Abstract
Background
Most patients seeking help for back pain are managed in primary care.
Aim
To describe the content and outcome of ‘usual care’ for low back pain in primary care trials.
Design of study
A systematic review of randomised controlled trials published since 1998.
Setting
Primary care.
Method
Randomised controlled trials of back pain in adults were scrutinised to obtain data on treatment and outcome measures in groups receiving usual primary care. A narrative review of the resulting heterogeneous data was undertaken.
Results
Thirty-three papers were identified for analysis. Overall the exact nature of the treatment received in the ‘usual’ primary care group was poorly recorded. Medication was frequently used, and there were suggestions that levels of opioid prescription were higher than might be expected from clinical guidelines. Requesting of plain-film X-rays occurred more often than recommended. There was very little information to suggest that doctors were promoting physical activity for patients with back pain. Disability scores (Roland–Morris Disability Questionnaire) and pain scores improved over time for patients with acute or subacute back pain, but not for those with chronic pain.
Conclusion
Treatment received by patients with back pain was varied and often not in line with back-pain guidelines, particularly with respect to opioid prescription and X-ray investigation. The content of the ‘usual care’ arm in trials is crucial to interpreting the outcome of studies, but was poorly described in the papers reviewed. Future trials should more fully describe the ‘usual care’ arm.
Keywords: back pain, family practice, general practice, primary health care
INTRODUCTION
Low back pain is a common condition that is frequently seen in primary care. In the UK there are between 3 and 7 million GP consultations for back pain in a year. Fifty-two million working days are lost each year and, at any one time, 6% of the working population will have had at least one day off work in the last 4 weeks due to back pain.1 The annual cumulative consultation rate of patients presenting to their GP with back pain is 6.4%.2
Despite evidence-based guidelines for the management of low back pain,3,4 chronic or recurrent back pain is common and it continues to pose considerable challenges and frustrations for patients and practitioners. Attempts have been made to address this situation using educational programmes for GPs to promote the adoption of guidelines, but these have failed to show significant changes in everyday clinical practice.3,4 One reason for this may be that the nature of routine clinical practice in primary care has not been adequately considered when producing guidelines.
‘Usual care’ is often used as the control or comparator group in randomised controlled trials. It is important to know the content of these control treatments in order to interpret the effect sizes published in trials. The current study is a systematic review with the following specific objectives:
to describe the treatments contained within ‘usual care’ approaches to low back pain, as reported in primary care-based randomised controlled trials published between 1994 and 1997 (a period when many clinical guidelines were published); and
to describe the clinical course of patients randomised to the ‘usual care’ approaches outlined in the first objective.
METHOD
Inclusion criteria for studies to review
Types of studies
Randomised controlled trials published in any language from 1998 only were included. This date range was chosen as it follows the publication date of many national guidelines on the care of low back pain in primary care worldwide,5–7 and hence reflects current clinical practice.
Types of participants
Participants aged 18 years or over with non-specific low back pain of any duration, who had been treated in primary care, were included. Low back pain was defined as pain in the back located below the scapulae and above the natal cleft of the buttocks, with or without pain radiating to the leg.8 Studies involving specific pathological processes or surgical techniques were excluded.
Types of treatments
A randomised controlled trial was included for review if at least one treatment group involved usual care of low back pain in primary care. Any interventions used to provide this usual care were recorded.
Types of outcome measures
For the study's first objective of describing usual care approaches to treat low back pain, relevant outcome measures were consultation rates, advice, medication usage (prescribed to the patient or purchased by the patient without prescription), investigations, and referrals. For the second objective of describing the clinical course of low back pain in those receiving usual care, information was gathered on pain scores (Visual Analogue Scale, modified Von Korff Pain Scale, Aberdeen Back Pain Scale, and the Extended Aberdeen Spine Pain Scale), overall satisfaction, back-specific functional scores (Roland–Morris Disability Questionnaire [RMDQ]), and work absence.
Search strategy for identification of studies
Relevant studies meeting the inclusion criteria were identified by a computer search of the electronic databases MEDLINE (1966–2007), EMBASE (1966–2007), CINAHL (1982–2007), AMED, DARE, and ISI Web of Science. The search strategy looked for terms within the subject heading, title, and abstract, and included the following terms: random, clinical trials, low back pain, back pain, backache, physicians-family, family practice, general practice, family medicine, primary care, and primary medical care (Appendix 1). The search was augmented by examination of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials and references given in the identified randomised controlled trials and appropriate reviews.
How this fits in
Despite back pain being a common problem in primary care, it is poorly described and its treatment appears at odds with guideline recommendations. A better understanding of primary care is needed to facilitate the incorporation of evidence-based medicine into routine consultations.
Methods of review
Study selection
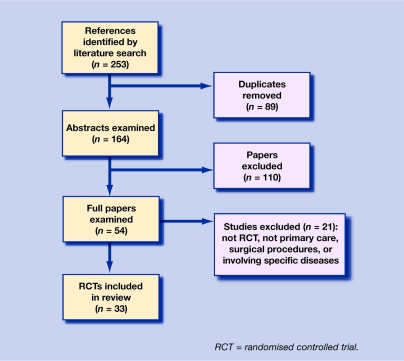
The principal researcher performed the initial database search using the search strategy. The number of potential studies was reduced by the removal of duplicates. Studies were excluded if it was immediately apparent from their abstract that they did not meet the inclusion criteria. Trials in the remaining group were then assessed by examining the full paper.
Methodological quality assessment
One researcher scored all papers; each paper was also independently assessed by other researchers. Disagreements about the methodological score were resolved by discussion.
The Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group publishes guidelines on systematic reviews. It recommended an 11-point scoring system for assessing methodological quality, including items relating to internal and external validity. Studies with a score of ≥6 out of 11 are judged to be of high quality, as they are above the arbitrary cut-off point of 50%.9,10
Subsequently, it has been suggested that the list of assessment criteria can be reduced to just the five points relating to internal validity,11 which are: (1) concealment of treatment allocation; (2) blinding of patients; (3) blinding of outcome assessor; (4) intention-to-treat analysis; (5) and an acceptable drop-out rate. In this review a study was judged to be of high quality if it achieved a score of ≥3 out of 5.
There was disagreement between reviewers about quality scores of six out of 33 papers. In every case disagreements were resolved by the two researchers involved, without the need to call on a third reviewer to adjudicate.
Data extraction
This was performed by the lead researcher and other independent reviewers. One key aspect of the review was to determine whether usual care had been adequately described in terms of types of treatments that health professionals had at their discretion to use (‘allowed’), and what treatments actually took place (‘actual’). Each reviewer was instructed to make their own judgement as to whether allowed and actual usual care had been adequately described. Disagreements were resolved by discussion.
