Abstract
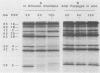
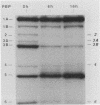
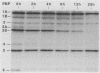
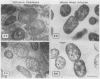
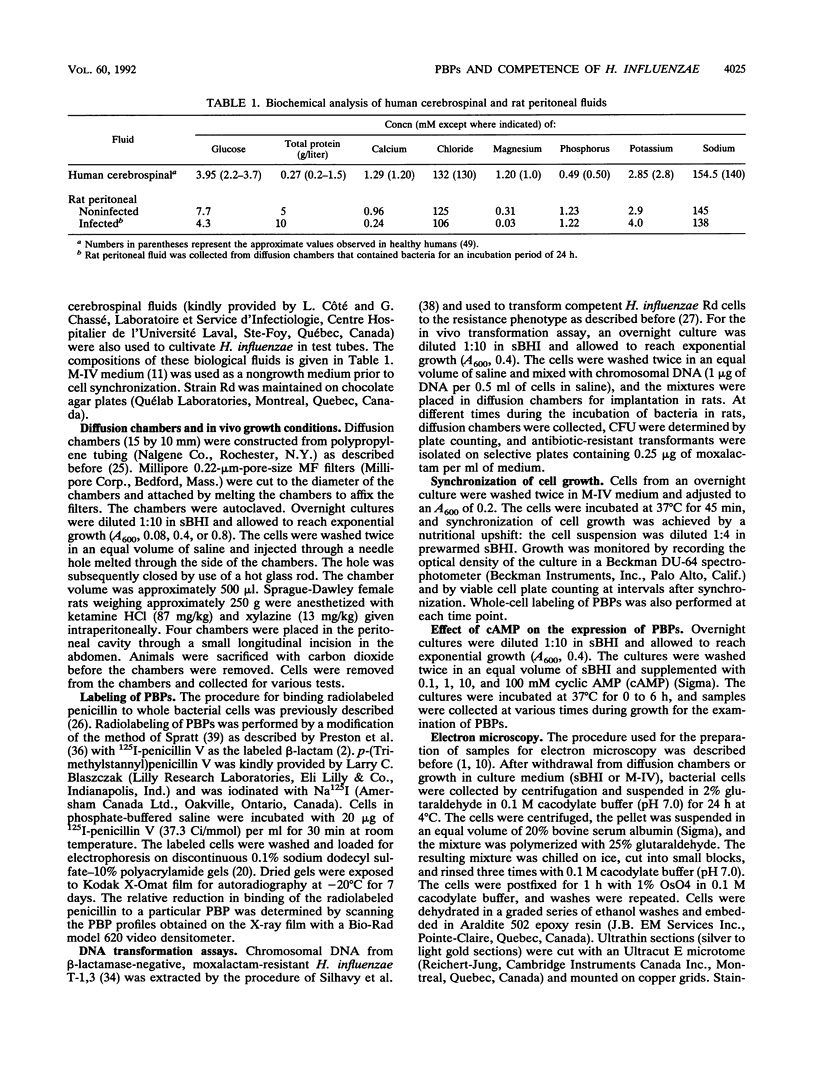
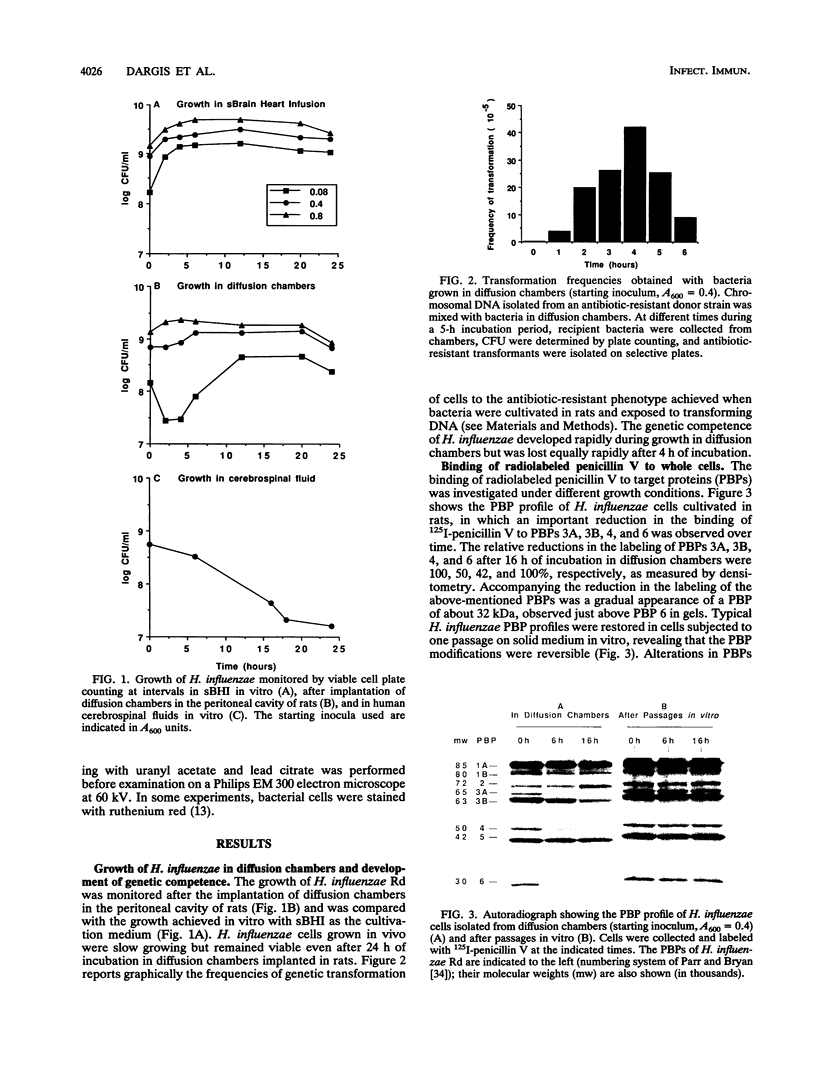
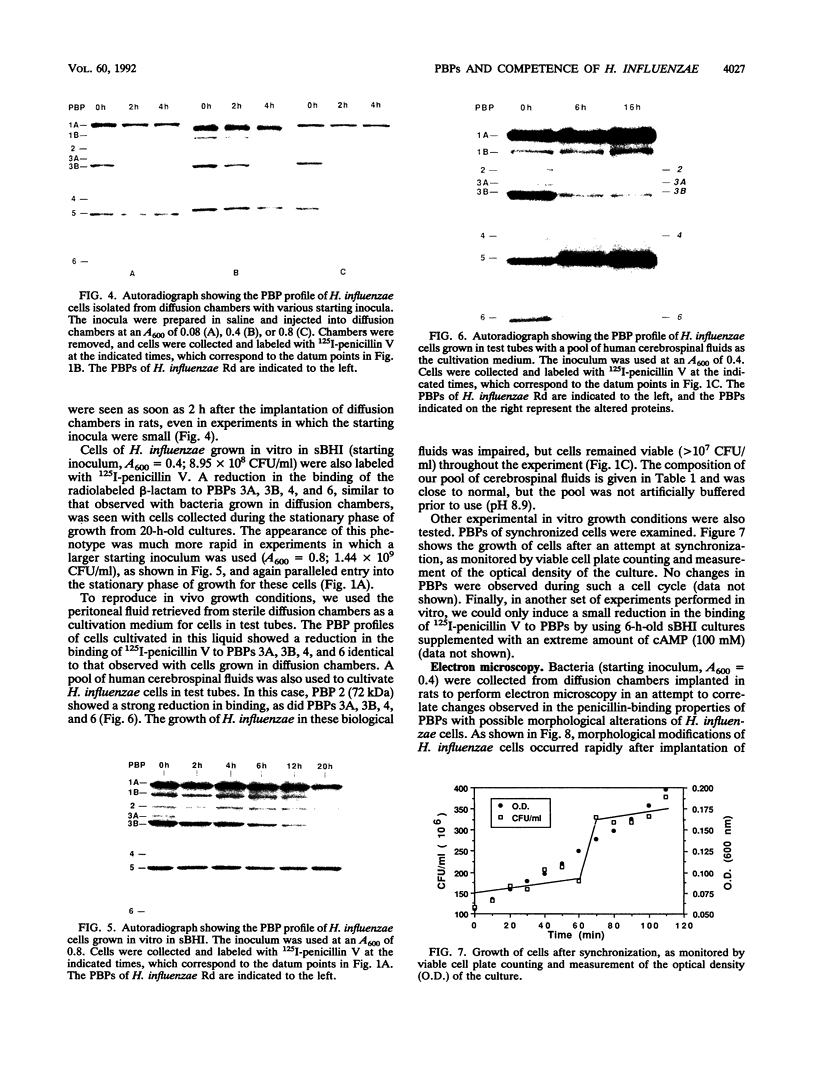
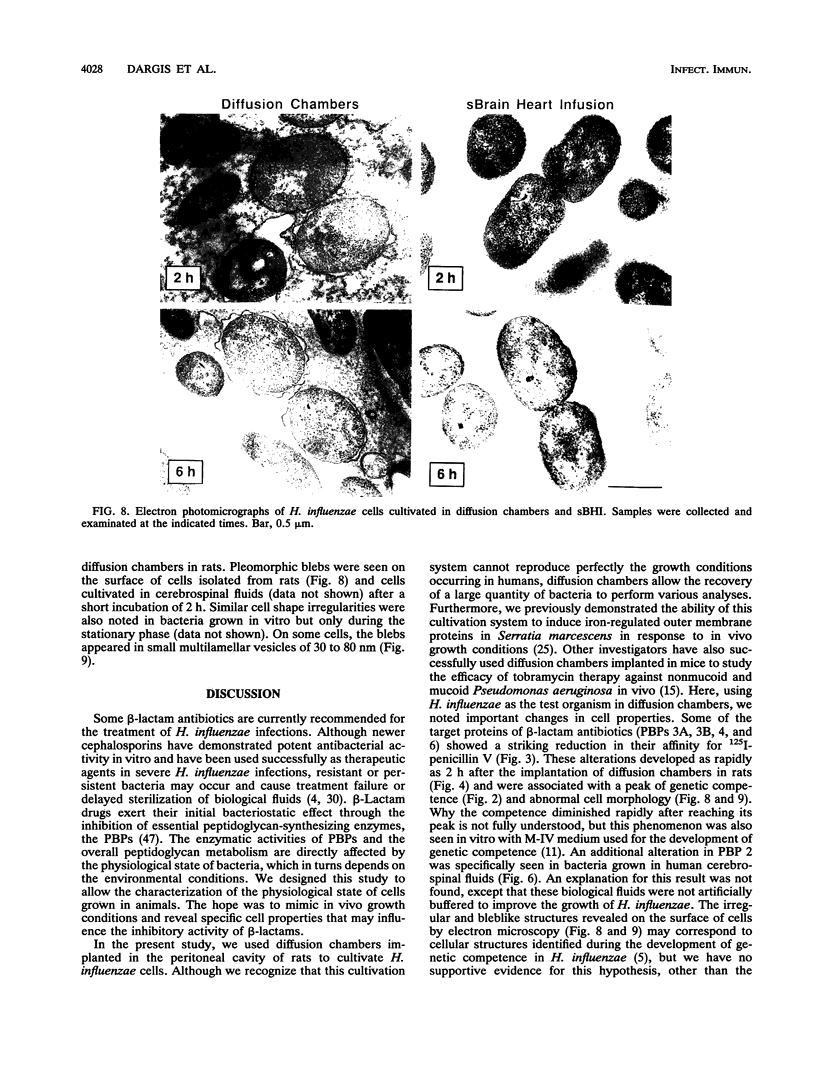
By using whole-cell labeling assay with 125I-penicillin V, we observed a reduction in the binding of the radiolabeled beta-lactam to four or five penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) in Haemophilus influenzae cells cultivated under specific conditions. PBPs 3A, 3B, 4, and 6 were altered after the growth of bacteria in diffusion chambers implanted in the peritoneal cavity of rats. PBP 2 was also modified when cells were cultivated in human cerebrospinal fluids. Because this observation may have important consequences on the efficacy of beta-lactams during antibiotic therapy, we characterized the physiological state of bacteria cultivated in animals in the hope of explaining how such important changes in cell properties develop in vivo. Since the development of natural genetic competence occurs at the stationary phase of growth in H. influenzae, we used a DNA transformation assay to evaluate the physiological state of bacteria grown in diffusion chambers implanted in rats. Chromosomal DNA isolated from an antibiotic-resistant donor strain was mixed with bacteria in diffusion chambers. At different times during a 5-h incubation period, recipient bacteria were collected from the chambers, CFU were determined by plate counting, and antibiotic-resistant transformants were isolated on selective plates. Genetic competence rapidly developed in cells grown in rats, and the frequency of transformation by test DNA was elevated. Electron microscopy revealed an irregular cell shape and blebs at the surface of bacteria cultivated in animals and in cerebrospinal fluids. In an attempt to induce a similar physiological state in vitro, we supplemented broth cultures with cyclic AMP or synchronized cultures by a nutritional upshift. No changes in PBPs were observed with supplemental cyclic AMP or during a single cell cycle. Finally, a reduction in the affinity of PBPs for 125I-penicillin V identical to that observed in bacteria grown in rats was observed in cells isolated from the stationary phase of growth in vitro. These results clearly indicate that H. influenzae cells grown in animals undergo a rapid change to a physiological state similar to that found in late-stationary-phase cultures in vitro. This observation indicates that the rational design of future and improved antibiotic therapy of H. influenzae infections should consider cell properties of slow-growing or latent bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beauchamp D., Pellerin M., Gourde P., Pettigrew M., Bergeron M. G. Effects of daptomycin and vancomycin on tobramycin nephrotoxicity in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):139–147. