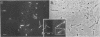Abstract
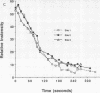
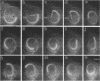
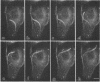
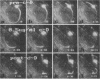
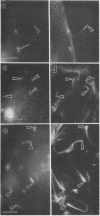
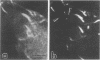
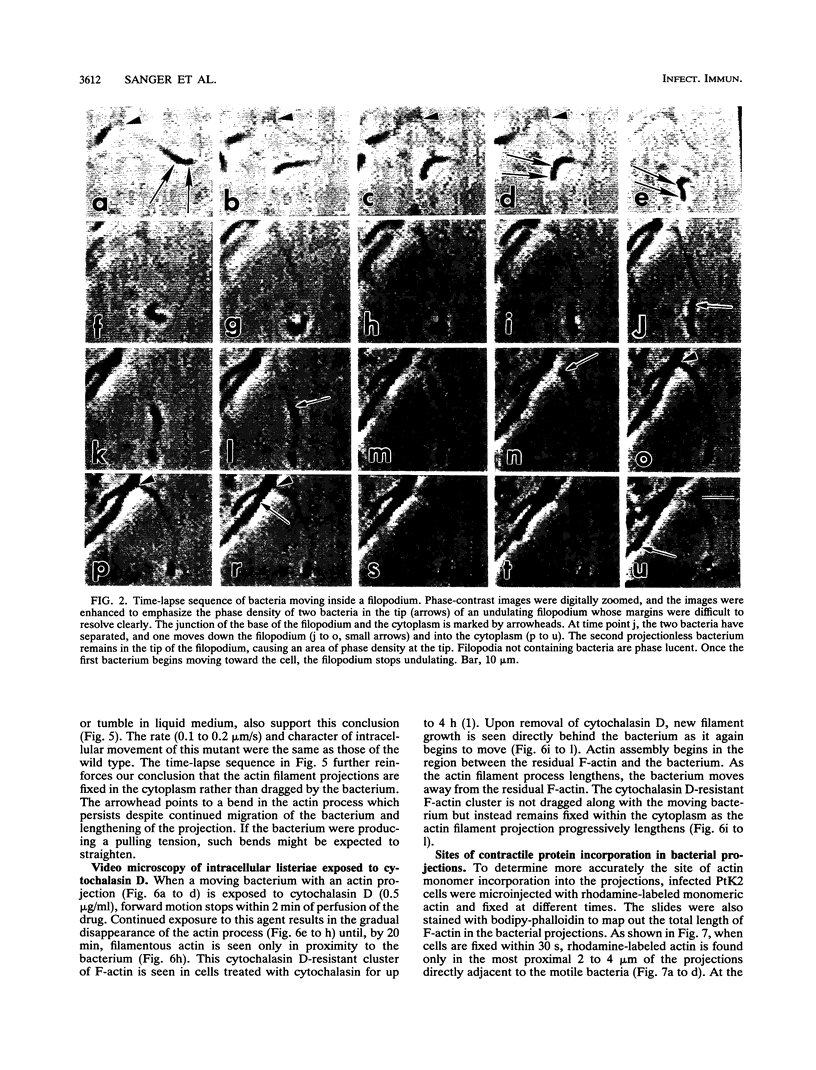
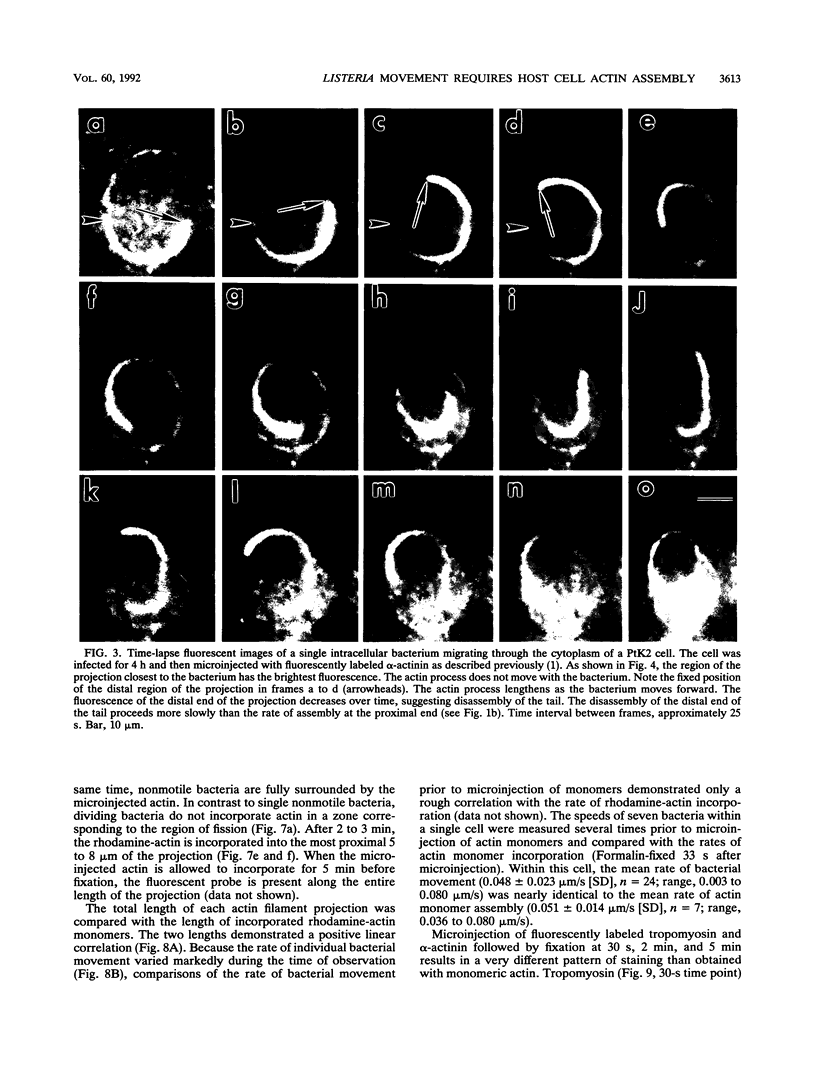
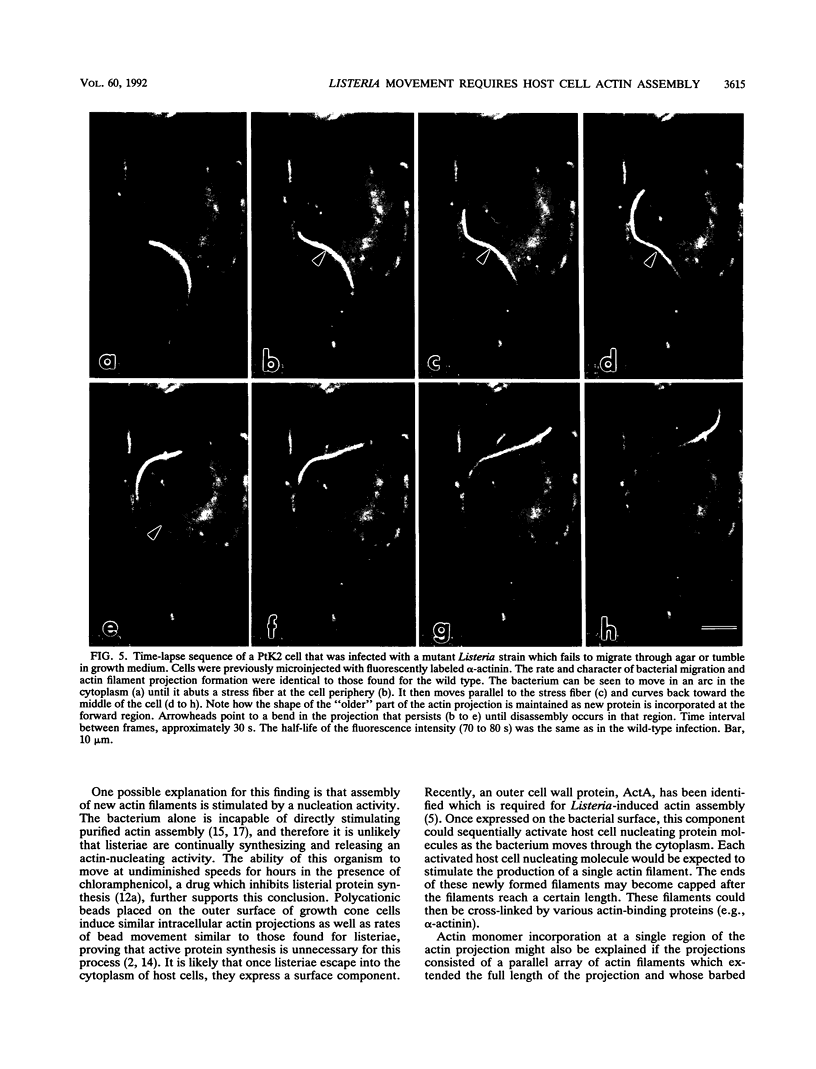
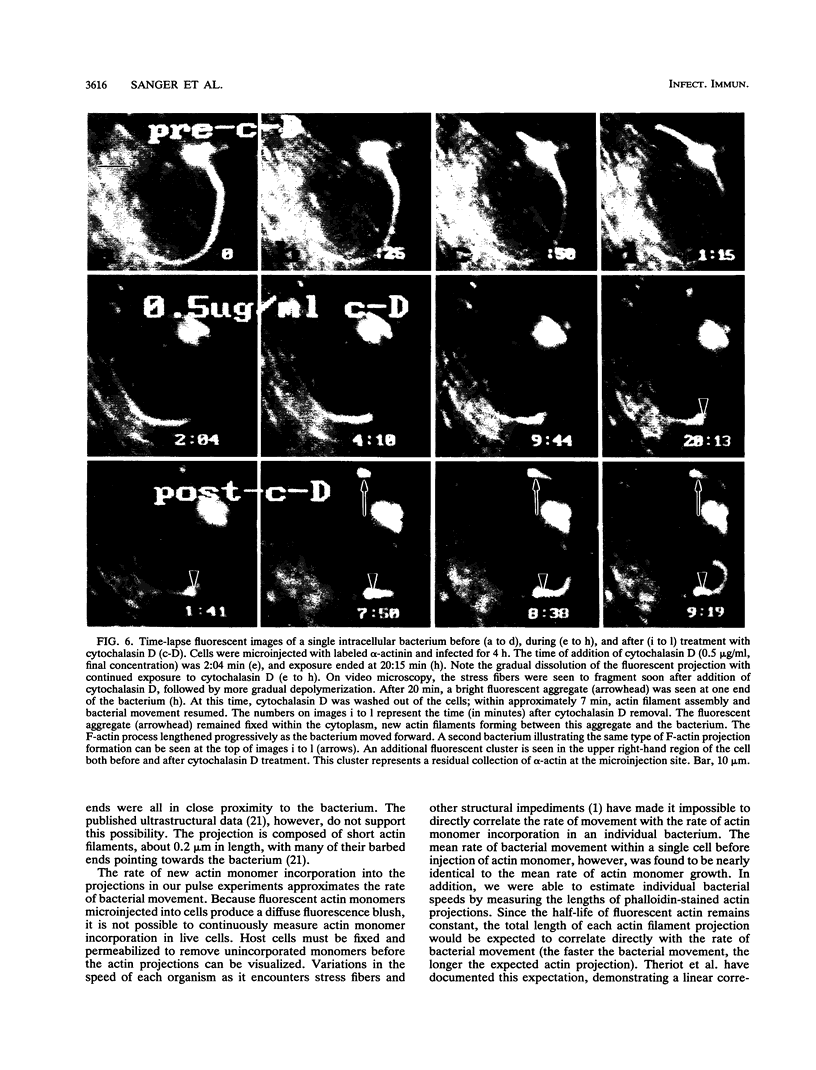
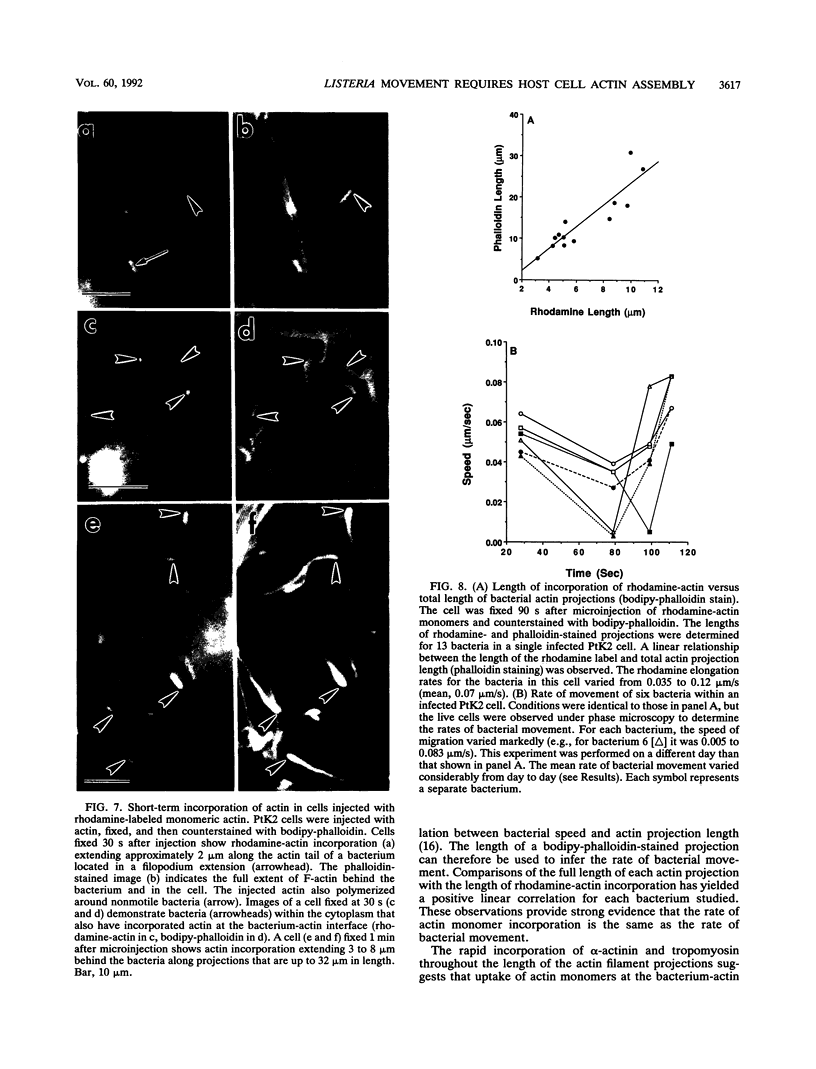
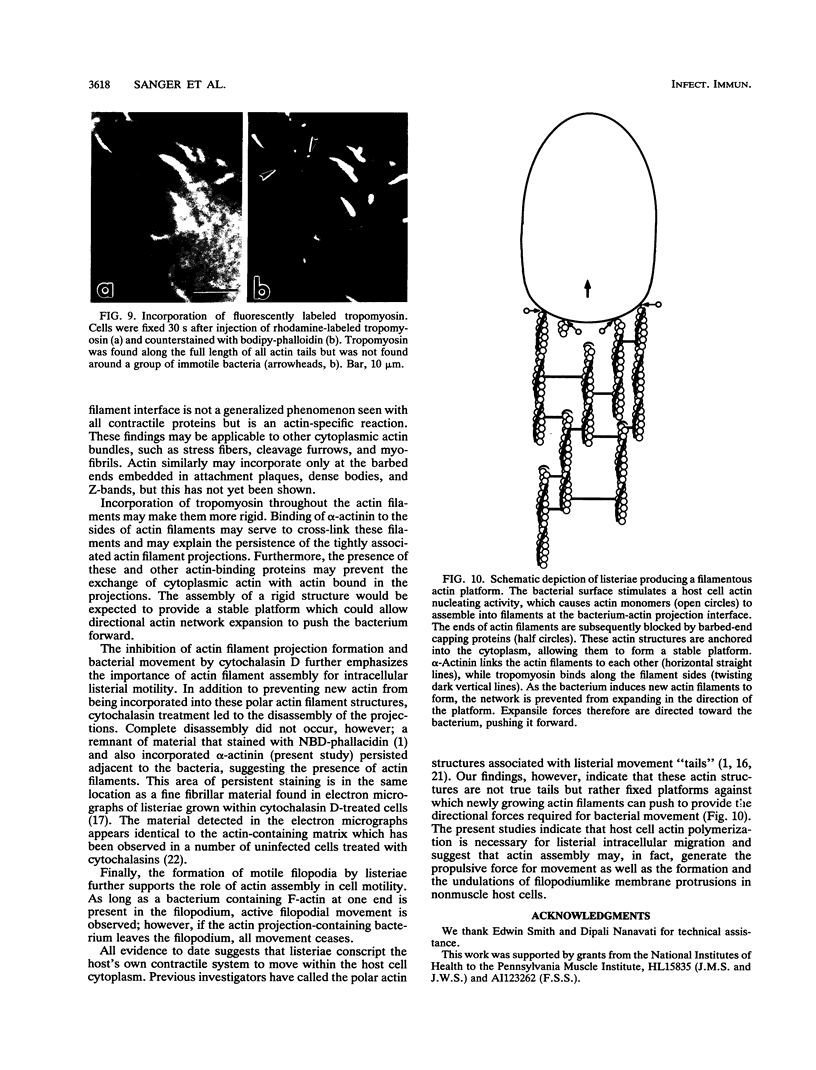
Listeria monocytogenes is able to escape from the phagolysosome and grow within the host cell cytoplasm. By 3 h after initiation of infection, actin filaments begin to concentrate at one end of the bacterium. Polarization of F-actin is associated with intracellular bacterial movement, long projections of actin filaments forming directly behind the moving bacteria. New actin monomers are added to the region of the projection in proximity to the bacterium. The rate of new actin filament growth correlates closely with the speed of bacterial migration. This actin structure is anchored within the cytoplasm, serving as a fixed platform for directional expansion of the actin filament network. The actin projection progressively