Abstract
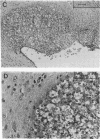
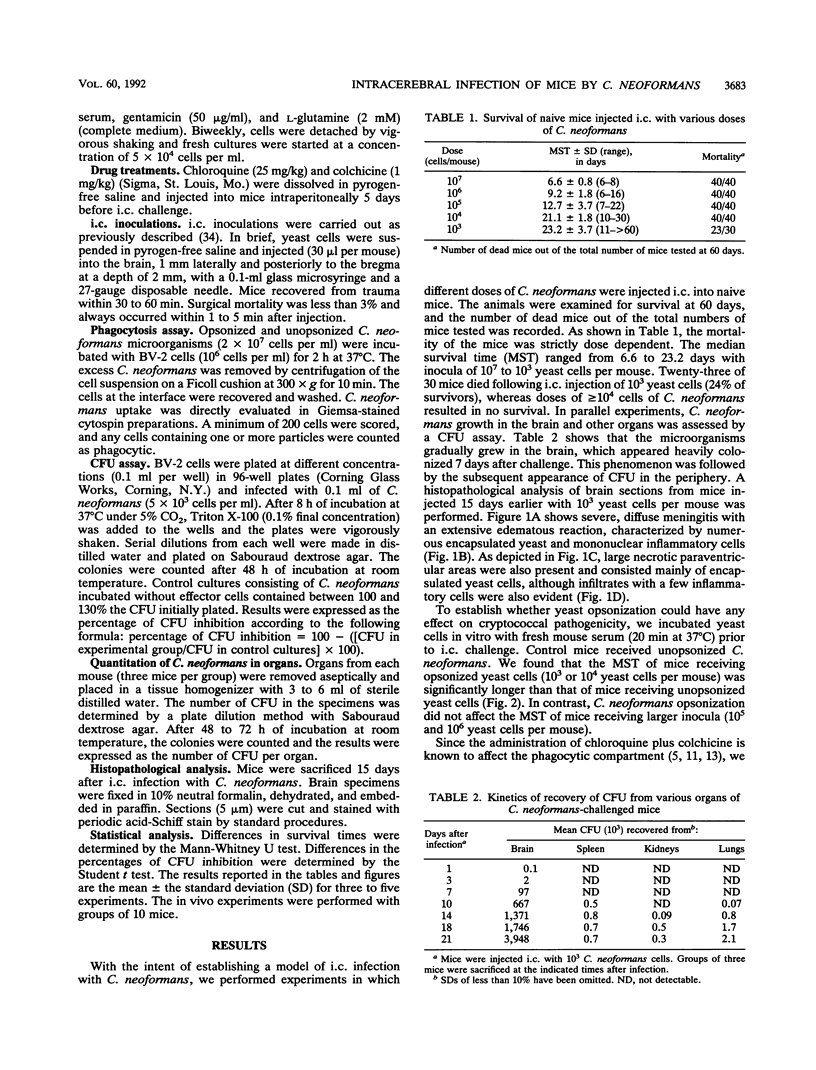
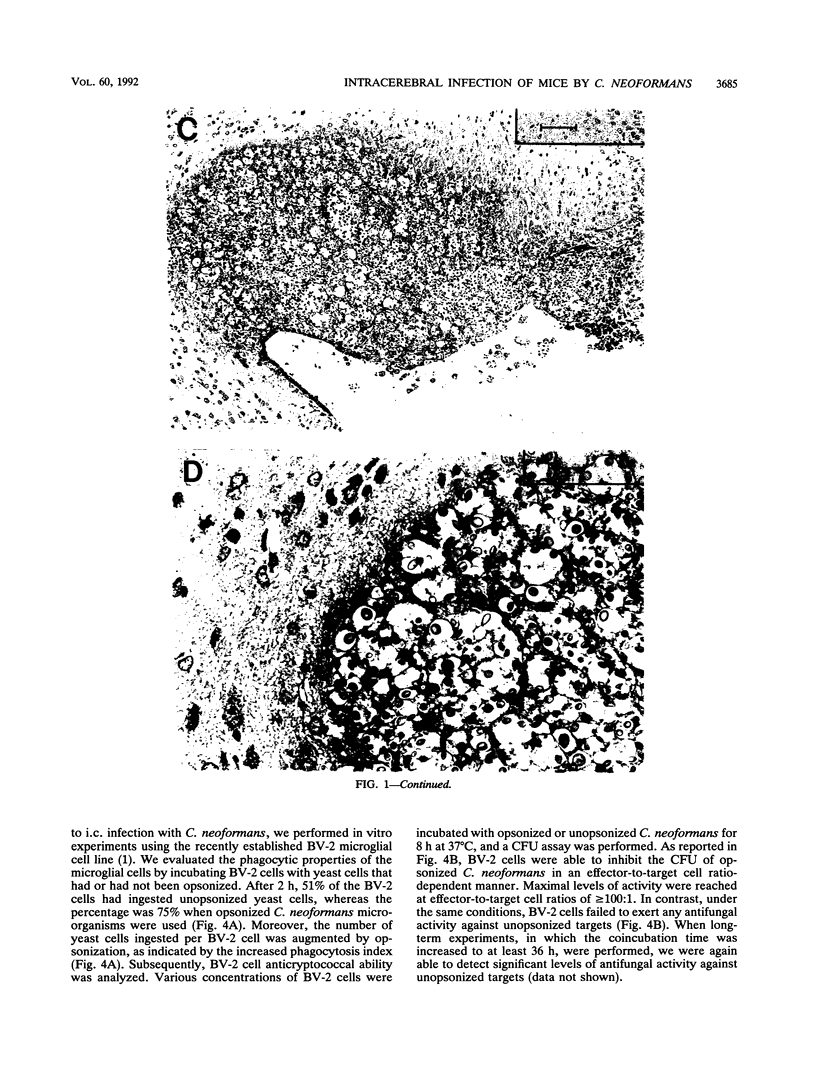
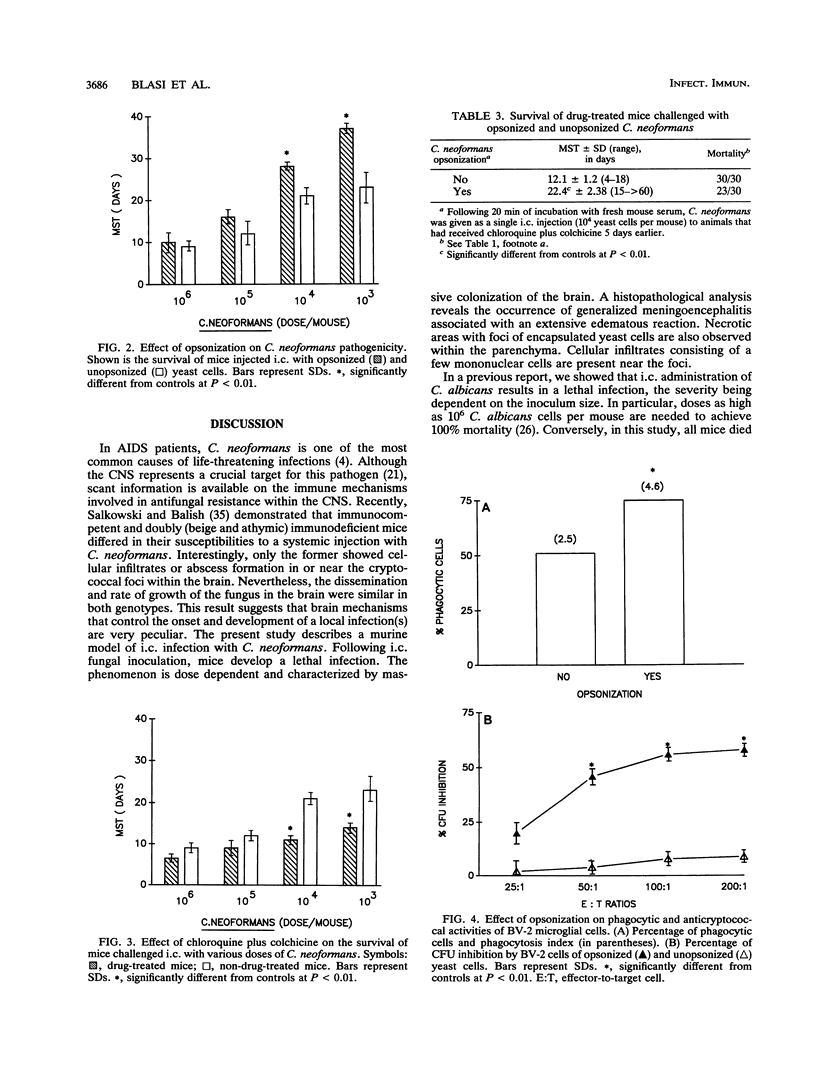
A murine model of intracerebral (i.c.) infection with Cryptococcus neoformans in which naive mice receiving an i.c. fungal inoculation developed a severe disease has been established. The effect was strictly dependent on the number of microorganisms injected and evolved as lethal meningoencephalitis. Murine susceptibility to i.c. infection with C. neoformans was enhanced by treatment with chloroquine and colchicine, agents known to greatly affect the host phagocytic compartment. Furthermore, the life spans of both naive and drug-treated mice were significantly augmented when opsonized fungi were injected. Therefore, phagocyte-mediated mechanisms are likely involved in local resistance to i.c. infection with C. neoformans. Further support for this conclusion was supplied by in vitro data showing that microglial cells were proficient anticryptococcal effectors, provided opsonized microorganisms were used.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blasi E., Barluzzi R., Bocchini V., Mazzolla R., Bistoni F. Immortalization of murine microglial cells by a v-raf/v-myc carrying retrovirus. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 May;27(2-3):229–237. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90073-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi E., Mazzolla R., Barluzzi R., Mosci P., Bartoli A., Bistoni F. Intracerebral transfer of an in vitro established microglial cell line: local induction of a protective state against lethal challenge with Candida albicans. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Jun;32(3):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90195-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauley L. K., Murphy J. W. Response of congenitally athymic (nude) and phenotypically normal mice to Cryptococcus neoformans infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):644–651. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.644-651.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler F. W. Pathology of the mycoses in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Curr Top Med Mycol. 1985;1:1–23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-9547-8_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins H. L., Bancroft G. J. Encapsulation of Cryptococcus neoformans impairs antigen-specific T-cell responses. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3883–3888. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3883-3888.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. F., Clifford D. P., Hoidal J. R., Repine J. E. Opsonic requirements for the uptake of Cryptococcus neoformans by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):870–874. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Allison A. C. Nature of the effector cells responsible for antibody-dependent cell-mediated killing of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):716–720. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.716-720.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D. Antibody-dependent killing of Cryptococcus neopormans by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Nature. 1974 Jan 18;247(5437):148–150. doi: 10.1038/247148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng R. H., Bishburg E., Smith S. M., Kapila R. Cryptococcal infections in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1986 Jul;81(1):19–23. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Schwamberger G., Kaufmann S. H. Fungicidal activity of IFN-gamma-activated macrophages. Extracellular killing of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3219–3224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Baker T. J. Characterization of ameboid microglia isolated from developing mammalian brain. J Neurosci. 1986 Aug;6(8):2163–2178. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-08-02163.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Chen J., Ingeman J. E., George J. K., Noponen M. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in wound healing after traumatic injury to adult mammalian brain. J Neurosci. 1989 Dec;9(12):4416–4429. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-12-04416.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. L., Perfect J. R., Durack D. T. Macrophage-mediated fungistasis in vitro: requirements for intracellular and extracellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):672–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes G. M., Woodroofe M. N., Cuzner M. L. Characterisation of microglia isolated from adult human and rat brain. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Sep;19(3):177–189. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidore M. R., Nabavi N., Sonleitner F., Murphy J. W. Murine natural killer cells are fungicidal to Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1747–1754. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1747-1754.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffnagle G. B., Yates J. L., Lipscomb M. F. T cell-mediated immunity in the lung: a Cryptococcus neoformans pulmonary infection model using SCID and athymic nude mice. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1423–1433. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1423-1433.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Highison B., Stratton C. J. Localization on encapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans of serum components opsonic for phagocytosis by macrophages and neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):574–579. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.574-579.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Pfrommer G. S., Guerlain A. S., Highison B. A., Highison G. J. Strain variation in phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans: dissociation of susceptibility to phagocytosis from activation and binding of opsonic fragments of C3. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2794–2800. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2794-2800.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Pfrommer G. S., Redelman D. Activated neutrophils exhibit enhanced phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans opsonized with normal human serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Oct;70(1):238–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., DiBenedetto D. J. Differential stimulation of murine resident peritoneal cells by selectively opsonized encapsulated and acapsular Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2544–2551. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2544-2551.