonal B cell activation induced by a protein secreted by Streptococcus mutans. Scand J Immunol. 1988 May;27(5):549–554. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A., Melchers F. A plaque assay for all cells secreting Ig of a given type or class. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Aug;6(8):588–590. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyypiä T., Eskola J., Laine M., Salmi A., Meurman O. Polyclonal activation of B cells during rubella infection. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Jun;21(6):615–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'age-Stehr J., Teichmann H., Gershon R. K., Cantor H. Stimulation of regulatory T cell circuits by immunoglobulin-dependent structures on activated B cells. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Jan;10(1):21–26. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minoprio P., Itohara S., Heusser C., Tonegawa S., Coutinho A. Immunobiology of murine T. cruzi infection: the predominance of parasite-nonspecific responses and the activation of TCRI T cells. Immunol Rev. 1989 Dec;112:183–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Yetter R. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Retroviral induction of acute lymphoproliferative disease and profound immunosuppression in adult C57BL/6 mice. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):766–784. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahwa S., Pahwa R., Saxinger C., Gallo R. C., Good R. A. Influence of the human T-lymphotropic virus/lymphadenopathy-associated virus on functions of human lymphocytes: evidence for immunosuppressive effects and polyclonal B-cell activation by banded viral preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8198–8202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E. Lipopolysaccharide pseudomonas vaccine: efficacy against pulmonary infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jul;140(1):73–80. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson U. Lipopolysaccharide-induced suppression of the primary immune response to a thymus-dependent antigen. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):789–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro A. dos S., Arala-Chaves M. P., Vilanova M., Porto M. T., Coutinho A. Role of B and T lymphocytes in the specific immunosuppression induced by a protein released by porcine monocytes infected with African swine fever virus. Int Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(2):165–174. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.2.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringdén O., Paulin T., Sundqvist V. A., Wahren B., Pihlstedt P. Induction of immunoglobulin secretion and DNA synthesis in human lymphocytes in vitro by cytomegalovirus preparations. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Sep;24(3):273–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., Scott P. A., Asofsky R., Sher F. A. Cutaneous leishmaniasis in anti-IgM-treated mice: enhanced resistance due to functional depletion of a B cell-dependent T cell involved in the suppressor pathway. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):2072–2077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santarém M. M., Porto M. T., Ferreira P., Soares R., Arala-Chaves M. P. Semi-purification of an immunosuppressor substance secreted by Streptococcus mutans that plays a role in the protection of the bacteria in the host. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Dec;26(6):755–761. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Lane H. C., Higgins S. E., Folks T., Fauci A. S. Direct polyclonal activation of human B lymphocytes by the acquired immune deficiency syndrome virus. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1084–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.3016902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taswell C. Limiting dilution assays for the determination of immunocompetent cell frequencies. I. Data analysis. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1614–1619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vendrell J. P., Rabesandratana H., Huguet M. F., Cannat A., Serre A. Brucella fractions behave as nonspecific mitogens and polyclonal B-cell activators for human lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):310–316. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.310-316.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


