Abstract
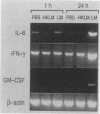
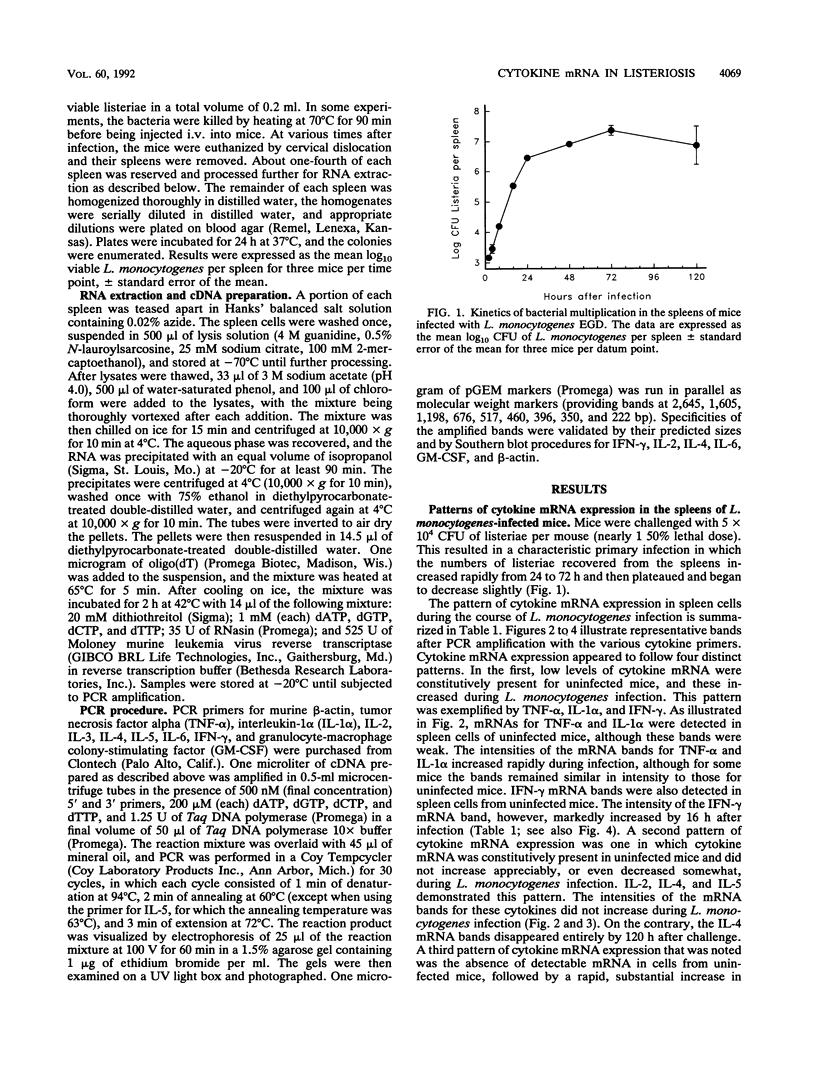
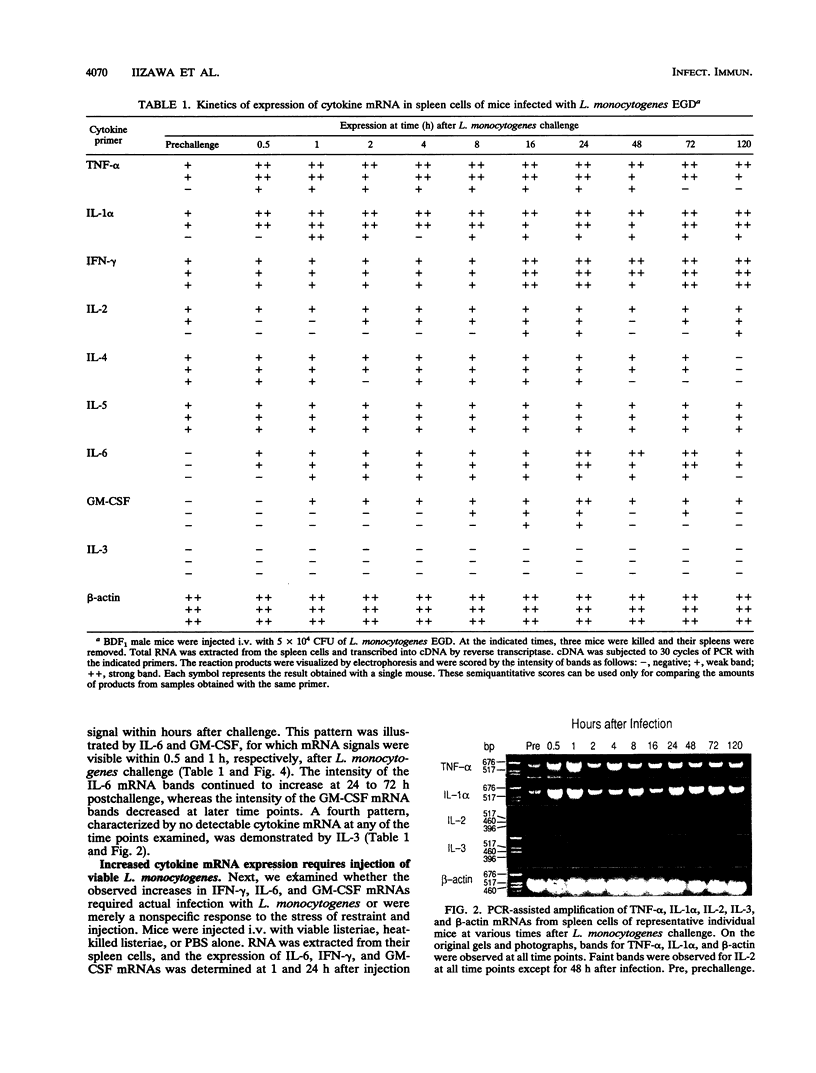
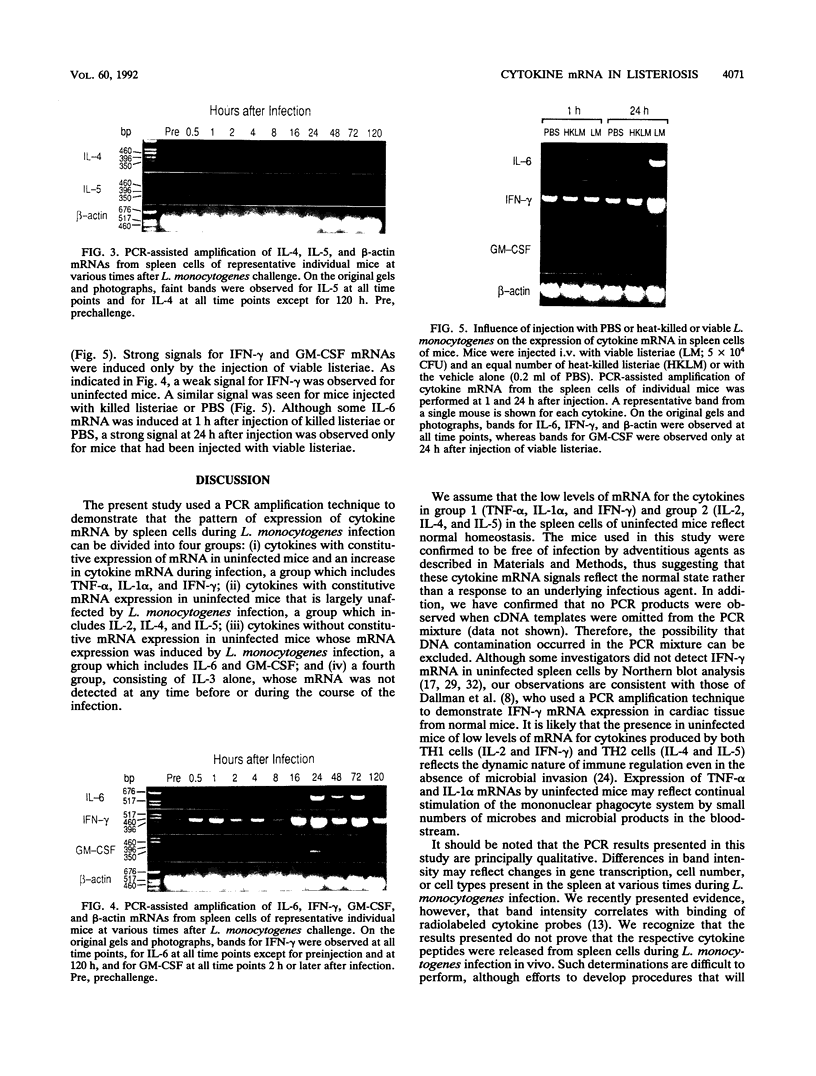
Protective immunity first becomes evident at 3 to 4 days after inoculation of mice with a sublethal dose of Listeria monocytogenes. Recent evidence suggests that production of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) occurs earlier (within the first 24 h of infection). The purpose of this study was to define better the sequence of cytokine mRNA expression during the early stages of L. monocytogenes infection. Cytokine mRNA expression was detected by polymerase chain reaction-assisted amplification of RNA extracted from the spleen cells of individual mice euthanized at 0.5 to 120 h after L. monocytogenes challenge. By using this method, mRNAs for tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1 alpha), IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, and IFN-gamma were detected in RNA from the spleen cells of uninfected mice. The intensity of the bands for IFN-gamma, however, was increased greatly at 16 h after intravenous injection of 5 x 10(4) CFU (nearly 1 50% lethal dose) of L. monocytogenes. IL-6 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor mRNAs were not detected in spleen cell RNA from uninfected mice but were induced within 30 and 60 min, respectively, after inoculation with L. monocytogenes. Increased amounts of mRNAs for IFN-gamma, IL-6, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor were detected after injection of viable, but not killed, L. monocytogenes. IL-3 mRNA was not detected at any time in RNA extracted from the spleen cells of uninfected or L. monocytogenes infected mice. These results suggest that infection with L. monocytogenes elicits a detectable cytokine mRNA response within the first few hours of infection.