Abstract
Background. Hepatocellular carcinoma is one of the leading causes of death for compensated chronic liver disease.
Aim. The evaluation of technical success as primary ablation rate, local tumor progression, safety, and long-term patients outcome of radiofrequency ablation in single (less than 3.5 cm in diameter) or multiple nodules (up to 3, sized less than 3 cm) of hepatocellular carcinoma associated to chronic liver disease without cirrhosis.
Materials and Methods. 25 consecutive patients, mainly chronic hepatitis C, with surgical unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma due to comorbidity or tumor location recruited from a local sonographic screening, were treated.
Results. Primary ablation was obtained in 96% of patients (24 out of 25) and in 93 % of nodules (27 out of 29). 1, 3, and 5-year local tumor progression rates after treatment were 4, 14, and 14%. Survival rates at 1,3, and 5-year were 92, 72, and 64%. No treatment-related deaths and severe complications were recorded.
Conclusions. Radiofrequency ablation is effective with 96% of primary ablation with few tumoral recurrence and limited morbidity in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma associated with chronic liver disease without cirrhosis, it could represent a valid alternative treatment whenever surgical therapy is not safe.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Radiofrequency ablation, Therapy, Survival, Ultrasound, Efficacy, Chronic liver disease, cirrhosis
INTRODUCTION
The risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection is extremely high, with an incidence ranging between 2% and 8% per year in patients who have developed cirrhosis 1.
Surveillance programs addressed to the early detection of small nodular type HCC in patients with chronic liver diseases are increasing the eligibility for local or surgical treatments 2,3.
Radical therapies, feasible in up to 30% of cases, include surgical resection, orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT), ultrasound (US) guided percutaneous ablation with ethanol injection (PEI), and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) 1,4. These different therapeutical options are tailored to each individual patient's needs, taking into account general clinical factors, underlying diseases, tumor staging and nodule location within the liver.
In a small proportion of patients with underlying cirrhosis, surgical resection is possible and liver transplantation is considered even more effective 5. Patients not candidates to surgery are considered eligible for percutaneous ablative treatments like RFA, which is currently considered the best technique to obtain the destruction of the neoplastic nodules 5-11 and is cost-effective for patients in waiting list for OLT longer than 6 months 12.
The screening guidelines and the curative therapies indications concern only patients with cirrhosis 1,4. However, in the clinical practice, even patients with B-viral and C-viral chronic liver disease (CLD) without any definite diagnosis of cirrhosis undergo surveillance by means of a yearly US 3, as the transition from bridging fibrosis to cirrhosis cannot be determined clinically and HCC develops with a stepwise progression of hepatic fibrosis 13.
In this group of patients surgical resection is considered the optimal treatment and it is preferred to OLT, which does not show any benefit in terms of survival 14.
We are not aware of any review in the RFA therapy literature focused on the efficacy of RFA for HCC associated with CLD without cirrhosis, and current guide lines on this topic are limited.
Aim of this study was to investigate treatment with RFA for nodular HCC with no indications for surgery or OLT, evaluating ablative efficacy, local progression, new lesions onset, safety and survival in a cohort of consecutive patients with CLD without cirrhosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
According to our local US screening protocol, patients with Child A/B cirrhosis and those with non-cirrhotic chronic liver disease were evaluated with abdominal ultrasound every 6 or 12 months respectively. Among patients with newly diagnosed non-resectable HCC (either due to the anatomic distribution of tumor lesions or comorbidity) and among patients not eligible for OLT, those with a single nodule smaller than 3.5 cm or with up to 3 nodules sized less than 3 cm were enrolled for RFA. In our policy, trans arterial chemo embolisation (TACE) is reserved for patients with good liver function having more than 3 nodules or any nodule at an intermediate stage sized more than 3.5 cm. Exclusion criteria were liver cirrhosis, eligibility for surgical resection or OLT, and previous treatments with either PEI or TACE. As in our district there is not a liver transplant unit, any possible candidate to liver transplant was evaluated in regional hospitals having a liver transplant program. Three patients with previous hepatic resection were included in the study. Written informed consent was obtained from all the patients according to the local ethic committee. No patients refused the proposed treatment.
