Abstract
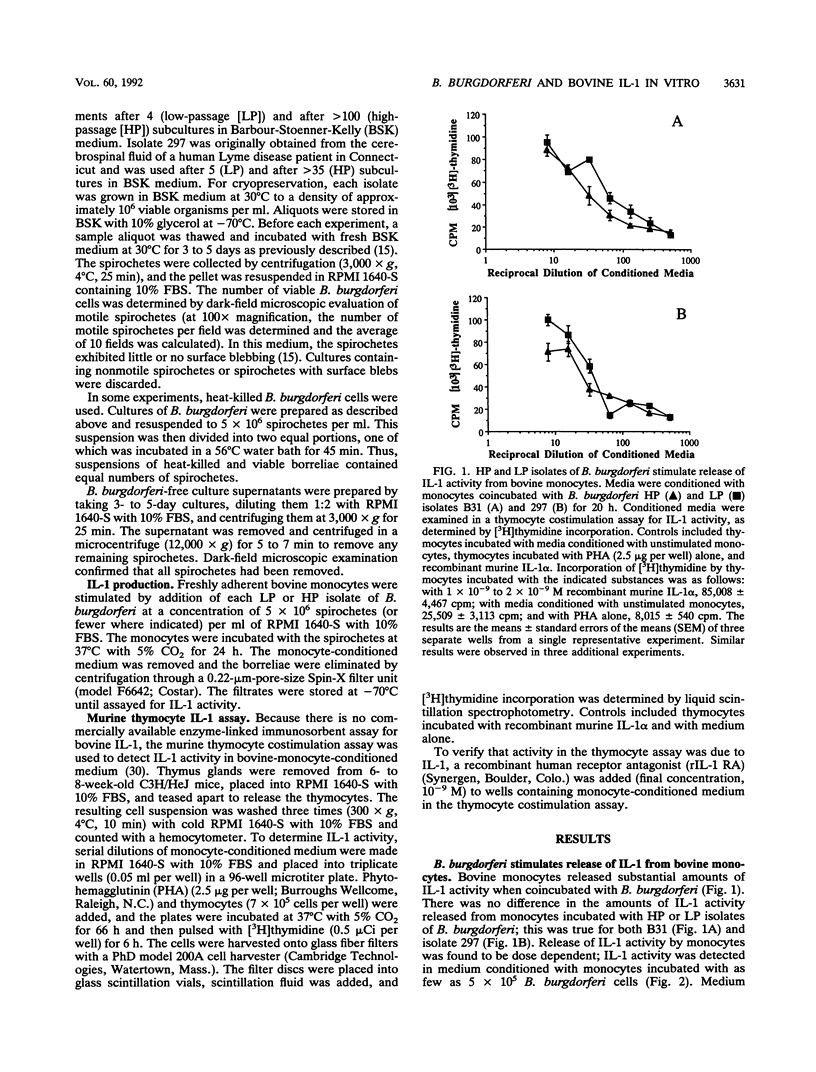
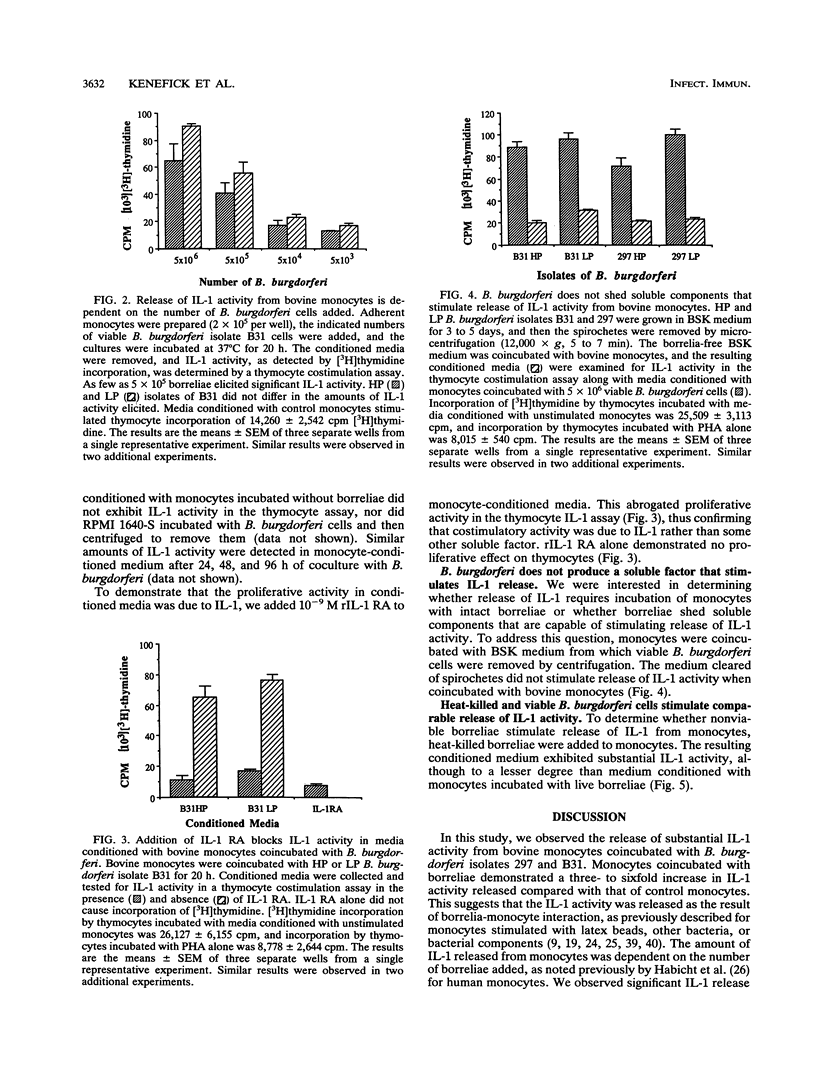
Infection with Borrelia burgdorferi is suspected to be a cause of lameness and arthritis in cattle. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) activity has been detected in joint fluids from human patients affected by various arthritides, including Lyme arthritis. In addition, human monocytes and murine macrophages have been reported to release IL-1 activity when incubated with B. burgdorferi in vitro. To address a possible mechanism by which B. burgdorferi might cause a bovine arthritic syndrome, we determined whether bovine peripheral blood monocytes released IL-1 activity when coincubated with B. burgdorferi in vitro. High-passage and low-passage isolates of B. burgdorferi stimulated release of IL-1 activity from bovine monocytes. The amount of IL-1 activity released was dependent on the number of borreliae added to the monocyte cultures. In addition, live and heat-killed B. burgdorferi cells stimulated release of similar amounts of IL-1. We also obtained no evidence that soluble components released from in vitro-cultured B. burgdorferi stimulated IL-1 release from bovine monocytes. A recombinant IL-1 receptor antagonist blocked the proliferative activity of monocyte-conditioned medium in a thymocyte costimulation assay, thus demonstrating that the costimulatory activity detected was due to IL-1.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist. A new member of the interleukin 1 family. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1445–1451. doi: 10.1172/JCI115453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Massoni R. J. Effects of immune complexes on production by human monocytes of interleukin 1 or an interleukin 1 inhibitor. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3868–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Laboratory aspects of Lyme borreliosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Oct;1(4):399–414. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.4.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Plasmid analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):475–478. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.475-478.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck G., Benach J. L., Habicht G. S. Isolation of interleukin 1 from joint fluids of patients with Lyme disease. J Rheumatol. 1989 Jun;16(6):800–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck G., Benach J. L., Habicht G. S. Isolation, preliminary chemical characterization, and biological activity of Borrelia burgdorferi peptidoglycan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 28;167(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91734-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck G., Habicht G. S., Benach J. L., Coleman J. L., Lysik R. M., O'Brien R. F. A role for interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of Lyme disease. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):133–136. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Bosler E. M., Hanrahan J. P., Coleman J. L., Habicht G. S., Bast T. F., Cameron D. J., Ziegler J. L., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W. Spirochetes isolated from the blood of two patients with Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):740–742. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blyden G., Handschumacher R. E. Purification and properties of human lymphocyte activating factor (LAF). J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1631–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosler E. M., Cohen D. P., Schulze T. L., Olsen C., Bernard W., Lissman B. Host responses to Borrelia burgdorferi in dogs and horses. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:221–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt M. E., Riley B. S., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Immunogenic integral membrane proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi are lipoproteins. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):983–991. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.983-991.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess E. C. Borrelia burgdorferi infection in Wisconsin horses and cows. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:235–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess E. C., Gendron-Fitzpatrick A., Wright W. O. Arthritis and systemic disease caused by Borrelia burgdorferi infection in a cow. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1987 Dec 1;191(11):1468–1470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callister S. M., Case K. L., Agger W. A., Schell R. F., Johnson R. C., Ellingson J. L. Effects of bovine serum albumin on the ability of Barbour-Stoenner-Kelly medium to detect Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):363–365. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.363-365.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter D. B., Deibel M. R., Jr, Dunn C. J., Tomich C. S., Laborde A. L., Slightom J. L., Berger A. E., Bienkowski M. J., Sun F. F., McEwan R. N. Purification, cloning, expression and biological characterization of an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):633–638. doi: 10.1038/344633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D., Bosler E. M., Bernard W., Meirs D., 2nd, Eisner R., Schulze T. L. Epidemiologic studies of Lyme disease in horses and their public health significance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:244–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. L., Benach J. L. Isolation of antigenic components from the Lyme disease spirochete: their role in early diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):756–765. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Biology of interleukin 1. FASEB J. 1988 Feb;2(2):108–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and its biologically related cytokines. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:153–205. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60642-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Thompson R. C. Blocking IL-1: interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in vivo and in vitro. Immunol Today. 1991 Nov;12(11):404–410. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90142-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. P., Evans R. J., Arend W. P., Verderber E., Brewer M. T., Hannum C. H., Thompson R. C. Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of a human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):341–346. doi: 10.1038/343341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgilis K., Steere A. C., Klempner M. S. Infectivity of Borrelia burgdorferi correlates with resistance to elimination by phagocytic cells. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):150–155. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Davies P., Derr J., Krett N., Barranger J. A. Relationship between production and release of lymphocyte-activating factor (interleukin 1) by murine macrophages. 1. Effects of various agents. Cell Immunol. 1981 Nov 1;64(2):293–303. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90481-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habicht G. S., Beck G., Benach J. L., Coleman J. L., Leichtling K. D. Lyme disease spirochetes induce human and murine interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3147–3154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannum C. H., Wilcox C. J., Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Dripps D. J., Heimdal P. L., Armes L. G., Sommer A., Eisenberg S. P., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist activity of a human interleukin-1 inhibitor. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):336–340. doi: 10.1038/343336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovmark A., Asbrink E., Schwan O., Hederstedt B., Christensson D. Antibodies to Borrelia spirochetes in sera from Swedish cattle and sheep. Acta Vet Scand. 1986;27(4):479–485. doi: 10.1186/BF03548127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer J. A., Czuprynski C. J. Production and purification of bovine monocyte-derived interleukin 1. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Dec;23(3-4):201–211. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(89)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre K. W., Stepan G. J., Kolinsky K. D., Benjamin W. R., Plocinski J. M., Kaffka K. L., Campen C. A., Chizzonite R. A., Kilian P. L. Inhibition of interleukin 1 (IL-1) binding and bioactivity in vitro and modulation of acute inflammation in vivo by IL-1 receptor antagonist and anti-IL-1 receptor monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):931–939. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H., Anderle S. K., Brown R. R., Dalldorf F. G., Thompson R. C. Pro- and anti-inflammatory roles of interleukin-1 in recurrence of bacterial cell wall-induced arthritis in rats. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4436–4442. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4436-4442.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W. Antigenic changes of Borrelia burgdorferi as a result of in vitro cultivation. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):852–853. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.852-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Garon C. F. Changes in infectivity and plasmid profile of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, as a result of in vitro cultivation. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1831-1836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Burgdorfer W., Schrumpf M. E., Karstens R. H., Schwan T. G. Antibody to a 39-kilodalton Borrelia burgdorferi antigen (P39) as a marker for infection in experimentally and naturally inoculated animals. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):236–243. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.236-243.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Bocchieri M. H., Sherbin-Allen L., Borofsky M., Abruzzo J. L. Occurrence of interleukin-1 in human synovial fluid: detection by RIA, bioassay and presence of bioassay-inhibiting factors. Rheumatol Int. 1989;9(2):53–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00270245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Hardin J. A., Ruddy S., Askenase W., Andiman W. A. Erythema chronicum migrans and Lyme arthritis. The enlarging clinical spectrum. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):685–698. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczepanski A., Benach J. L. Lyme borreliosis: host responses to Borrelia burgdorferi. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):21–34. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.21-34.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Kiely J. M., Calderon J. The modulation of lymphocyte functions by molecules secreted by macrophages. II. Conditions leading to increased secretion. J Exp Med. 1976 Jul 1;144(1):155–166. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