lengthens as the bacterium migrates. Cytochalasin blocks both elongation of the projection and bacterial movement but does not result in complete depolymerization of the bacterially induced actin structure, residual actin and alpha-actinin persisting in proximity to one end of the bacterium. Bacteria initially migrate within the cortical cytoplasm but later move to the peripheral membrane, where they form filopodiumlike structures which pivot and undulate in the extracellular medium. In the filopodia, bacteria are occasionally seen to abruptly change direction, turn 180 degrees, and move back into the medullary region of the host cell. All filopodium movement ceases once the bacterium containing the F-actin projection returns to the cortical cytoplasm. These results indicate that host cell actin polymerization is necessary for intracellular migration of listeriae and suggest that directional actin assembly may in fact generate the propulsive force for bacterial and filopodial movement.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dabiri G. A., Sanger J. M., Portnoy D. A., Southwick F. S. Listeria monocytogenes moves rapidly through the host-cell cytoplasm by inducing directional actin assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6068–6072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forscher P., Lin C. H., Thompson C. Novel form of growth cone motility involving site-directed actin filament assembly. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):515–518. doi: 10.1038/357515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Synthesis and secretion of interferon by murine fibroblasts in response to intracellular Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):787–792. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.787-792.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocks C., Gouin E., Tabouret M., Berche P., Ohayon H., Cossart P. L. monocytogenes-induced actin assembly requires the actA gene product, a surface protein. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):521–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90188-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Prévost M. C., Mounier J., Sansonetti P. J. A nonvirulent mutant of Listeria monocytogenes does not move intracellularly but still induces polymerization of actin. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3477–3486. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3477-3486.