PATIENTS AND HCC CHARACTERISTICS
From July 1st 1997 to June 30th 2006, 200 consecutive patients fulfilling the inclusion criteria were treated with RFA : 175 out of 200 with liver cirrhosis, and 25 out of 200 (12.5%) without cirrhosis according to Knodell's hystological classification 15,16.
Pre-treatment assessment was performed before each treatment with ordinary liver function tests, prothrombine time, alpha-fetoprotein platelets counts, abdominal spiral computed tomography, chest X-ray, abdominal ultrasound with contrast media when applicable (Sonovue Bracco Italy).
The HCC diagnosis was hystologically confirmed in 16 out of 25 patients (64%) in the remaining cases the diagnosis was considered consistent with HCC according with current guide lines for cirrhosis 1. Surgical resection was not possible in 2 cases for previous liver resection, in 10 cases for comorbidity, in 6 cases for difficult sided nodules, in 1 case for refusal, in 4 cases due to two nodules in different segments of the liver and, in the remaining 2 cases during laparotomy of previously planned resection.
Patients and HCC main features are summarised in Table 1.
Table 1.
Characteristics of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with chronic liver disease without cirrhosis or with CLD without cirrhosis treated with radiofrequency ablation (RFA).
| Characteristics | HCC\ CLD without Cirrhosis Number (%) |
|---|---|
| Number of patients | 25 |
| Sex, females | 6 (24) |
| Age | 70.28±7.07 |
| range = 55-84 | |
| Etiology | HCV= 21 (84) |
| HBV= 1 (4) | |
| ETOX= 1 (4) | |
| Others= 2 (8) | |
| A-fetoprotein | 0-20 = 16 (80 ) |
| 21-100 = 3 (15 ) | |
| >100 = 1 (5 ) | |
| Total numbers of tumors | 29 (1.04 per patient) |
| 1 tumor = 21 (84) | |
| 2 tumors = 4 (16) | |
| Size of main tumor | 25.4±6.48 |
| range = 12-35 | |
| 1-20= 8 (32,0) | |
| >20 = 17 (68,0) | |
| US pattern of main tumor | IPER= 3 (12) |
| IPO= 19 (76) | |
| MX= 3 (12) | |
| Histology | Well differentiated= 13 |
| Poorly differentiated = 3 |
The pathogenesis of the underlying liver disease is reported in Table 1. The etiologies classified as “others” were C-virus associated with alcohol abuse (1 case) and metabolic steatosis (1 case).
The employed instrumental equipment and procedure techniques are described in a previous our paper 17.
All RFAs were performed either by the operator with the main experience in PEI (A.S.) or under his supervision.
The surveillance protocol included a primary ablation rate and early treatment response assessment, by contrast-enhanced spiral CT performed within 1 month after the end of the treatment, and a long term response evaluation, with alfafetoprotein measurement and hepatic ultrasound performed with or without injection of contrast media (Sonovue, Bracco Italy) every 3 months and spiral CT performed every 6 months.
The aim of this monitoring was to detect signs of both local tumor progression and new lesions separated from the previously treated nodule. Multicentric disease was defined as onset of more than 3 nodules or portal thrombosis or extrahepatic disease. An intra-nodular/peripheral enhancement at CT scan and/or an increased size of the nodule were accounted as local progression. In case of local tumor progression, if the patient still met the inclusion criteria, RFA treatment was repeated, while in case of multicentric hepatocellular carcinoma, either TACE or only symptomatic relief care was performed when required.
