Abstract
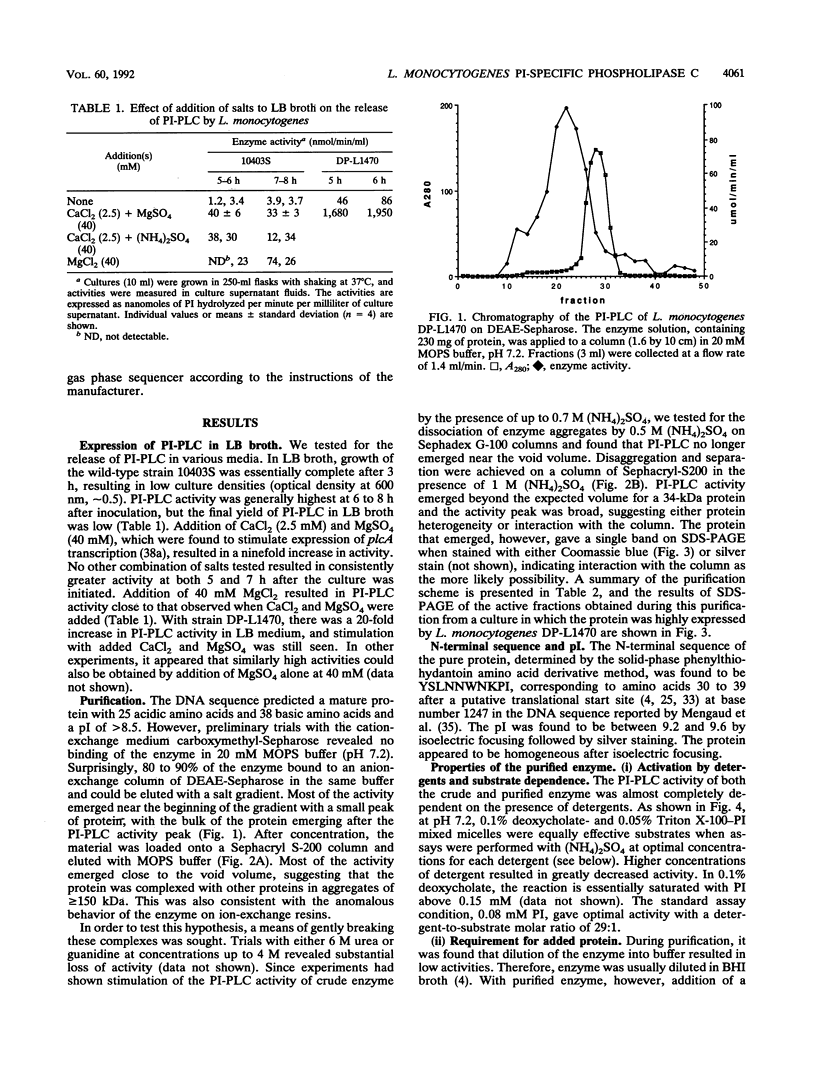
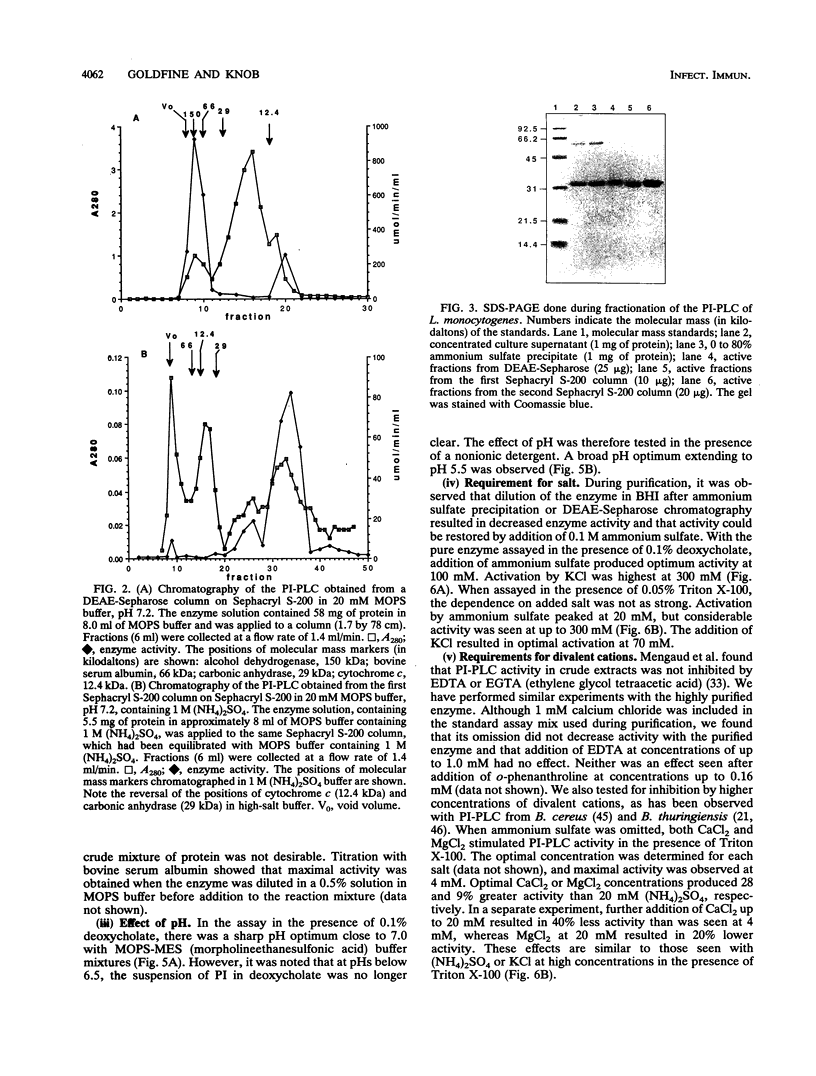
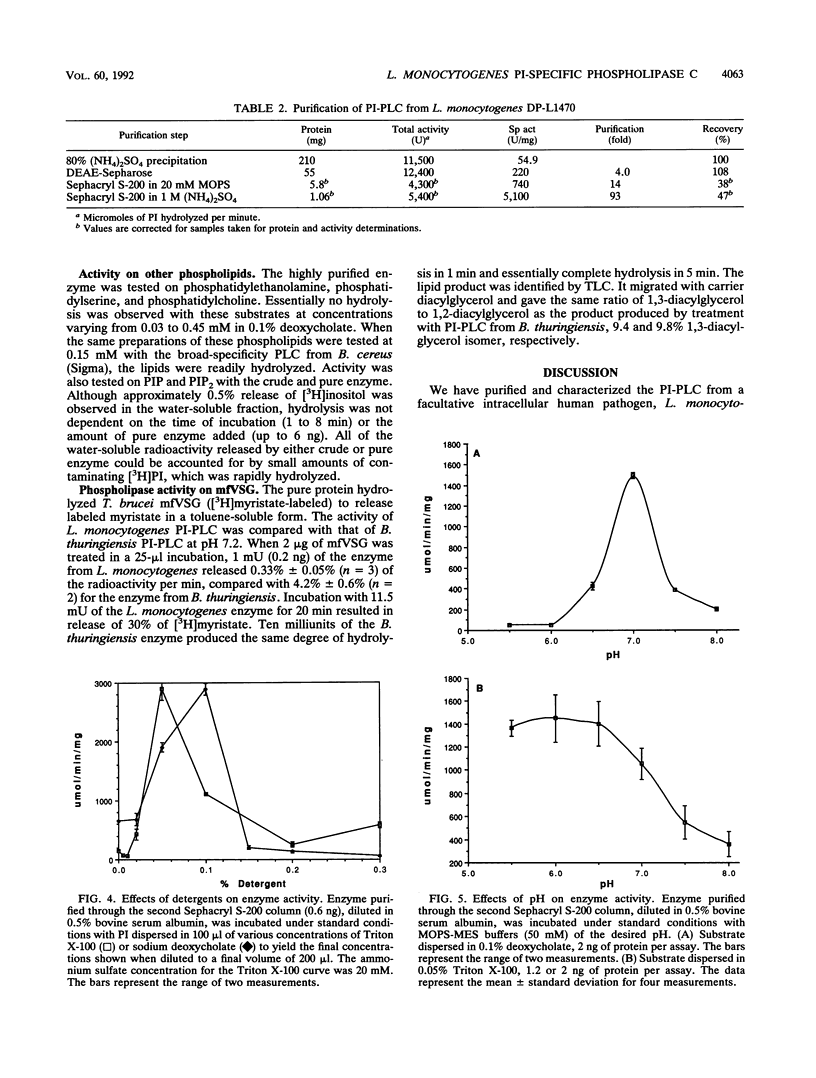
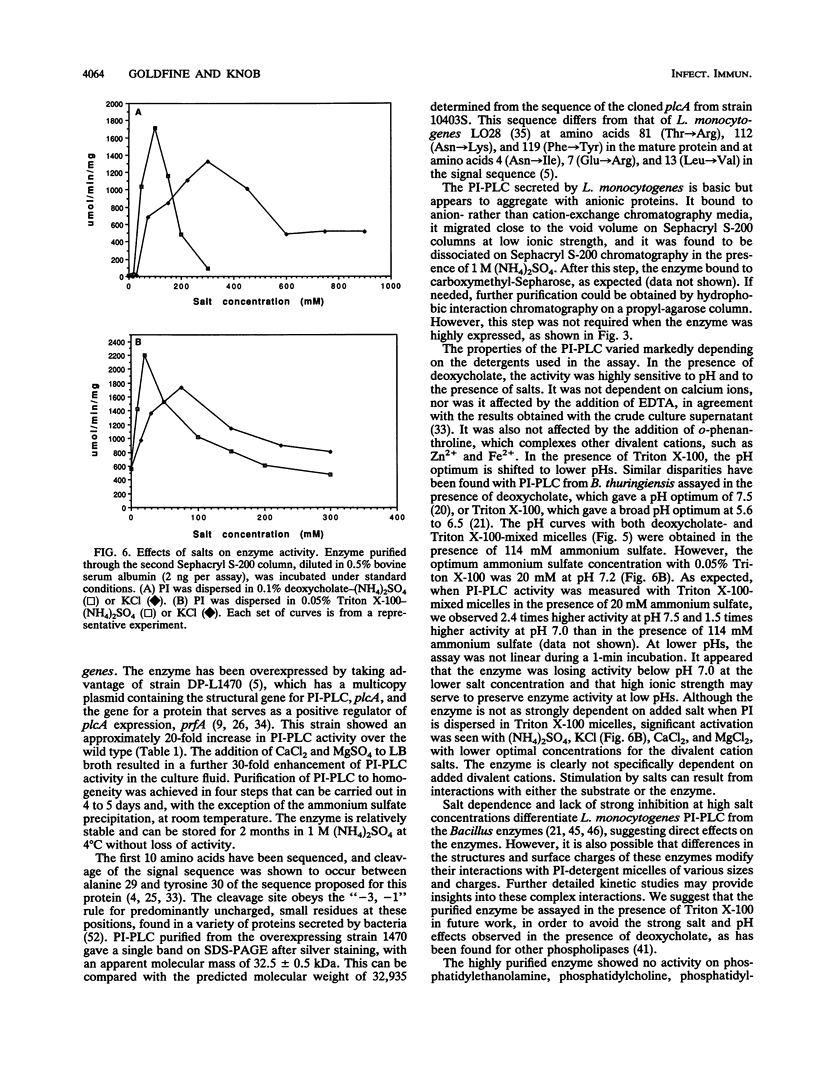
We have purified to homogeneity the 33-kDa phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) from the culture fluid of Listeria monocytogenes, a facultative intracellular pathogen. The protein was overexpressed, and secretion of PI-PLC was further enhanced by the addition of divalent cations to the culture medium. The basic protein (pI, approximately 9.4) was complexed with anionic proteins in the crude culture fluid. It bound to DEAE-Sepharose and was eluted from Sephacryl S-200 near the void volume in low-ionic-strength