Abstract
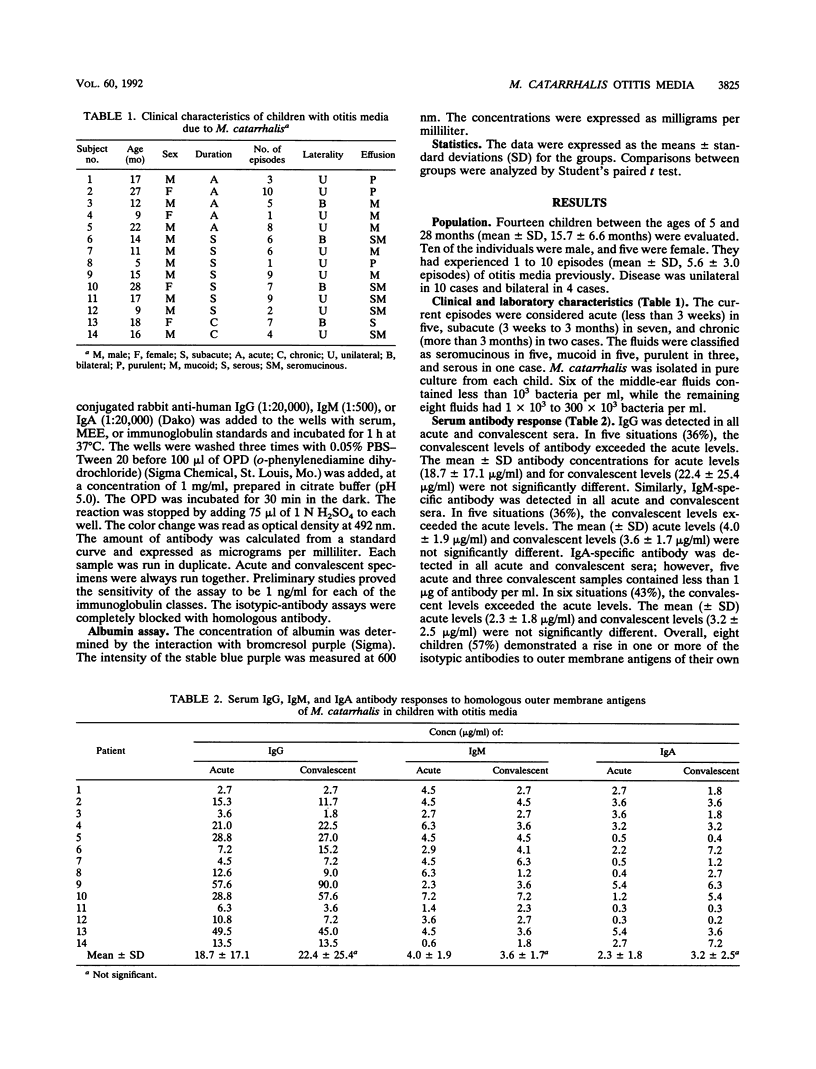
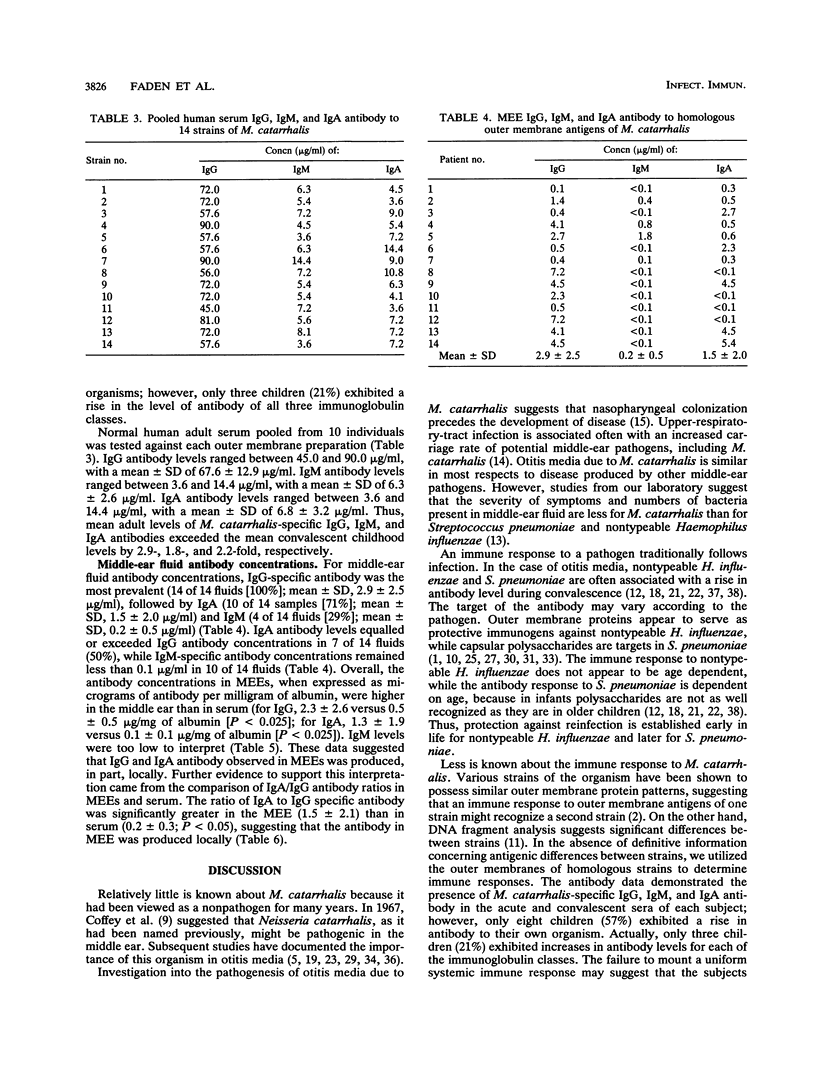
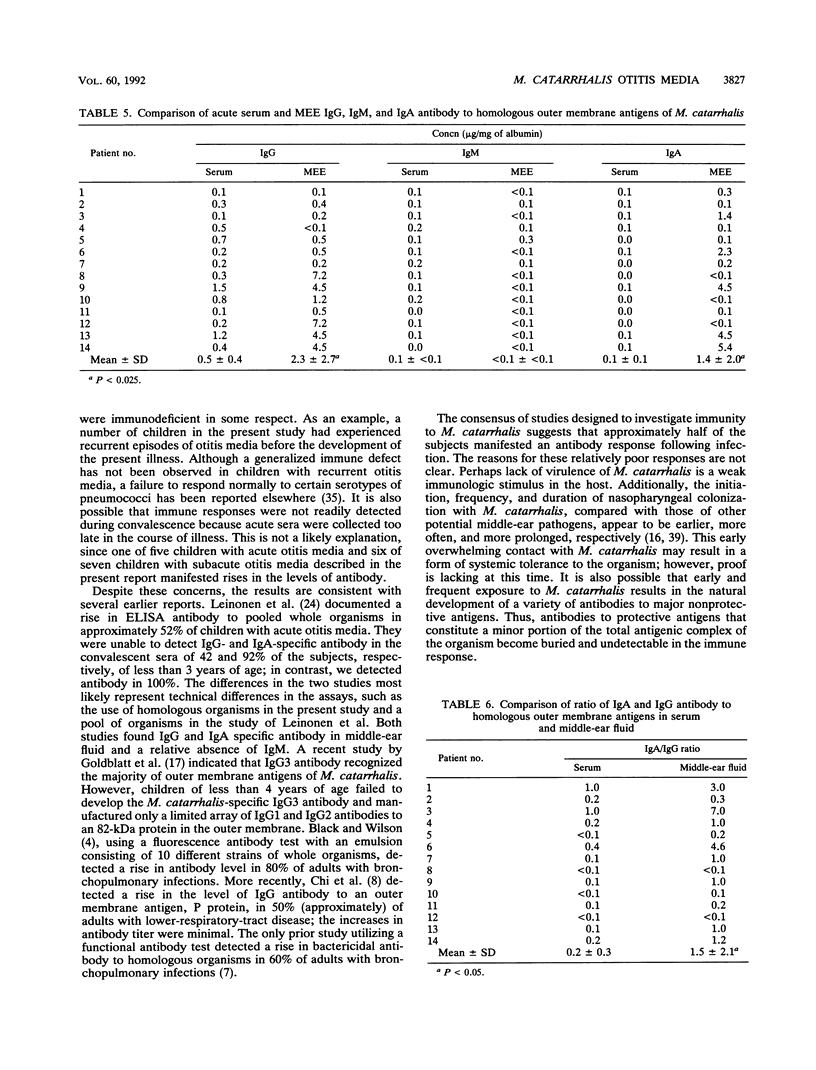
The systemic and local antibody responses to homologous strains of Moraxella catarrhalis were investigated in 14 children with otitis media. A total of 8 children (57%) demonstrated a rise in serum antibody of the immunoglobulin G (IgG) (5 of 14), IgM (5 of 14), or IgA (6 of 14) classes of immunoglobulin to outer membrane antigens. Local antibody consisted of IgG (100%), IgM (29%), and IgA (71%). The IgG and IgA specific antibody present in middle-ear effusions appeared to represent local production rather than passive diffusion from the systemic circulation. These data suggest that young children develop an antibody response to M. catarrhalis in the middle ear during otitis media but fail to develop systemic antibody in a uniform manner.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barenkamp S. J. Protection by serum antibodies in experimental nontypable Haemophilus influenzae otitis media. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):572–578. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.572-578.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartos L. C., Murphy T. F. Comparison of the outer membrane proteins of 50 strains of Branhamella catarrhalis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):761–765. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk S. L. From Micrococcus to Moraxella. The reemergence of Branhamella catarrhalis. Arch Intern Med. 1990 Nov;150(11):2254–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black A. J., Wilson T. S. Immunoglobulin G (IgG) serological response to Branhamella catarrhalis in patients with acute bronchopulmonary infections. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Mar;41(3):329–333. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.3.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bluestone C. D. Otitis media and sinusitis in children. Role of Branhamella catarrhalis. Drugs. 1986;31 (Suppl 3):132–141. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198600313-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Branhamella catarrhalis: an organism gaining respect as a pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Oct;3(4):293–320. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.4.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman A. J., Jr, Musher D. M., Jonsson S., Clarridge J. E., Wallace R. J., Jr Development of bactericidal antibody during Branhamella catarrhalis infection. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):878–882. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi D. S., Verghese A., Moore C., Hamati F., Berk S. L. Antibody response to P-protein in patients with Branhamella catarrhalis infections. Am J Med. 1990 May 14;88(5A):25S–27S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90257-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey J. D., Jr, Martin A. D., Booth H. N. Neisseria catarrhalis in exudate otitis media. Arch Otolaryngol. 1967 Oct;86(4):403–406. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1967.00760050405009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deich R. A., Anilionis A., Fulginiti J., Metcalf B. J., Quataert S., Quinn-Dey T., Zlotnick G. W., Green B. A. Antigenic conservation of the 15,000-dalton outer membrane lipoprotein PCP of Haemophilus influenzae and biologic activity of anti-PCP antisera. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3388–3393. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3388-3393.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson D. P., Loos B. G., Dryja D. M., Bernstein J. M. Restriction fragment mapping of Branhamella catarrhalis: a new tool for studying the epidemiology of this middle ear pathogen. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):205–208. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden H., Bernstein J., Brodsky L., Stanievich J., Krystofik D., Shuff C., Hong J. J., Ogra P. L. Otitis media in children. I. The systemic immune response to nontypable Hemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):999–1004. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden H., Bernstein J., Brodsky L., Stanievich J., Ogra P. L. Effect of prior antibiotic treatment on middle ear disease in children. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1992 Jan;101(1):87–91. doi: 10.1177/000348949210100119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden H., Stanievich J., Brodsky L., Bernstein J., Ogra P. L. Changes in nasopharyngeal flora during otitis media of childhood. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1990 Sep;9(9):623–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden H., Waz M. J., Bernstein J. M., Brodsky L., Stanievich J., Ogra P. L. Nasopharyngeal flora in the first three years of life in normal and otitis-prone children. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1991 Aug;100(8):612–615. doi: 10.1177/000348949110000802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt D., Turner M. W., Levinsky R. J. Branhamella catarrhalis: antigenic determinants and the development of the IgG subclass response in childhood. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1128–1135. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray B. M., Dillon H. C., Jr Epidemiological studies of Streptococcus pneumoniae in infants: antibody to types 3, 6, 14, and 23 in the first two years of life. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):948–955. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie V. M., Ploussard J. H., Lester R. L., Jr Otitis media: a clinical and bacteriological correlation. Pediatrics. 1970 Jan;45(1):29–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskela M., Leinonen M., Luotonen J. Serum antibody response to pneumococcal otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1982 Jul-Aug;1(4):245–252. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198207000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskela M. Serum antibodies to pneumococcal C polysaccharide in children: response to acute pneumococcal otitis media or to vaccination. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Jun;6(6):519–526. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198706000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinonen M., Luotonen J., Herva E., Valkonen K., Mäkelä P. H. Preliminary serologic evidence for a pathogenic role of Branhamella catarrhalis. J Infect Dis. 1981 Dec;144(6):570–574. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.6.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R. Protection of infant rats from Haemophilus influenzae type b infection by antiserum to purified outer membrane protein a. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2612–2618. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2612-2618.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackowiak P. A. The normal microbial flora. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jul 8;307(2):83–93. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198207083070203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchant C. D. Spectrum of disease due to Branhamella catarrhalis in children with particular reference to acute otitis media. Am J Med. 1990 May 14;88(5A):15S–19S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90255-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLinn S. E., Daly J. F., Jr, Jones J. E. Cephalexin monohydrate suspension. Treatment of otitis media. JAMA. 1975 Oct 13;234(2):171–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Purification and partial characterization of outer membrane proteins P5 and P6 from Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):544–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.544-549.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C. Purification and analysis with monoclonal antibodies of P2, the major outer membrane protein of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1084–1089. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1084-1089.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C., Rice P. A., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Apicella M. A. Identification of a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein on nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae as a target for human serum bactericidal antibody. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):1020–1027. doi: 10.1172/JCI112656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C. Surface-exposed and antigenically conserved determinants of outer membrane proteins of Branhamella catarrhalis. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):2938–2941. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.2938-2941.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilson B. W., Poland R. L., Thompson R. S., Morehead D., Baghdassarian A., Carver D. H. Acute otitis media: treatment results in relation to bacterial etiology. Pediatrics. 1969 Mar;43(3):351–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prellner K., Kalm O., Pedersen F. K. Pneumococcal antibodies and complement during and after periods of recurrent otitis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1984 Mar;7(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5876(84)80052-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurin P. A., Marchant C. D., Kim C. H., Van Hare G. F., Johnson C. E., Tutihasi M. A., Knapp L. J. Emergence of beta-lactamase-producing strains of Branhamella catarrhalis as important agents of acute otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1983 Jan-Feb;2(1):34–38. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198301000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurin P. A., Pelton S. I., Tager I. B., Kasper D. L. Bactericidal antibody and susceptibility to otitis media caused by nontypable strains of Haemophilus influenzae. J Pediatr. 1980 Sep;97(3):364–369. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloyer J. L., Jr, Howie V. M., Ploussard J. H., Ammann A. J., Austrian R., Johnston R. B., Jr Immune response to acute otitis media in children. I. Serotypes isolated and serum and middle ear fluid antibody in pneumococcal otitis media. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1028–1032. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1028-1032.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenfors L. E., Räisänen S. Occurrence of middle ear pathogens in the nasopharynx of young individuals. A quantitative study in four age groups. Acta Otolaryngol. 1990 Jan-Feb;109(1-2):142–148. doi: 10.3109/00016489009107426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