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clairoux N., Picard M., Brochu A., Rousseau N., Gourde P., Beauchamp D., Parr T. R., Jr, Bergeron M. G., Malouin F. Molecular basis of the non-beta-lactamase-mediated resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in strains of Haemophilus influenzae isolated in Canada. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jul;36(7):1504–1513. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.7.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Pokowski L. H. Delayed cerebrospinal fluid sterilization, in vitro bactericidal activities, and side effects of selected beta-lactams. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1990;73:31–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deich R. A., Hoyer L. C. Generation and release of DNA-binding vesicles by Haemophilus influenzae during induction and loss of competence. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):855–864. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.855-864.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doern G. V., Jorgensen J. H., Thornsberry C., Preston D. A., Tubert T., Redding J. S., Maher L. A. National collaborative study of the prevalence of antimicrobial resistance among clinical isolates of Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Feb;32(2):180–185. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.2.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorward D. W., Garon C. F., Judd R. C. Export and intercellular transfer of DNA via membrane blebs of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2499–2505. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2499-2505.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García del Portillo F., de Pedro M. A., Joseleau-Petit D., D'Ari R. Lytic response of Escherichia coli cells to inhibitors of penicillin-binding proteins 1a and 1b as a timed event related to cell division. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4217–4221. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4217-4221.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell W., Tomasz A. Alteration of Escherichia coli murein during amino acid starvation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1009–1016. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1009-1016.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herriott R. M., Meyer E. M., Vogt M. Defined nongrowth media for stage II development of competence in Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):517–524. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.517-524.