Abstract
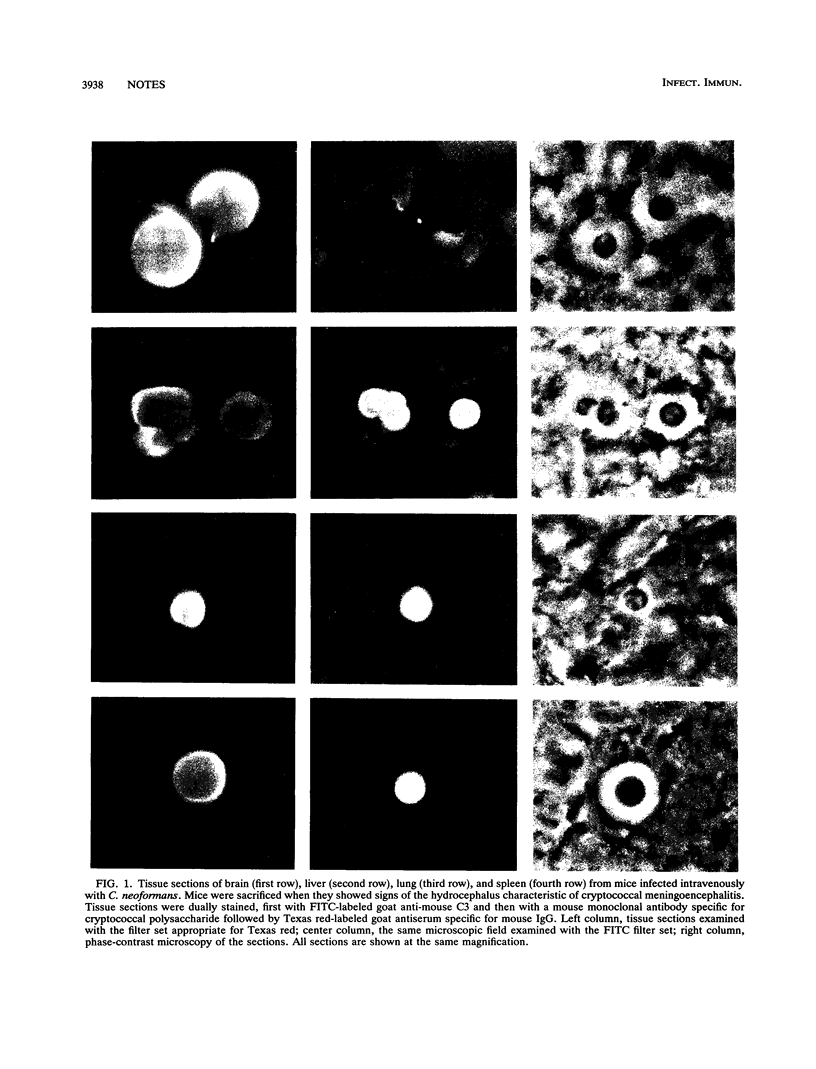
Tissues from mice infected with Cryptococcus neoformans were examined by immunofluorescence to determine the extent of deposition of complement component C3 on encapsulated cryptococci. The relative percentages of cryptococci in each tissue having readily visible C3 were greatest for liver and lung tissues, with the kidney tissue having the next highest percentage and the spleen having the lowest percentage. Binding of C3 fragments to cryptococci in brain tissue was essentially absent.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Diamond R. D., May J. E., Kane M. A., Frank M. M., Bennett J. E. The role of the classical and alternate complement pathways in host defenses against Cryptococcus neoformans infection. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2260–2270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujardin B. C., Driedijk P. C., Roijers A. F., Out T. A. The determination of the complement components C1q, C4 and C3 in serum and cerebrospinal fluid by radioimmunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Jun 25;80(2):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadebusch H. H., Johnson A. G. Natural host resistance to infection with Cryptococcus neoformans. IV. The effect of some cationic proteins on the experimental disease. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):551–565. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B., Warren J. Immunofluorescence studies of reactions at the Cryptococcal capsule. J Infect Dis. 1968 Apr;118(2):215–229. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Pfrommer G. S., Guerlain A. S., Highison B. A., Highison G. J. Strain variation in phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans: dissociation of susceptibility to phagocytosis from activation and binding of opsonic fragments of C3. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2794–2800. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2794-2800.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Wilson M. A., Murphy J. W. Early events in initiation of alternative complement pathway activation by the capsule of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3101–3110. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3101-3110.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macher A. M., Bennett J. E., Gadek J. E., Frank M. M. Complement depletion in cryptococcal sepsis. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1686–1690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. C. Contribution of complement component C5 to the pathogenesis of experimental murine cryptococcosis. Sabouraudia. 1985 Jun;23(3):225–234. doi: 10.1080/00362178585380331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiropulu C., Eppard R. A., Otteson E., Kozel T. R. Antigenic variation within serotypes of Cryptococcus neoformans detected by monoclonal antibodies specific for the capsular polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3240–3242. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3240-3242.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. A., Kozel T. R. Contribution of antibody in normal human serum to early deposition of C3 onto encapsulated and nonencapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):754–761. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.754-761.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]