buffer, suggesting aggregates of greater than or equal to 150 kDa. Gel filtration chromatography on Sephacryl S-200 in the presence of 1 M ammonium sulfate resulted in disaggregation and complete separation of PI-PLC, which interacted with the column matrix. Amino-terminal sequencing of the pure protein gave results consistent with the previously deduced sequence and showed that the signal cleavage site was between alanine 29 and tyrosine 30. The enzyme was specific for PI and showed no activity with phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylcholine, or phosphatidylserine. It did not cleave PI-4-phosphate or PI-4,5-bisphosphate, but it was active on the membrane form of the variable surface glycoprotein from Trypanosoma brucei, a PI-glycan-anchored protein. When assayed with deoxycholate-mixed micelles of PI, activity was highly dependent on added salt. Activation by salt was also observed with Triton X-100-mixed micelles. The optimal concentration of CaCl2 or MgCl2 was lower than that of KCl or (NH4)2SO4, but activity was not specifically dependent on divalent cations and was not inhibited by addition of EDTA. With deoxycholate, the optimum pH was 7.0. A broader pH optimum ranging from 5.5 to 6.5 was observed with Triton X-100-mixed micelles. These results are consistent with a postulated role for secreted PI-PLC in the acidified primary phagocytic vesicle of infected cells.