The primary effectiveness rate was assessed on every single nodule on the basis of the absence of vital tumor following 1 or 2 treatment sessions. The tumor necrosis was considered complete (complete response) when no area of enhancement was seen in the nodule or at its periphery on CT scan. A tumor persistence (enhancement area in the arterial phase in contrast imaging) of 30% or more after up to 2 treatment sessions was considered as incomplete ablation or treatment failure respectively. In case of treatment failure, when feasible, either PEI or TACE was performed. An ablation zone beyond the borders of the tumor was defined as ablation margin.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Survival rates were assessed using the Kaplan-Meier method. No actual dropout was recorded among patients, so that the only dropout event considered was death.
For the analysis of new events occurred during observation, i.e. local tumor progression, new lesions onset, and multicentric disease, a Survival analysis with the calculation of new events actuarial probability was run.
The maximum observation time was set to 60 months (5 years) for all patients, including those undergoing longer observation, in order to avoid different weighings.
RESULTS
Patients description for sex, age, etiology and size of the main tumor, location of tumors, US pattern, and alfa fetoprotein values are shown in Table 1.
Follow up observation time ranged from 6 to 107 months, but in the statistical analysis the maximum observation time was set to 60 months for all patients, in order to avoid different weightings. The mean follow up was 35.7 months.
On patients basis, a complete clinical response was obtained in 96% of patients (23 cases after 1 treatment and one more case after 2 treatments), and a partial response was recorded in 1 case, which could not be further treated because of the onset of multicentric diseases.
RFA efficacy, defined as primary complete ablation on nodular basis, was 93% (27/29).
30 treatments were performed in 29 nodules of 25 patients (1.03 treatments on average per nodule). A complete ablation was obtained in 27 nodules (93%), 26 requiring a single treatment session and the remaining one requiring 2 treatment sessions, leading to a 100% necrosis. In 3 cases an ablation margin was detected.
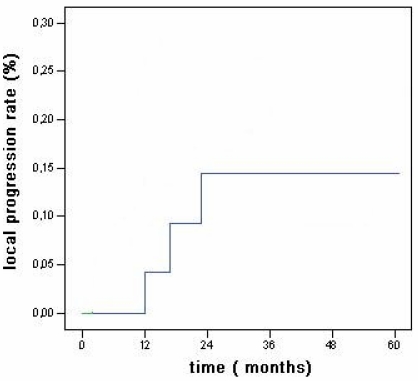
Within the observation time, local progression occurred in 3 cases (12%) (Fig 1): they were treated with RFA (2 cases) or PEI (1 case); 7 out of the 8 new lesions were treated with RFA (6 cases) or surgical resection (1 case), while no treatment was possible for the remaining one due to multicentric disease concomitant with bone metastasis.
Fig 1.
Local recurrence rates for the main tumor in HCC associated with CLD without cirrhosis.
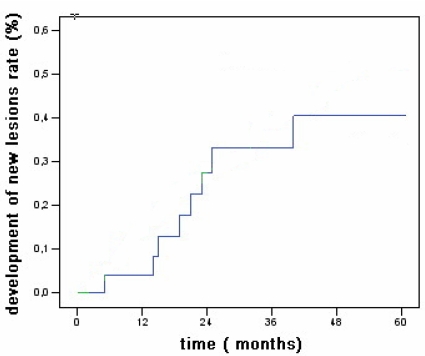
The new HCC lesions onset rates after 1, 3, and 5 years were 4%, 33%, and 41% of patients (Fig 2).
Fig 2.
Overall actuarial probability curves for new hepatocellular carcinoma associated with CLD without cirrhosis.