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., DiBenedetto D. J. Paradoxical role of capsule in murine bronchoalveolar macrophage-mediated killing of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):659–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim T. S., Murphy J. W. Transfer of immunity to cryptococcosis by T-enriched splenic lymphocytes from Cryptococcus neoformans-sensitized mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):5–11. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.5-11.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzolla R., Barluzzi R., Romani L., Mosci P., Bistoni F. Anti-Candida resistance in the mouse brain and effect of intracerebral administration of interleukin 1. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Aug;137(8):1799–1804. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-8-1799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. F., Mitchell T. G. Killing of Cryptococcus neoformans strains by human neutrophils and monocytes. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):24–28. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.24-28.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. F., Mitchell T. G., Storkus W. J., Dawson J. R. Human natural killer cells do not inhibit growth of Cryptococcus neoformans in the absence of antibody. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):639–645. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.639-645.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., Hidore M. R., Nabavi N. Binding interactions of murine natural killer cells with the fungal target Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1476–1488. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1476-1488.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., McDaniel D. O. In vitro reactivity of natural killer (NK) cells against Cryptococcus neoformans. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1577–1583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabavi N., Murphy J. W. Antibody-dependent natural killer cell-mediated growth inhibition of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):556–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.556-562.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani L., Fioretti M. C., Bianchi R., Nardelli B., Bonmassar E. Intracerebral adoptive immunotherapy of a murine lymphoma antigenically altered by drug treatment in vivo. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 May;68(5):817–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salkowski C. A., Balish E. Pathogenesis of Cryptococcus neoformans in congenitally immunodeficient beige athymic mice. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3300–3306. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3300-3306.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecchiarelli A., Cenci E., Puliti M., Blasi E., Puccetti P., Cassone A., Bistoni F. Protective immunity induced by low-virulence Candida albicans: cytokine production in the development of the anti-infectious state. Cell Immunol. 1989 Dec;124(2):334–344. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90135-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg P. B., Becker S., Granger D. L., Koren H. S. Growth inhibition of Cryptococcus neoformans by human alveolar macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Nov;136(5):1242–1247. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.5.1242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]