A standardised form was used by each reviewer to record their findings. Information gathered was collated using a Microsoft Office Access database.
Data analysis
Due to the sparseness and heterogeneity of the data, it was appropriate to perform a qualitative assessment rather than a meta-analysis. Also, the purpose of this study was to describe and statistically summarise treatment and outcome measures relating to the usual care arm of trials, rather than to compare effect sizes.
Frequencies were presented of specific elements of care, for example, consultation rates, medication usage (prescribed or purchased over the counter), and referrals. Mean scores with standard deviations (SDs) were extracted from each paper (if stated) and presented for pain (Visual Analogue Scale, modified Von Korff Pain Scale, Aberdeen Back Pain Scale) and RMDQ score. Measures of pain and satisfaction were all converted to a 0–10-point scale (a higher score indicated greater pain or greater satisfaction respectively) to facilitate interpretation and comparison across studies.
Duration of back pain in each study was classified pragmatically as acute (0–6 weeks), subacute (6–12 weeks), chronic (more than 12 weeks), or mixed (any duration included in study). It should be acknowledged that such classification may not reflect clinical practice, where back pain often fluctuates with time and recurrent acute attacks may be indistinguishable from relapses of a chronic problem.
RESULTS
Study selection
The initial search yielded 164 potentially relevant studies. After examining the full text of 54 papers, 33 were included in the review.3,12–43 This process is detailed in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Systematic review flowchart.
Study characteristics
Study characteristics are presented in detail in Appendix 2. Type of care given or intended to be given in the usual care control group is described, in addition to the outcome of the experimental intervention compared with usual care.
Of the 33 studies identified, eight investigated patients with acute back pain,13–15,32,34–36,39 11 with patients who had subacute pain,16,18–21,23,27,33,38,41,42 six examined patients with chronic pain,17,24–26,31,37 and eight studies investigated patients with mixed-duration pain.3,12,22,28–30,40,43
Baseline RMDQ score, where appropriate, is given to describe the severity of back pain in participants entering the trials. The studies were conducted in Australia, Canada, Finland, Mallorca, the Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, UK, and US. Thirty out of 33 studies assessed were deemed to be of good quality (that is, they achieved a quality score of ≥3 out of 5).
Methodological quality
In the 33 studies, one study scored 1,34 two scored 2,27,30 13 scored 3,12,17,19–22,26,29,32,37,40–42 16 scored 4,3,14–16,18,23–25,28,31,33,35,36,38,39,43 and one scored 5 out of a maximum score of 5.13 In 16 out of 33 studies it was not possible to tell if the outcome assessor was blinded,3,12,17–22,26,27,29,30,34,37,41,42 and in only three of 33 studies were the patients blinded to the nature of the treatment group.3,13,18 In two studies it was not stated if the treatment allocation was concealed,30,40 and in three it was not possible to tell if the analysis was by intention to treat.27,32,34 All papers reported the drop-out rates.
Content of usual care approaches
Adequacy of description of usual care
Of 33 studies, 11 had no description of either the allowed or actual treatment in the control group,14,17,18,22,24,27,28,30,32,40,42 seven had a description of both,15,23,26,29,35,38,41 six described just the actual treatment,3,22,25,33,34,43 and nine just the allowed treatment.12,13,16,19,20,31,36,37,39
The 10 most commonly recorded aspects of usual care are presented in Table 1. Of these 10 common aspects, a mean of 3.1 items (SD 2.2) were reported in the studies included in the review. Appendix 3 gives more information about aspects of consultations and demonstrates the wide variation in the detail of recording of usual care.
Table 1.
Ten most commonly recorded aspects of usual care.
| Consultation activity record | Number of studies recorded | Percentage of studies recorded |
|---|---|---|
| Radiology used | 11 | 33 |
| Other investigation ordered | 2 | 6 |
| Medication used (prescribed or over the counter) | 11 | 33 |
| Sick note issued | 22 | 67 |
| Written advice given | 9 | 27 |
| Activity level recorded | 3 | 9 |
| Exercise advice recorded | 4 | 12 |
| Seen by physiotherapist | 15 | 45 |
| Hospital referral made | 8 | 24 |
| Consultation rate details | 17 | 52 |
See Appendix 3 for reference details.
Consultation rates with GP
Due to the heterogeneous ways in which data about consultations were collected, it was not possible to perform a comprehensive quantitative analysis. Overall, 17 of 33 papers reported data on consultation rates. The following qualitative data were found:
Acute back pain. Four of eight studies described consultation rates per patient, one found a rate of 3.9 (no SD stated) consultations in 1 year,36 and another 3.3 (SD 1.6) in 8 weeks.15 Another found that 60% of patients presented to their GP once, 31% twice, and 9% more than twice in the course of a year.13 A fourth states that consultation rates were similar for patients in the experimental and control arms, although figures are not given.39
Subacute back pain. Four of 11 studies provide data on consultations for subacute back pain. One found 62.5% of patients presented to their GP in the first 3 months of the trial, and 51.1% in the second 3 months.33 A second study reported that 21% consulted once, 3% twice, and 5% three or more times in the first 6 months, and 16%, 3%, and 5% respectively at 9 months.21 Mean number of visits to the GP in 1 year was six in a further study.20 Jellema et al found that 24% of patients were seeking additional help from their GP in the first 6 weeks, and 28% in the remainder of the year of the study.18
Chronic back pain. Two of six studies reported data on consultations for chronic back pain. One reported a mean of 13.2 (SD: 5) visits in one year,31 and another reported a mean of 1.2 at baseline for the previous year and 1.7 in the year of the study.25
Mixed-duration back pain. Of eight papers, one found the mean number of visits to be 3.6,29 and one found 4.8 visits for mixed-duration back pain.22 Thomas et al reported that 40% of patients presented to the GP in the first 12 weeks of their study.43
Medication
Only 12 out of 33 studies gave information about medication taken by patients for their back pain.3,15,21,24–26,31,33,38,39,41,43
Many patients were taking medication at baseline, with figures reported of 69%,39 80%,24 90%,43 and 69% (prescribed) and 73% (over the counter).21
Two papers gave information about opioid prescription: 34% of patients in a US study,15 and 18.7% in the UK3 were prescribed them. Unfortunately, there was no information about the strength of the opiates or whether combination drugs were prescribed.
Work absence
Information about absence from work was quite heterogeneous due to the way in which authors recorded this information and differences in the type of usual care; some studies only recruited patients who were absent from work because of back pain.33,35 It is important to remember this when comparing data about sick notes from different countries. The different procedures for obtaining a sick notes in different countries may give a false interpretation of the data. As mentioned in the paper Dutch GPs do not give sick notes, British GPs do.