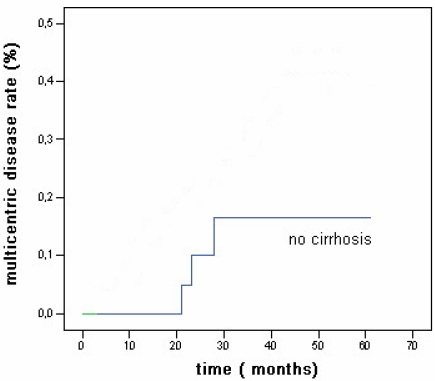
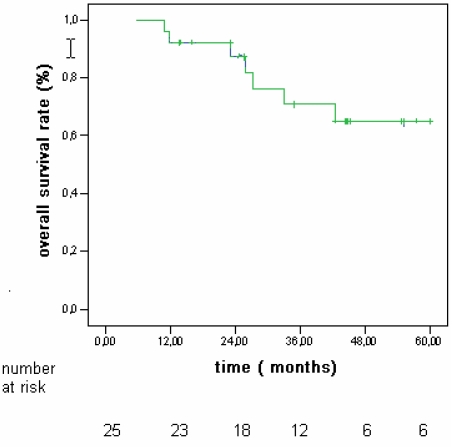
The 5 year probability to develop multicentric disease was 16% (Fig 3). Actuarial survival rates after 1, 3, and 5 years were 92%, 72%, and 64% (Fig 4).
Fig 3.
Overall actuarial probability curve for multicentric hepatocellular carcinoma after RFA in patients without cirrhosis.
Fig 4.
Overall actuarial survival rates in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) associated to CLD without cirrhosis.
During the follow-up period, 7 out of 25 patients died. Causes of death were neoplasia propagation (3 cases, one of which with bone metastasis), myocardial infarction (1 case), acute leukemia (1 case), and were unknown in the remaining 2 cases.
Only one major complication, subcutaneous tumoral seeding, was recorded: it occurs 24 months after treatment and was surgically removed.
Minor complications were in 5 cases self-limited post-RFA syndrome (fatigue, low level fever and flu-like syndrome), transient right shoulder pain in 2 cases for nodule sited in right sub-diaphragm liver's segment.
DISCUSSION
The prevalence of HCC association with CLD without cirrhosis in our study group (12.5%) is comparable with that found in a previous local case-control study 18.
Two recent Japanese reviews about HCC treatment with RFA reported a prevalence of patients with CLD without cirrhosis equal to 12% and 18% respectively 8, 19. However, they did not describe the outcome of this subgroup of patients. We can assume that also surgical reviews on this topic found analogous prevalence without reporting them.
In a recent meta-analysis evaluating RFA efficacy, factors dependent on the tumor features, such as diameter, pathology, proximity to large vessels, subcapsular location, as well as RFA electrodes and other physician dependent factors, were considered, but not pathology of the surrounding liver tissue 20,21.
It has been supposed that the cirrhotic tissue could enable a better thermal ablation through a specific mechanism known as oven effect 21, 7. Due to fibrosis and increased thickness, the cirrhotic tissue around the nodule would work as a thermal insulation, avoiding the dispersion of the heat generated around the RFA needle electrode. In the current study we found that the HCC nodules primary complete ablation rate in patients affected by CLD without cirrhosis is very high (96%) and comparable with best results reported in literature for cirrhotic patients.
As recently reported for RFA in HCC sized less than 3.5 cm, the technical efficacy (complete tumor ablation) in 1 or 2 sessions range from 76 % to 96 % of nodules, with a mean of 1.2 - 1.4 treatments 22,23 and up to 100 % with a mean of 2.2 treatments on nodular basis 24.
The 5-years survival estimated from a cohort of patients with cirrhosis and tumours below 3 cm or 3.5 cm treated by RF is 40 % and 33% respectively 25,26.
Recent evidence support percutaneous local ablation therapy for small hepatocellular carcinoma considered as effective as surgical resection 27,28.
Data recently reported indicate that RFA can be considered the treatment of choice for patients with single HCC <or= 2.0 cm, even when surgical resection is possible for patients with cirrhosis 28.
In our group survival rates after 1, 3, and 5 years were 92%, 72%, and 64% (fig 4). The incidence of adverse events of RFA shows mortality rates ranging from 0.3% to 0.5%, and morbidity rates ranging from 2.2% to 8.9% 29,30. We had no deaths and few complications without any impact on the outcome.