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier J., Ryter A., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular and cell-to-cell spread of Listeria monocytogenes involves interaction with F-actin in the enterocytelike cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1048–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1048-1058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. M., Mittal B., Pochapin M. B., Sanger J. W. Myofibrillogenesis in living cells microinjected with fluorescently labeled alpha-actinin. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2053–2066. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. W., Mittal B., Sanger J. M. Analysis of myofibrillar structure and assembly using fluorescently labeled contractile proteins. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):825–833. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. W., Sanger J. M. Cell motility. Beads, bacteria and actin. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):442–442. doi: 10.1038/357442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J., Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. The rate of actin-based motility of intracellular Listeria monocytogenes equals the rate of actin polymerization. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):257–260. doi: 10.1038/357257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Connelly P. S., Portnoy D. A. Actin filament nucleation by the bacterial pathogen, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2979–2988. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Inoué S. Acrosomal reaction of Thyone sperm. II. The kinetics and possible mechanism of acrosomal process elongation. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):820–827. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Inoué S. Acrosomal reaction of the Thyone sperm. III. The relationship between actin assembly and water influx during the extension of the acrosomal process. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1273–1283. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Kallenbach N. Polymerization of actin. VI. The polarity of the actin filaments in the acrosomal process and how it might be determined. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):608–623. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Rathke P. C., Osborn M., Franke W. W. Distribution of actin and tubulin in cells and in glycerinated cell models after treatment with cytochalasin B (CB). Exp Cell Res. 1976 Oct 15;102(2):285–297. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]