Acute back pain
One study reported that 81% of patients had no certified sick leave, fewer than 9% had 10 or more days of certified sick leave in a year, and overall there was a mean of 3 days' sick leave.13 Another reported a mean 2.2 days (SD: 3.4) of sick leave since randomisation at 8 weeks' follow-up.15
Subacute back pain
Patients reported a mean of 14 days of sick leave at baseline,21 and 15 in the 3 months before commencement of the study.19
Chronic back pain
Varied information was found related to work absence for chronic back pain. Two studies reported that 50%,31 and 57.3%17 of patients were off sick at baseline, whereas in another study the patients only had 3 days off sick at baseline.25
Activity levels and exercise advice
Three studies gave details on the activity levels of patients before they presented to their GP19,32,33 and three reported the advice given to patients about exercise during the trial.15,31,33
Physiotherapy
For acute back pain, 7%15 and 8.6%39 of patients were referred to physiotherapy. For subacute back pain, 18%,18 31%,21 and 92.9%33 of patients receiving usual care were referred to physiotherapy at baseline or in the first 6 weeks. For mixed-duration back pain 49% were referred within the first 12 weeks.43 In the case of chronic back pain it was not possible to compare data in a meaningful way, due to heterogeneity as discussed in relation to work absence.
Radiology
Use of plain film X-rays in the management of back pain varied, particularly between countries. The percentages of patients having this investigation were 19% (US),15 53.6% (Canada),33 7% (UK),21 and 4% (UK).29
Clinical course of patients randomised to usual care
Functional disability (RMDQ score)
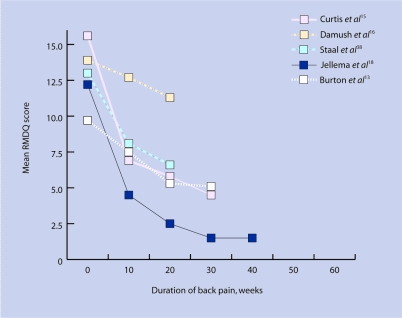
The data shown in Figures 2a and 2b suggest that the speed at which RMDQ scores improve is inversely related to the duration of back pain: that is, the longer the duration of pain, the slower the rate of improvement. In acute and subacute pain there was a definite trend for improvement. The single study that did not follow this trend16 involved usual care provided by university-affiliated clinics and the emergency department of a hospital in an inner-city setting in the US; as such, these patients may not be representative of patients normally managed in primary care.
Figure 2a.
Change in Roland–Morris Disability Questionnaire (RMDQ) scores over time according to duration of acute/subacute back pain.
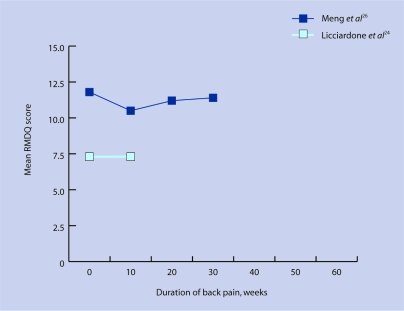
Figure 2b.
Change in Roland–Morris Disability Questionnaire (RMDQ) scores over time according to duration of chronic back pain.
Pain score
For acute and subacute pain there was a general trend for pain scores to improve with time, as observed on the 0–10-point pain scale used to rate the studies. In two studies acute pain mean pain scores improved by 5.8 and 2.0 between baseline and their endpoints respectively.13,35 For subacute pain, mean pain scores improved by 1.2, 5.0, 2.0, 1.0, and 3.9 respectively.16,18,19,21,33
For patients with chronic pain, the pain score changed little over the course of the study, with changes in mean pain scores of 0.9, −0.8, 0.6 and −1.8 respectively (a negative value meaning reduction of pain).24–26,31
Satisfaction
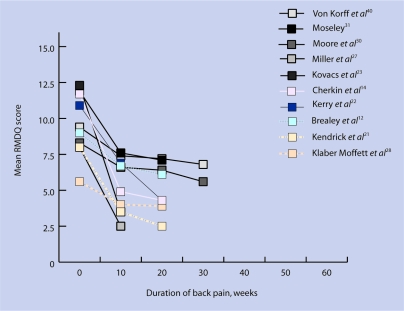
For acute pain, mean satisfaction scores at study endpoint were 7.2 (treatment),35 7.0 (explanation),35 and 4.1 (overall), according to the 0–10-point satisfaction scale used to rate the studies.15 In subacute pain, endpoint satisfaction scores were 4.7,33 and 4.1.19 In one study on chronic back pain the mean endpoint satisfaction score was 4.4.24 A study on mixed-duration back pain expressed this differently, with the number of patients who were very satisfied or satisfied at 85% following their initial consultation, and at 70% after 6 weeks (Figure 2c).22
Figure 2c.
Change in Roland–Morris Disability Questionnaire (RMDQ) scores over time according to duration of mixed back pain.
DISCUSSION
Methodological quality
That many studies did not have blinding of patients or outcome assessors is not unusual. Often blinding is not possible, or even sensible, due to the pragmatic nature of the trial design, the interventions used, or ethical constraints.
Studies were presented in different ways, which made quality assessment and data extraction difficult to carry out. Future randomised controlled trials on back pain should be presented in line with Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) recommendations.44
Overall, most papers reviewed were of an acceptable quality according to the study's quality scale. A small number of trials failed to describe concealment of allocation to treatment,30,40 or intention-to-treat analysis.27,32,34
Direct comparison between studies was difficult due to the differing ways in which data were recorded. For example, pain experienced by patients was assessed using Visual Analogue Scale, modified Von Korff Pain Scale, Aberdeen Back Pain Scale, and the Extended Aberdeen Spine Pain Scale. Nevertheless, the patterns of changes in pain were similar to those for disability, with patients with acute and subacute back pain showing larger improvements than participants with chronic back pain.
Description of usual care
Overall, usual care was poorly described in these studies. Historically, there has been a tendency to allow care in the control group to be according to the normal practice of the care provider, with little or no recording of what actually took place. This contrasts with the intervention treatment, against which usual care is compared, which is often described in great detail.
It is clear that healthcare providers vary widely in their preferred practices, due to many factors including their experience and the expectations of the population in which the studies are set. As such, control groups in separate studies reviewed here may receive a range of different treatments. This makes comparison between studies difficult.
Although the practice of comparing a new treatment with the prevailing current practice is well accepted, interpretation of such studies is problematic when the usual care groups vary so widely and are not adequately described. This is particularly pertinent given that a healthcare provider may act differently purely by knowing their practice is under scrutiny.