Local progression rates vary widely between 2% to 60% 20. Shina et al. recorded the lower local progression rate of 2% at 3 years 24 while in our study local progression occurred in 3 cases (12%) (Fig 1).
The new HCC lesions onset rates after 1, 3, and 5 years were 4%, 33%, and 41% of patients (Fig 2) less than reported for patients with cirrhosis (81% at 5 years as reported by Lencioni et al 31 and the 5 years probability to develop multicentric disease was 16 %. (Fig 3)
At the moment, no other studies of RFA therapy of HCC associated with CLD without cirrhosis are available and this is a limitation of actual guide lines. Our results would need to be confirmed using larger groups of patients and prospectively compared with patients affected by hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis.
The ideal treatment for HCC associated with non-cirrhotic CLD is resection, even in case of large tumors. However, in some cases it could not be feasible or safe, due to the nodule location or to the possible comorbidity, and it could even be burdened with an excessive mortality risk.
Our findings suggest that in cases of tumors less than 3.5 cm in diameter RFA could be a treatment of choice also for patients affected by CLD without cirrhosis not surgically resectable.
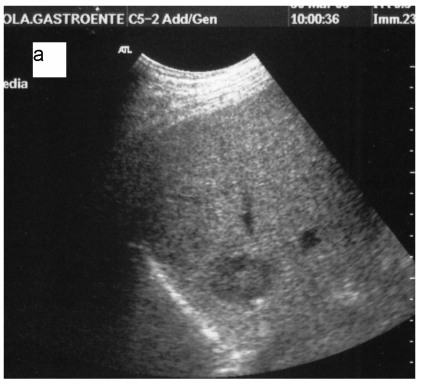
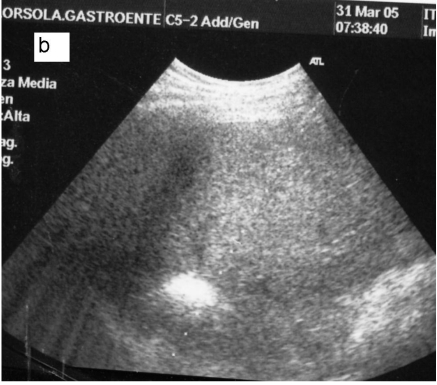
Fig 5.
a: Ipoechoic nodule of the VII liver segment in a non cirrhotic liver pattern, normal hepatic vein. b: The same nodule after RF session.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Dr Anna Caroli for her help in the English language revision of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Bruix J, Sherman M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2005;42:1208–1236. doi: 10.1002/hep.20933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bolondi L, Sofia S, Siringo S et al. Surveillance programme of cirrhotic patients for early diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a cost effectiveness analysis. Gut. 2001;48:251–259. doi: 10.1136/gut.48.2.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bolondi L. Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. Journal of Hepatology. 2003;39:1076–1084. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(03)00349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bruix J, Llovet JM. Prognostic prediction and treatment strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2002;35:519–524. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.32089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Martin H, Cosmi AB. Liver transplantation for malignancy. The Oncologist. 2005;10:269–281. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.10-4-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rossi S, Buscarini E, Garbagnati F et al. Percutaneous treatment of small hepatic tumors by an expandable RF needle electrode. AJR. 1998;170:1015–1022. doi: 10.2214/ajr.170.4.9530052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gazelle GS, Goldberg SN, Solbiati L et al. State of the Art Tumor Ablation with Radio-frequency Energy. Radiology. 2000;217:633–646. doi: 10.1148/radiology.217.3.r00dc26633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shiina S, Teratani T, Obi S et al. A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation with ethanol injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:122–130. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lin SM, Lin C-J, Lin C-C et al. Randomised controlled trial comparing percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation, percutaneous ethanol injection, and percutaneous acetic acid injection to treat hepatocellular carcinoma of 3 cm or less. Gut. 2005;4:1151–1156. doi: 10.1136/gut.2004.045203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ebara M, Okabe S, Kita K et al. Percutaneous ethanol injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma: therapeutic efficacy based on 20 years observation. J Hepatol. 2005;43:377–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.03.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sutherland LM, Williams J, Padbury R et al. Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors A systematic review. Arch Surg. 2006;141:181–190. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.141.2.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lu DSK, Yu NC, Raman SS, Lassman C et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma as a bridge to liver transplantation. Hepatology. 2005;41:1130–37. doi: 10.1002/hep.20688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Takano S, Yokosuka O, Imazeki F et al. Incidence of hepatocellular carcinomain chronic hepatitis B and C: a prospective study of 251patients. Hepatology. 