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques M., Gottschalk M., Foiry B., Higgins R. Ultrastructural study of surface components of Streptococcus suis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):2833–2838. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.2833-2838.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Doern G. V., Maher L. A., Howell A. W., Redding J. S. Antimicrobial resistance among respiratory isolates of Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Streptococcus pneumoniae in the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2075–2080. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly N. M., Rawling E. G., Hancock R. E. Determinants of the efficacy of tobramycin therapy against isogenic nonmucoid and mucoid derivatives of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 growing in peritoneal chambers in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1207–1211. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Prakash N., Agarwal K. N. Cyclic AMP control of the envelope growth in Escherichia coli: envelope morphology of the mutants in cya and crp genes. Indian J Exp Biol. 1979 Apr;17(4):325–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S. Properties of adenyl cyclase and cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate receptor protein-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):545–555. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.545-555.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusser W., Ishiguro E. E. Lysis of nongrowing Escherichia coli by combinations of beta-lactam antibiotics and inhibitors of ribosome function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):451–455. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorian V. In vitro simulation of in vivo conditions: physical state of the culture medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2403–2406. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2403-2406.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maidhof H., Johannsen L., Labischinski H., Giesbrecht P. Onset of penicillin-induced bacteriolysis in staphylococci is cell cycle dependent. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2252–2257. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2252-2257.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malouin F., Bryan L. E. Haemophilus influenzae penicillin-binding proteins 1a and 3 possess distinct and opposite temperature-modulated penicillin-binding activities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):498–502. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malouin F., Bryan L. E. Modification of penicillin-binding proteins as mechanisms of beta-lactam resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malouin F., Campbell G. D., Halpenny M., Becker G. W., Parr T. R., Jr Outer membrane and porin characteristics of Serratia marcescens grown in vitro and in rat intraperitoneal diffusion chambers. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1247–1253. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1247-1253.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malouin F., Parr T. R., Jr, Bryan L. E. Identification of a group of Haemophilus influenzae penicillin-binding proteins that may have complementary physiological roles. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):363–365. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malouin F., Schryvers A. B., Bryan L. E. Cloning and expression of genes responsible for altered penicillin-binding proteins 3a and 3b in Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):286–291. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelman P. M., Chaffin D. O., Krilov L. R., Kalaitzoglou G., Serfass D. A., Onay O., Wiley E. A., Overturf G. D., Rubin L. G. Cefuroxime treatment failure of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae meningitis associated with alteration of penicillin-binding proteins. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1118–1123. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelman P. M., Chaffin D. O., Stull T. L., Rubens C. E., Mack K. D., Smith A. L. Characterization of non-beta-lactamase-mediated ampicillin resistance in Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):235–244. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: a review of clinical aspects, surface antigens, and the human immune response to infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parr T. R., Jr, Bryan L. E. Mechanism of resistance of an ampicillin-resistant, beta-lactamase-negative clinical isolate of Haemophilus influenzae type b to beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jun;25(6):747–753. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.6.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. K., Young K. D. Lysis of Escherichia coli by beta-lactams which bind penicillin-binding proteins 1a and 1b: inhibition by heat shock proteins. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4021–4026. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4021-4026.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston D. A., Wu C. Y., Blaszczak L. C., Seitz D. E., Halligan N. G. Biological characterization of a new radioactive labeling reagent for bacterial penicillin-binding proteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 May;34(5):718–721. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.5.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serfass D. A., Mendelman P. M., Chaffin D. O., Needham C. A. Ampicillin resistance and penicillin-binding proteins of Haemophilus influenzae. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Oct;132(10):2855–2861. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-10-2855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. J., Carlson C. A. The biology of natural transformation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:211–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Cozens R. Changes in peptidoglycan composition and penicillin-binding proteins in slowly growing Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5308–5310. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5308-5310.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Durack D. T., Tomasz A. Antibiotic tolerance among clinical isolates of bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Oct;30(4):521–527. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.4.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Markiewicz Z., Tomasz A. Autolysis-resistant peptidoglycan of anomalous composition in amino-acid-starved Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1373-1376.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E. Phenotypic tolerance: the search for beta-lactam antibiotics that kill nongrowing bacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jul-Aug;8 (Suppl 3):S279–S291. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.supplement_3.s279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsumi R., Nakamoto Y., Kawamukai M., Himeno M., Komano T. Involvement of cyclic AMP and its receptor protein in filamentation of an Escherichia coli fic mutant. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):807–812. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.807-812.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsumi R., Tanabe H., Nakamoto Y., Kawamukai M., Sakai H., Himeno M., Komano T., Hirota Y. Inhibitory effect of adenosine 3',5'-phosphate on cell division of Escherichia coli K-12 mutant derivatives. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):1105–1109. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.1105-1109.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Penicillin-binding proteins and the mechanism of action of beta-lactam antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:825–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.004141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise E. M., Jr, Alexander S. P., Powers M. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate as a regulator of bacterial transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):471–474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhanel G. G., Karlowsky J. A., Davidson R. J., Hoban D. J. Effect of pooled human cerebrospinal fluid on the postantibiotic effects of cefotaxime, ciprofloxacin, and gentamicin against Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 May;36(5):1136–1139. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.5.1136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]