Attempts to standardise usual care have shown little effect in changing clinician behaviour.3 It is important to accept that usual care is heterogeneous, and this needs to be taken into account when interpreting the results of studies. The present authors suggest that a minimum dataset about usual care is recorded to improve understanding of the treatments received in the usual care group (Table 1 and Appendix 2). This includes information about radiology usage, other investigations ordered, medications used (prescribed or over-the-counter), sick notes issued, use of written materials, recording of activity levels, details of exercise advice given, consultation rates, physiotherapy undertaken, and hospital referrals.3
Content of usual care
It is difficult to draw any firm conclusions about how frequently primary care consultation is allowed or what actually happens in the usual care approaches. Marked differences existed in the control groups due to the country involved, variation in the study designs, and methods of recording consultation activity; only half of studies reported data and the results showed no pattern.
Similarly, the overall recording of medication use was quite poor. This is disappointing in that medication use has significant financial costs for the patient and the health economy, and is associated with a not-insignificant number of side-effects.
This review found that many patients take over-the-counter medication for their back pain, and GPs often provided additional medication. Data were limited, but there was a suggestion that levels of opioid prescription were quite high,3,15 given the message in back-pain management guidelines that suggest using weak opioids as ‘add-on’ treatments when paracetamol or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs provide insufficient pain relief.8,45 Compound analgesics are not recommended as they do not allow separate titration of the constituent medications, and there are concerns about dependence with strong opioids.8,45
Unfortunately, in the studies in this review, information was not recorded about the strength of opiates or whether combination products were used. It may be that the concerns about strong and combination opioids are overemphasised, particularly when the majority of patients will recover from their back pain in a few weeks. A GP faced with a patient who is in pain, despite taking simple painkillers, may well decide that it is appropriate to prescribe these drugs in the short term, but with close monitoring for side-effects and over-usage. It is important to record more detailed information about the types of drugs used to treat back pain, and their effectiveness and safety.
It is generally accepted that plain-film X-rays are not helpful in the management of most patients with back pain and represent an avoidable source of radiation.6,46–48 This review found that the use of X-rays varied widely between countries, from 4% of cases in the UK,29 to 53.6% in Canada.33 Reasons for requesting investigations are complex and involve many factors including patient and doctor beliefs and knowledge, country-specific healthcare systems, and patient satisfaction.
The tension between guideline advice and actual clinical behaviour is illustrated by a survey of GPs that found that they would almost always or sometimes refer for X-ray in 70% of patients with non-recurrent backache of less than a month's duration: 88% per cent of requests were to reassure the patient, and 78% to reassure the doctor.49 This finding is not confined to low back pain consultations, and it has been shown that perceived patient pressure, rather than clinical need, is the reason behind a significant minority of investigations.50 Clearly, it is desirable to reduce patient exposure to radiation, but to achieve this goal a guideline must be of practical use to doctors in primary care. The guideline must include adequate explanation of the rationale behind each recommendation, address the needs for reassurance on the part of the patient and doctor, and be adaptable to local resources (for example, it is no use advocating magnetic resonance imaging instead of plain-film X-rays if it is not readily available).
The clear messages from trials and guidelines are that patients with low back pain should continue with normal activities, even if uncomfortable, and stay at or return to work.8 The papers included in this review did not, in general, report on this important aspect of patient care. One possible reason for this might be that is not the normal practice of GPs to record this information. Also GPs may not feel able to give specific advice about exercise, due either to lack of training or fear of litigation should the patient develop a problem related to exercising. GPs are well placed to give exercise advice to patients, and there is a need to address these issues to encourage and support people who would benefit from increasing their activity.51
Course of symptoms
The relatively small number of studies involved makes it difficult to undertake a meaningful data synthesis and arrive at firm conclusions. However, Figures 2a and 2b suggest that the speed at which the RMDQ score changed over time depended on the duration of the back disorder. For acute pain there was a trend for RMDQ scores to fall rapidly over the first few weeks (Figure 2a), and this improvement was maintained throughout the study period. For chronic pain sufferers the outlook was much less promising, and RMDQ scores did not tend to improve with time.
Usual care groups in the studies in this review were given a range of treatments but, despite this, it appears that the effectiveness of usual care (if measured as improvement of RMDQ score) may be related more to the duration of the episode than to the type of care given.
Usual care is variable in content and effectiveness. That it is also poorly described compounds this problem and makes comparison between studies even more difficult. As such, it is important that usual care is not regarded as a uniform control against which interventions are compared without attempting to understand what it consists of. This heterogeneity may undermine the fundamental basis for calculating sample sizes in future trials. Agreement is needed as to what information should be recorded in future trials, and conformity to CONSORT needs to be improved.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Jo Jordon for her help with systematic review training
Appendix 1. Search strategy for identification of studies.
Relevant studies meeting the inclusion criteria were identified by:
A computer search of MEDLINE (1966–2007), EMBASE (1966–2007), CINAHL (1982–2007), AMED, DARE, and ISI Web of Science. The following search strategies were used. They were restricted to adults, human participants, and publication since 1998:
-
▸
MEDLINE
(random$ OR clinical trial$([pt,sh, ti, ab]) AND (low back pain OR back pain or backache [sh,ti,ab.]) AND (physicians-family OR family pract$ OR general pract$ OR family medicine OR primary health care OR primary medical care [sh,ti,ab.])
-
▸
EMBASE
(random$ OR clinical trial$ [pt,sh,ti,ab]) AND (low back pain OR back pain OR backache OR lumbago [sh,ti,ab]) AND (physicians-family OR family pract$ OR general pract$ OR family medicine OR primary health care OR primary medical care [sh,ti,ab.])
-
▸
CINAHL
(random$ OR controlled clinical trial$ [pt,sh,ti,ab]) AND (low back pain OR back pain or backache) AND (low back pain OR back pain or backache [sh,ti,ab.]) AND (physicians-family OR family pract$ OR general pract$ OR family medicine OR primary health care OR primary medical care [sh,ti,ab.])
-
2.
Examination of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials.
-
3.
Examination of references given in the identified randomised controlled trials and appropriate reviews.