1995;21:650–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Otto G. Heuschen U, Hofman WJ et al. Survival and recurrence after liver transplantation versus liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective analysis. Ann Surg. 1998;227:424–432. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199803000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Desmet VJ, Gerber M, Hoofnagle JH et al. Classification of chronic hepatitis:doagnosis,grading and staging. Hepatology. 1994;19:1513–1520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Leevy CM, Sherlock S Diseases of the Liver and Biliary Tract. Standardization of Nomenclature, Diagnostic Criteria and Prognosis. New York: Raven Press; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Salmi A, Turrini R, Lanzani G et al. Long term effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma of 3.5 cm or less. Hepatogastroenterology. 2008;55:191–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chiesa R, Donato F, Tagger A et al. Etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in Italian patients with and without cirrhosis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2000;9(2):213–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hong SN, Lee SY, Choi MS et al. Comparing the outcomes of radiofrequency ablation and surgery in patients with a single small hepatocelular carcinoma and well preserved liver function. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005;39:247–52. doi: 10.1097/01.mcg.0000152746.72149.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mulier S, Ni Y, Jamart J, Ruers T et al. Local recurrence after hepatic radiofrequency coagulation. Multivariate meta-analysis and review of contributing factors. Ann Surg. 2005;242:158–171. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000171032.99149.fe. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S et al. Small hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment with radio-frequency ablation versus ethanol injection. Radiology. 1998;210:655–661. doi: 10.1148/radiology.210.3.r99fe40655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lin SM, Lin C-J, Lin C-C et al. Randomised controlled trial comparing percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation, percutaneous ethanol injection, and percutaneous acetic acid injection to treat hepatocellular carcinoma of 3 cm or less. Gut. 2005;54:1151–1156. doi: 10.1136/gut.2004.045203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Llovet JM, Vilana R, Bru´ C et al. Increased risk of tumor seeding after radiofrequency thermal ablation for single hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2001;33:1124–1129. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.24233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shiina S, Teratani T, Obi S, et al Sato S, Tateishi R, Fujishima T. A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation with ethanol injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:122–130. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rossi S, Di Stasi M, Buscarini E et al. Percutaneous RF interstitial thermal ablation in the treatment of hepatic cancer. Am J Roentgenol. 1996;167:759–68. doi: 10.2214/ajr.167.3.8751696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Buscarini L, Buscarini E, Di Stasi M et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of small hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results. Eur Radiol. 2001;11:914–921. doi: 10.1007/s003300000659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kaido T, Uemoto S. Recent evidence in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 2008;55(85):1460–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Guglielmi A, Ruzzenante A, Valdegamberi A et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008;12(1):192–8. doi: 10.1007/s11605-007-0392-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Livraghi T, Solbiati L, Meloni MF et al. Treatment of focal liver tumors with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation: complications encountered in a multicenter study. Radiology. 2003;226:441–2008. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2262012198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mulier S, Mulier P, Ni Y et al. Complications of radiofrequency coagulation of liver tumors. Br J Surg. 2002;89:1206–1222. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2168.2002.02168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lencioni R, Cioni D, Crocetti L et al. Early stage hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: long term results of percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation. Radiology. 2005;234:961–967. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2343040350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]