Full text
PDF




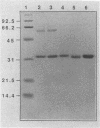
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barclay R., Threlfall D. R., Leighton I. Haemolysins and extracellular enzymes of Listeria monocytogenes and L. ivanovii. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Oct;30(2):111–118. doi: 10.1099/00222615-30-2-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bütikofer P., Lin Z. W., Chiu D. T., Lubin B., Kuypers F. A. Transbilayer distribution and mobility of phosphatidylinositol in human red blood cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16035–16038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilli A., Goldfine H., Portnoy D. A. Listeria monocytogenes mutants lacking phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C are avirulent. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):751–754. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabiri G. A., Sanger J. M., Portnoy D. A., Southwick F. S. Listeria monocytogenes moves rapidly through the host-cell cytoplasm by inducing directional actin assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6068–6072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M., Peterkin P. I. Listeria monocytogenes, a food-borne pathogen. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):476–511. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.476-511.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Low M. G., Cross G. A. Glycosyl-sn-1,2-dimyristylphosphatidylinositol is covalently linked to Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14547–14555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitag N. E., Youngman P., Portnoy D. A. Transcriptional activation of the Listeria monocytogenes hemolysin gene in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1293–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1293-1298.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Frehel C., Gouin E., Cossart P. Entry of L. monocytogenes into cells is mediated by internalin, a repeat protein reminiscent of surface antigens from gram-positive cocci. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1127–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90009-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascard P., Tran D., Sauvage M., Sulpice J. C., Fukami K., Takenawa T., Claret M., Giraud F. Asymmetric distribution of phosphoinositides and phosphatidic acid in the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Oct 14;1069(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90100-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy C., Gaillard J. L., Alouf J. E., Berche P. Purification, characterization, and toxicity of the sulfhydryl-activated hemolysin listeriolysin O from Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1641–1646. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1641-1646.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy C., Raveneau J., Beretti J. L., Lecroisey A., Vazquez-Boland J. A., Alouf J. E., Berche P. Purification and characterization of an extracellular 29-kilodalton phospholipase C from Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2382–2388. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2382-2388.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. H., Volwerk J. J., Kuppe A. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipases C from Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis. Methods Enzymol. 1991;197:493–502. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)97175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner D. J., Yang M., Chen E., Hellmiss R., Rodriguez H., Low M. G. Sequence of the Bacillus thuringiensis phosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase C. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10383–10383. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereld D., Krakow J. L., Bangs J. D., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. A phospholipase C from Trypanosoma brucei which selectively cleaves the glycolipid on the variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13813–13819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. A., Hitchin B. W., Low M. G. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Bacillus thuringiensis as a probe for the distribution of phosphatidylinositol in hepatocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1989 May 1;259(3):913–916. doi: 10.1042/bj2590913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikezawa H. Bacterial PIPLCs-unique properties and usefulness in studies on GPI anchors. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1991 Nov;15(11):1115–1131. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(91)90059-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupke T., Lechner M., Kaim G., Götz F. Improved purification and biochemical properties of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from Bacillus thuringiensis. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Oct 20;185(1):151–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppe A., Evans L. M., McMillen D. A., Griffith O. H. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Bacillus cereus: cloning, sequencing, and relationship to other phospholipases. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6077–6083. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6077-6083.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner M., Kupke T., Stefanovic S., Götz F. Molecular characterization and sequence of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Bacillus thuringiensis. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):621–626. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Domann E., Chakraborty T. Detection of a gene encoding a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C that is co-ordinately expressed with listeriolysin in Listeria monocytogenes. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):361–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Haffner C., Domann E., Goebel W., Chakraborty T. Identification of a gene that positively regulates expression of listeriolysin, the major virulence factor of listeria monocytogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8336–8340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from Staphylococcus aureus. Methods Enzymol. 1981;71(Pt 100):741–746. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)71087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Saltiel A. R. Structural and functional roles of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol in membranes. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3276003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. The glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor of membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 6;988(3):427–454. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Braun-Breton C., Cossart P. Identification of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity in Listeria monocytogenes: a novel type of virulence factor? Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Dramsi S., Gouin E., Vazquez-Boland J. A., Milon G., Cossart P. Pleiotropic control of Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors by a gene that is autoregulated. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2273–2283. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Vicente M. F., Cossart P. Transcriptional mapping and nucleotide sequence of the Listeria monocytogenes hlyA region reveal structural features that may be involved in regulation. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3695–3701. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3695-3701.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier J., Ryter A., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular and cell-to-cell spread of Listeria monocytogenes involves interaction with F-actin in the enterocytelike cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1048–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1048-1058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The relative importance of blood monocytes and fixed macrophages to the expression of cell-mediated immunity to infection. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):521–534. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S. H., Dufrenne J., Leimeister-Wächter M., Domann E., Chakraborty T. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity as a marker to distinguish between pathogenic and nonpathogenic Listeria species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Sep;57(9):2666–2670. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.9.2666-2670.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Chakraborty T., Goebel W., Cossart P. Molecular determinants of Listeria monocytogenes pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1263–1267. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1263-1267.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds L. J., Washburn W. N., Deems R. A., Dennis E. A. Assay strategies and methods for phospholipases. Methods Enzymol. 1991;197:3–23. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)97129-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross T. S., Whiteley B., Graham R. A., Majerus P. W. Cyclic hydrolase-transfected 3T3 cells have low levels of inositol 1,2-cyclic phosphate and reach confluence at low density. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9086–9092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun A. N., Camilli A., Portnoy D. A. Isolation of Listeria monocytogenes small-plaque mutants defective for intracellular growth and cell-to-cell spread. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3770–3778. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3770-3778.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundler R., Alberts A. W., Vagelos P. R. Enzymatic properties of phosphatidylinositol inositolphosphohydrolase from Bacillus cereus. Substrate dilution in detergent-phospholipid micelles and bilayer vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4175–4179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi R., Asahi Y., Ikezawa H. Purification and properties of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Bacillus thuringiensis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 14;619(1):48–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi R., Ikezawa H. Phosphatidyl inositol-specific phospholipase C from Clostridium novyi type A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Feb;186(1):196–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90480-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rooijen L. A., Seguin E. B., Agranoff B. W. Phosphodiesteratic breakdown of endogenous polyphosphoinositides in nerve ending membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 May 16;112(3):919–926. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91705-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Boland J. A., Kocks C., Dramsi S., Ohayon H., Geoffroy C., Mengaud J., Cossart P. Nucleotide sequence of the lecithinase operon of Listeria monocytogenes and possible role of lecithinase in cell-to-cell spread. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):219–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.219-230.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volwerk J. J., Wetherwax P. B., Evans L. M., Kuppe A., Griffith O. H. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus: improved purification, amino acid composition, and amino-terminal sequence. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Mar;39(3):315–325. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth R., An F. Y., Clewell D. B. Highly efficient protoplast transformation system for Streptococcus faecalis and a new Escherichia coli-S. faecalis shuttle vector. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):831–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.831-836.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]