Appendix 2. Study characteristics.
| Study (first author) | Setting | Duration of back pain | Participants: n, mean age in years, % female | Baseline mean RMDQ score (SD) | Intervention | Control | Outcome of usual care: mean (SD) unless stated | Outcome of intervention in comparison with usual care | Methodological quality score (0–5, with 5 being best) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brealey12 | UK general practice | Mixed | 338, 42.5, 53 | 9 (3.9) | Physical treatments; exercise | Best care | RMDQ: base 9 (3.9), 3 months 6.8 (0.3), 12 months 6.1 (0.3) versus exercise group. Pain (MVK): base 60.5 (17.6), 3 months 49.3 (1.6), 12 months 48.4 (1.7) versus exercise group | Compared with best care — exercise: small benefit at 3 months, nil at 12 months. Manipulation: small to moderate benefit at 3 months and small benefit at 12 months. Manipulation + exercise: moderate benefit at 3 months and small benefit at 12 months | 3 |
| Burton13 | UK 5 general practices and 1 osteopath practice | Acute | 79, 44.7, 48 | 9.7 (4.6) | Back book (biopsychosocial) or handy-hints pamphlet (biomedical) | Usual care + pamphlet | RMDQ: base 9.7 (4.6), 12 months ∼4.5 (–). Pain (VAS 0–100) worst/best: base 68.7 (18.5)/50.8 (27.8) 12 months 15.6 (18.7)/10.6 (17.8) | Improved beliefs about low back pain; reduced fear-avoidance and RMDQ score; no effect on pain | 5 |
| Cherkin14 | US primary care | Acute | 66, 40.1, 42 | 11.7 (5.4) | Physical therapy; chiropractic booklet | Usual care + booklet | RMDQ: base 11.7 (1.3), 4 weeks 4.9 (1.1), 12 weeks 4.3 (1.2) | Physical and chiropractic therapy improves satisfaction, but nothing else | 4 |
| Curtis15 | US, primary care | Acute | 143, 42.7, 57 | 15.6 (5.4) | Manual therapy given by GP | Enhanced care patient-centred approach, careful examination, including palpation and functional assessment, use of national guidelines and patient handouts regarding activities of daily living and exercise. Option to use standard prescription, bed rest, trigger-point injections referral to others | RMDQ at base 15.6 (5.4); improvement in RMDQ from randomisation: base 2.6 (5.7), 2 weeks 8.7 (8.0), 4 weeks 9.8 (7.3), 8 weeks 11.1 (7.9). Pain (0–10): 4.6 (2.1). Satisfaction (1–5, 1 = best): endpoint 2.1 (1.1) | GP giving limited manual therapy offers very modest benefit compared with enhanced care alone. However, only 43% of patients in manual treatment group given full treatment course by the GP | 4 |
| Damush16 | US inner-city health centres and emergency rooms | Subacute | 106, 45.5, 75 | 13.9 (6.8) | Self-management programme for patients on low income with acute low back pain: long-term outcomes (1 year) | Usual care referral to occupational health, physical therapy, or a neurologist; analgesics, back exercise advice sheets | RMDQ: base 13.9 (6.8), 12 months 11.3 (8.1). Satisfaction (higher score better): base 24.3 (5.7), 12 months 25.4 (5.4) | At 12 months patients who participated in the self-management programme showed significantly better RMDQ scores, mental functioning, self-efficacy to manage acute low back pain, time in physical activity, and reduced fear of movement/re-injury | 4 |
| Dey3 | UK primary care | Mixed | 1138, 41.3, 54.3 | – | Education of GPs to promote use of guidelines on low back pain | Usual care | Patients receiving the following (%): X-ray 13.7, sick note 19.2, opiates/muscle relaxant 18.7, referral to secondary care 2.3, referral to physiotherapy 13.8 | No difference between study and control patients in terms of proportion referred to X-ray, given a sick certificate, prescribed opioids or muscle relaxants, or referred to secondary care. Only 21% of patients had evidence that they were given advice about avoiding bed rest; 0.6% in both arms recommended to take bed rest. Suggested that GPs know about guidelines but feel pressurised by patient expectations to behave differently | 4 |
| Molde Hagen17 | Norway spine clinic | Chronic | 220, 41.1, 48 | – | Light mobilisation | Usual care | 19.6 days of compensated sick leave in 2 years | Brief examination, information giving, reassurance and encouragement to resume physical activity reduces long-term sick leave in the first year. Those returning to work mainly do so in the first year | 3 |
| Hagen42 | Norway spine clinic | Subacute | 457, 41, 48 | – | Reassurance about prognosis and advice | Usual care | – | – | 3 |
| Jellema18 | The Netherlands primary care | Subacute | 171, 42, 47 | 12.2 (5); median 13 IQR (8–16) | Assessment and modification of psychological factors | Usual care as per Dutch College of GP guidelines | RMDQ: base 12.2 (5.0);a base 13 (8–16), 6 weeks 4 (1–10); 13 weeks 2 (0–5), 26 weeks 1 (0–3), 1 year 1 (0–4). Pain (0–10):a base 5 (3–6), 6 weeks 2 (0–4), 13 weeks 1 (0–3), 26 weeks 0 (0–2), 1 year 0 (0–2) | No difference in outcome measures versus usual care | 4 |
| Karjalainen19 | Finnish primary care | Subacute | 57, 43, 60 | – | Mini-intervention versus usual care, 2-year follow-up | Leaflet + usual care | Disability (ODI) mean (range): base 34 (13–67), 3 months 25 (0–76), 6 months 21 (0–51), 1 year 19 (0–51), 2 years 18 (0–51). Pain (0–10): base 5.7 (1–10), 3 months 4.1 (0–9), 6 months 3.7 (0–10), 1 year 3.7 (0–10), 2 years 3.4 (0–9) | Examination, information, support, and simple advice reduces daily symptoms and sick leave, and increases satisfaction and adaptation by patients, without increasing healthcare costs | 3 |
| Karjalainen20 primary care | Finland | Subacute | 57, 43, 60 | – | Mini-intervention (involving light mobilisation, graded activity programme, addressing patient concerns) versus usual care, 1-year follow-up | Leaflet + usual care | As above | As above | 3 |
| Kendrick21 | UK primary care | Subacute | 211, 39,a 60 | 8 (4–12)a | X-rays for low back pain | Usual care | Median (IQR) RMDQ: base 8 (4–12), 3 months 3 (1–7). Pain (0–10): base 2 (1–2), 3 months 1 (0–2). Satisfaction (EuroQol): base 20 (17.75–22), 3 months (19–23) | X-rays don't improve care of low back pain sufferers, but increase doctors' workload | 3 |
| Kerry22 | UK primary care | Mixed | 332, 41.1, 53 | 10.8 (5.4) | X-rays for first presentation of low back pain | Usual care | RMDQ: base 10.8 (5.4), 6 weeks 5.4 (0.3), 1 year 4.2 (0.3). Pain (SF-36 BP): base 45 (26), 6 weeks 56 (2), 1 year 65 (2) | Referral for lumbar X-ray doesn't improve pain, function, or disability. There is a small possible improvement in psychological status, but need to balance against radiation risk | 3 |
| Kovacs23 | Mallorca primary care | Chronic | 45, 45.6,a 66.7 | 12.17 (–) | Neuroreflexotherapy | Usual care | Median (range) RMDQ: base 12.2 (6.5–18.0), 1-year improvement 2.1 (−1.5 to 6.7). Pain (VAS): base 5.2 (4.1–8), 1-year improvement 1.9 (−1.3 to 2.0) | Neuroreflexotherapy reduced pain, disability, specialist referral, X-ray requests, drug costs, and sick leave | 4 |
| Licciardone24 | US university clinic | Chronic | 20, 49, 65 | 7.3 (5.4) | Osteopathic manipulation in chronic low back pain | Usual care | RMDQ: base 7.3 (5.4). Pain (VAS): base 3.1 (2.3), 6 months ∼3.9 (–). Global satisfaction: base ∼1.8 (–), 6 months ∼2.1 (–) | Osteopathic manipulation improved pain, treatment satisfaction, function, and mental health compared with usual care. Sham manipulation improved pain, treatment satisfaction, and function compared with usual care. There were no differences between osteopathic and sham manipulation | 4 |
| Linton25 | Sweden primary care | Chronic | 70, 45, 71 | – | CBT and different forms of information | Pamphlet | Pain (0–10): base 4.8 (0.45), 1 year 4.0 (0.55) | CBT caused a nine-fold reduction in sick leave and physician and physiotherapy usage | 4 |
| Meng26 | US various clinics in private and hospital sectors | Chronic | 24, 70, 62.5 | 11.8 (5.3) | Acupuncture for chronic low back pain | Usual care (narcotics, muscle relaxants, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, epidurals, trigger-point injections prohibited) | RMDQ: base 11.8 (5.3), 6 weeks improved by 0.6 (2.7). Pain (VAS): base 1.7 (1.0), 6 weeks worsened by 0.6 (1.2) | Acupuncture reduced RMDQ scores and was safe | 3 |
| Miller27 | UK primary care | Subacute | 211, 39, 16 | 8 (4–12)a | Cost effectiveness of X-rays | Usual care | Median (IQR) RMDQ: base 8 (4–12) Pain (VAS, 0–10): base 2 (1–2) Satisfaction (0–27): base 20 (17.8–22), 9 months (16–21) | X-rays are only cost-effective when patient satisfaction is high. Other ways of obtaining satisfaction are to be preferred | 2 |
| Klaber Moffett28 | UK primary care | Mixed | 98, 42.6, 56 | 5.56 (3.94) | Exercise programme | Usual care | RMDQ: base 5.56 (3.94), % of patients with improvement ≤2 points; 6 weeks 46, 6 months 47, 1 year 47.5 | High fear-avoiders benefit most from an exercise programme and the effect is maintained at 1 year. Patients who are depressed/distressed gained a short-term benefit | 4 |
| Moffett29 | UK primary care | Mixed | 98, 42.6, 56 | 5.56 (3.94) | Exercise programme | Usual care | RMDQ: base 5.56 (3.94), improvement from base 6; 6 weeks 1.94, 6 months 1.64, 1 year 1.77. Pain (ALBPS): 25.52 (10.85), improvement from base; 6 weeks 8.99, 6 months 8.11, 1 year 8.48 | Exercise programme reduced pain, disability, and healthcare usage | 3 |
| Moore30 | US HMO clinics | Mixed | 113, 49.1, 49.6 | 8.29 (5.88) | Self-care (CBT) | Book on back care | RMDQ: 8.29 (5.88), 3 months 6.55 (6.13), 6 months 6.4 (5.99), 1 year 5.56 (5.8). Pain (0–10): base 5.2 (1.95), 3 months 4.06 (2.17), 6 months 3.71 (2.28), 1 year 2.98 (1.99) | CBT approach reduced back-related worry, fear-avoidance, pain, and functional problems | 2 |
| Moseley31 | Australia physiotherapy clinic | Chronic | 28, 398, 54 | 11.9 (3.2) | Combined physiotherapy and education | Usual care | RMDQ: base 11.9 (3.2), 1-year improvement 4.3. Pain (0–10): base 4.7 (1.5), 1-year improvement 1.4 | A combined programme of manual therapy, exercise, and education reduced pain and disability | 4 |
| Roberts32 | UK primary care | Acute | 28, 29.2, 32 | – | Back-care leaflet | Usual care | – | The leaflet improved posture but had no effect on function | 3 |
| Rossignol33 | Canadian worker compensation scheme | Subacute | 56, 38.3, 23.2 | – | Advice and support for physicians treating low back pain | Usual care | Pain (VAS, 0–100): base 52.4 (20.7), 3 months 10.9 (24.0), 6 months 12.8 (27.0). Satisfaction (0–65, best–worst): base 30.3 (12.8), little change during trial | Advice and support to doctors about management of low back pain reduces patient sick leave, pain, dysfunction, and X-ray usage. It improves exercise levels | 4 |
| Schectman34 | US HMO clinics | Acute | 590, 45.5, 54 | – | Physician education versus patient educational material versus both versus neither | Usual care | – | Education of physicians improves compliance with low back pain guidelines. Patient educational material has no effect | 1 |
| Seferlis35 | Sweden hospital clinic | Acute | 60, 38, 47 | – | Manual therapy versus intensive training versus usual care | Usual care | – | Most patients return to work by 1 month regardless of treatment. Satisfaction is improved by manual therapy or intensive training | 4 |
| Seferlis36 | Swedish hospital clinic previous study | Acute | 60, 38, 47 | – | Cost-minimisation analysis of conservative treatment for back pain | Usual care | – | Usual care has lowest cost | 4 |
| Skouen37 | Norway hospital clinic | Chronic | 86, 44, 64 | – | Extensive versus light multidisciplinary treatments versus usual care | Usual care | – | Light programme more effective than usual care. Extensive programme no more effective than usual care | 3 |
| Staal38 | The Netherlands occupational health airline | Subacute | 67, 37, 7 | 13 (4.9) | Graded activity | Usual care | RMDQ: base 13.0 (4.9), improvement frame base: 3 months 4.9 (6.2), 6 months 6.4 (6.6). Pain (0–10): base 6.4 (1.7), improvement frame base: 3 months 2.5 (2.8), 6 months 2.7 (2.8) | Graded activity reduces days of work lost due to low back pain | 4 |
| Thomas43 | UK acupuncture clinics and primary care | Mixed | 241, 44, 58 | – | Acupuncture | Usual care | Disability (ODI): baseline 31.4 (14.2), 12 months 19.6 (15.4), 24 months 21.0 (14.2). Pain (SF-36 BP, 0–100): baseline 30.4 (18.0), 12 months 58.3 (22.2), 24 months 59.5 (23.4). Pain (MPQ): baseline 2.7 (1.0), 12 months 1.53 (0.9), 24 months 1.71 (1.1) | Weak evidence that acupuncture has an effect on persistent back pain at 2 months, stronger evidence of a smaller effect at 24 months | 3 |
| Underwood39 | UK primary care | Acute | 40, 41, 45 | – | Back extension exercises | Usual care | Disability (ODI): base 35.6, 1 year 24% patients had a score <20. Pain (VAS): base 50.4, 1 year 18% had score <20 | No evidence to show that it is more effective than usual care | 4 |
| Von Korff40 | US primary care | Mixed | 126, 50.3, 56 | 9.4 (6.5) | Lay-led selfmanagement | Usual care | RMDQ (approximate): base 9.0, 3 months 7.4, 6 months 7.3, 1 year 7.0. Pain (average): base 5.7 (2.1), 3 months 4.0 (2.1), 6 months 4.1 (0.9), 1 year 3.8 (2.4) | Self-help group reduced worried, produced positive attitudes, and reduced activity limitations | 3 |
| Williams41 | UK primary care osteopathy clinic | Subacute | 106, –, – | – | Effectiveness and healthcare costs of a a primary care osteopathy service | Usual care | Pain (VAS, 0–100): base 46.3 (22.4), 2 months 6.8 (23.4), 6 months 10.1 (24.1) | Primary care osteopathy improved short-term physical and long-term psychological outcomes at a little extra cost | 3 |
Media (interquartile range). ALBPS = Aberdeen Low Back Pain Scale (0–100, 0 = best). CBT = cognitive behavioural therapy. HMO = health maintenance organisation. IQR = interquartile range. MPQ = McGill Pain Questionnaire (0–5, 0=best). MVK = modified Von Korff Pain Scale (0–100, 0 = best). ODI = Oswestry Disability Index (0–100, 0 = best). SF-16 BP = SF-16 Bodily Pain (0–100, 0 = best). RMDQ = Roland–Morris Disability Questionnaire (0–24, 0 = best). VAS = Visual Analogue Scale (0–100 or 0–10, best = 0).
Appendix 3. Record of activities within the consultation.
| Study (first author) | Case mix | Radiology figures | Other investigations | Any drug details (prescribed or OTC) | Sick note detail | Written advice recorded | Activity level details | Exercise prescription details | Physio therapy details | Hospital referral details | Consultation rate details | Item score (out of 10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burton13 | Acute | Y | Y | Y | 3 | |||||||
| Cherkin14 | Acute | Y | 1 | |||||||||
| Curtis15 | Acute | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 7 | |||
| Roberts32 | Acute | Y | Y | 2 | ||||||||
| Schectman34 | Acute | Y | Y | Y | 3 | |||||||
| Seferlis35 | Acute | Y | 1 | |||||||||
| Seferlis36 | Acute | Y | Y | Y | Y | 4 | ||||||
| Underwood39 | Acute | Y | Y | Y | Y | 4 | ||||||
| Damush16 | Subacute | 0 | ||||||||||
| Hagen42 | Subacute | Y | 1 | |||||||||
| Jellema18 | Subacute | Y | Y | Y | 3 | |||||||
| Karjalainen19 | Subacute | Y | Y | Y | 3 | |||||||
| Karjalainen20 | Subacute | Y | Y | Y | Y | 4 | ||||||
| Kendrick21 | Subacute | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 | ||||
| Kovacs23 | Subacute | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 | ||||
| Miller27 | Subacute | Y | 1 | |||||||||
| Rossignol22 | Subacute | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 8 | ||
| Staal38 | Subacute | Y | Y | Y | 3 | |||||||
| Williams41 | Subacute | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 | ||||
| Molde Hagen17 | Chronic | Y | 1 | |||||||||
| Licciardone24 | Chronic | Y | Y | 2 | ||||||||
| Linton25 | Chronic | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 5 | |||||
| Meng26 | Chronic | Y | 1 | |||||||||
| Moseley21 | Chronic | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 5 | |||||
| Skouen27 | Chronic | Y | 1 | |||||||||
| Brealey12 | Mixed | Y | Y | 2 | ||||||||
| Dey3 | Mixed | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 | ||||
| Kerry22 | Mixed | Y | Y | Y | 3 | |||||||
| Klaber Moffett28 | Mixed | 0 | ||||||||||
| Moffett29 | Mixed | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 5 | |||||
| Moore30 | Mixed | Y | 1 | |||||||||
| Thomas43 | Mixed | Y | Y | Y | 3 | |||||||
| Von Korff40 | Mixed | Y | 1 | |||||||||
| Number of studies giving data | 11 | 2 | 11 | 22 | 9 | 3 | 4 | 15 | 8 | 17 | ||
| % of studies giving data | 33 | 6 | 33 | 67 | 27 | 9 | 12 | 45 | 24 | 52 | ||
OTC = over the counter. Y = number of items recorded (out of 10).
Funding body
North Staffordshire Primary Care Research Consortium
Competing interests
The authors have declared that there are none
Discuss this article
Contribute and read comments about this article on the Discussion Forum: http://www.rcgp.org.uk/bjgp-discuss
REFERENCES
- 1.Clinical Standards Advisory Group. Epidemiology review: the epidemiology and cost of back pain. London: HMSO; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Croft PR, et al. Outcome of low back pain in general practice: a prospective study. BMJ. 1998;316(141):1356–1359. doi: 10.1136/bmj.316.7141.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dey P, et al. Implementation of RCGP guidelines for acute low back pain: a cluster randomised controlled trial. Br J Gen Pract. 2004;54(498):33–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Di ID. A survey of primary care physician practice patterns and adherence to acute low back problem guidelines. Arch Fam Med. 2000;9(10):1015–1021. doi: 10.1001/archfami.9.10.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.ACC. New Zealand acute low back pain guide. Wellington: ACC, The National Health Committee; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bigos S. Acute low back problems in adults. Clinical practice guideline no. 14. Rockford, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2004. AHCPR Publication No. 95-0642. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Royal College of General Practitioners. Clinical guidelines for the management of acute low back pain. London: Royal College of General Practitioners; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 8.van Tulder M. European guidelines for the management of acute nonspecific low back pain. doi: 10.1007/s00586-006-1071-2. http://www.backpaineurope.org/web/files/WG1_Guidelines.pdf (accessed 15 Apr 2008) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 9.van Tulder M. Method guidelines for systematic reviews in the Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group for Spinal Disorders. Spine. 1997;22(20):2323–2330. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199710150-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.van Tulder M. Updated method guidelines for systematic reviews in the Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group. Spine. 2003;28(12):1290–1299. doi: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000065484.95996.AF. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.van Tulder M. Exercise therapy for low back pain: a systematic review within the framework of the Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group. Spine. 2000;25(21):2784–2796. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200011010-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Brealey S, et al. UK Back Pain Exercise and Manipulation UK BEAM trial — national randomised trial of physical treatments for back pain in primary care: objectives, design and interventions [ISRCTN32683578] BMC Health Serv Res. 2003;13(1):16. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-3-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Burton AK. Information and advice to patients with back pain can have a positive effect. A randomized controlled trial of a novel educational booklet in primary care. Spine. 1999;24(23):2484–2491. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199912010-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cherkin DC, et al. A comparison of physical therapy, chiropractic manipulation, and provision of an educational booklet for the treatment of patients with low back pain. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(15):1021–1029. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199810083391502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Curtis P, et al. Training primary care physicians to give limited manual therapy for low back pain: patient outcomes. Spine. 2000;25(22):2954–2961. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200011150-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Damush T, et al. The long-term effects of a self-management program for inner-city primary care patients with acute low back pain. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163(21):2632–2638. doi: 10.1001/archinte.163.21.2632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Molde Hagen E. Does early intervention with a light mobilization program reduce long-term sick leave for low back pain: a 3-year follow-up study. Spine. 2003;28(20):2309–2315. doi: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000085817.33211.3F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Jellema P, et al. Should treatment of (sub)acute low back pain be aimed at psychosocial prognostic factors? Cluster randomised clinical trial in general practice. BMJ. 2005;331(7508):84–87. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38495.686736.E0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Karjalainen K, et al. Mini-intervention for subacute low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Spine. 2003;28(6):533–540. doi: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000049928.52520.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Karjalainen K, et al. Mini-intervention for subacute low back pain: two-year follow-up and modifiers of effectiveness. Spine. 2004;29(10):1069–1076. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200405150-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kendrick D, et al. Radiography of the lumbar spine in primary care patients with low back pain: randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2001;322(7283):400–405. doi: 10.1136/bmj.322.7283.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kerry S, et al. Radiography for low back pain: a randomised controlled trial and observational study in primary care. Br J Gen Pract. 2002;52(479):469–474. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kovacs F, et al. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness analysis of neuroreflexotherapy for subacute and chronic low back pain in routine general practice: a cluster randomized, controlled trial. Spine. 2002;27(11):1149–1159. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200206010-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Licciardone JC, et al. Osteopathic manipulative treatment for chronic low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Spine. 2003;28(13):1355–1362. doi: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000067110.61471.7D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Linton SJ. Can chronic disability be prevented? A randomized trial of a cognitive-behavior intervention and two forms of information for patients with spinal pain. Spine. 2000;25(21):2825–2831. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200011010-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Meng CF, et al. Acupuncture for chronic low back pain in older patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Rheumatology. 2003;42(12):1508–1517. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keg405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Miller P. Cost-effectiveness of lumbar spine radiography in primary care patients with low back pain. Spine. 2002;27(20):2291–2297. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200210150-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Klaber Moffett JA. High fear-avoiders of physical activity benefit from an exercise program for patients with back pain. Spine. 2004;29(11):1167–1172. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200406010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Moffett JK, et al. Randomised controlled trial of exercise for low back pain: clinical outcomes, costs, and preferences. BMJ. 1999;319(7205):279–283. doi: 10.1136/bmj.319.7205.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Moore JE, et al. A randomized trial of a cognitive-behavioral program for enhancing back pain self care in a primary care setting. Pain. 2000;88(2):145–153. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3959(00)00314-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Moseley L. Combined physiotherapy and education is efficacious for chronic low back pain. Aust J Physiother. 2002;48(4):297–302. doi: 10.1016/s0004-9514(14)60169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Roberts L, et al. The back home trial: general practitioner-supported leaflets may change back pain behavior. Spine. 2002;27(17):1821–1828. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200209010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rossignol M, et al. Coordination of primary health care for back pain. A randomized controlled trial. Spine. 2000;25(2):251–258. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200001150-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schectman J. Randomized controlled trial of education and feedback for implementation of guidelines for acute low back pain. J Gen Intern Med. 2003;18(10):773–780. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.2003.10205.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Seferlis T. Conservative treatment in patients sick-listed for acute low-back pain: a prospective randomised study with 12 months' follow-up. Eur Spine J. 1998;7(6):461–470. doi: 10.1007/s005860050109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Seferlis T. Cost-minimisation analysis of three conservative treatment programmes in 180 patients sick-listed for acute low-back pain. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2000;18(1):53–57. doi: 10.1080/02813430050202578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Skouen JS. Relative cost-effectiveness of extensive and light multidisciplinary treatment programs versus treatment as usual for patients with chronic low back pain on long-term sick leave: randomized controlled study. Spine. 2002;27(9):901–909. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200205010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Staal JB, et al. Graded activity for low back pain in occupational health care: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140(2):77–84. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-140-2-200401200-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Underwood MR. The use of a back class teaching extension exercises in the treatment of acute low back pain in primary care. Fam Pract. 1998;15(1):9–15. doi: 10.1093/fampra/15.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Von Korff M, et al. A randomized trial of a lay person-led self-management group intervention for back pain patients in primary care. Spine. 1998;23(23):2608–2615. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199812010-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Williams NH, et al. Randomized osteopathic manipulation study (ROMANS): pragmatic trial for spinal pain in primary care. Fam Pract. 2003;20(6):662–669. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmg607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hagen EM. Predictors and modifiers of treatment effect influencing sick leave in subacute low back pain patients. Spine. 2005;30(24):2717–2723. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000190394.05359.c7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Thomas KJ, et al. Randomised controlled trial of a short course of traditional acupuncture compared with usual care for persistent non-specific low back pain. BMJ. 2006;333(7569):623. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38878.907361.7C. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Altman DG, et al. The revised CONSORT statement for reporting randomized trials: explanation and elaboration. Ann InternMed. 2001;134(8):663–694. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-134-8-200104170-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Airaksinen O. European guidelines for the management of chronic non-specific low back pain. doi: 10.1007/s00586-006-1072-1. http://www.backpaineurope.org/web/files/WG2_Guidelines.pdf (accessed 15 Apr 2008) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 46.Royal College of Radiologists. Making the best use of a department of clinical radiology; guidelines for doctors. 5th edn. London: Royal College of Radiologists; 2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Borkan J, et al. [Guidelines for treating low back pain in primary care. The Israeli Low Back Pain Guideline Group] Harefuah. 1996;130(3):145–151. [In Hebrew] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Danish Institute for Health Technology Assessment. Low back pain. Frequency, management and prevention from an HTA perspective. Copenhagen: Danish Health Technology Assessment; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Owen JP, et al. Survey of general practitioners' opinions on the role of radiology in patients with low-back-pain. Br J Gen Pract. 1990;40(332):98–101. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Little P, et al. Importance of patient pressure and perceived pressure and perceived medical need for investigations, referral and prescribing in primary care: nested observational study. BMJ. 2004;328(7437):444–448. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38013.644086.7C. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Department of Health. At least five a week: evidence on the impact of physical activity and its relationship to health. London: Department of Health; 2004. [Google Scholar]