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson S. L., Gallin J. I. IL-4 inhibits superoxide production by human mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):625–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bello-Fernandez C., Oblakowski P., Meager A., Duncombe A. S., Rill D. M., Hoffbrand A. V., Brenner M. K. IL-4 acts as a homeostatic regulator of IL-2-induced TNF and IFN-gamma. Immunology. 1991 Feb;72(2):161–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Schreiber R. D. Requirement of endogenous interferon-gamma production for resolution of Listeria monocytogenes infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7404–7408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Haigh A. M., Kelso A., Metcalf D., Stanley E. R., Young A. M. Production of colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) during infection: separate determinations of macrophage-, granulocyte-, granulocyte-macrophage-, and multi-CSFs. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):247–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.247-251.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Brown J. F., Young K. M., Cooley A. J. Administration of purified anti-L3T4 monoclonal antibody impairs the resistance of mice to Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):100–109. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.100-109.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Brown J. F., Young K. M., Cooley A. J., Kurtz R. S. Effects of murine recombinant interleukin 1 alpha on the host response to bacterial infection. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):962–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Henson P. M., Campbell P. A. Killing of Listeria monocytogenes by inflammatory neutrophils and mononuclear phagocytes from immune and nonimmune mice. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Feb;35(2):193–208. doi: 10.1002/jlb.35.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallman M. J., Larsen C. P., Morris P. J. Cytokine gene transcription in vascularised organ grafts: analysis using semiquantitative polymerase chain reaction. J Exp Med. 1991 Aug 1;174(2):493–496. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers S., Smith K. A. Differentiation of T cell lymphokine gene expression: the in vitro acquisition of T cell memory. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):25–36. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlich H. A., Gelfand D., Sninsky J. J. Recent advances in the polymerase chain reaction. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1643–1651. doi: 10.1126/science.2047872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman G. M., Finbloom D. S. Induction and regulation of IL-4 receptor expression on murine macrophage cell lines and bone marrow-derived macrophages by IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 1;145(3):854–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gayá A., de la Calle O., Yagüe J., Alsinet E., Fernández M. D., Romero M., Fabregat V., Martorell J., Vives J. IL-4 inhibits IL-2 synthesis and IL-2-induced up-regulation of IL-2R alpha but not IL-2R beta chain in CD4+ human T cells. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4209–4214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haak-Frendscho M., Brown J. F., Iizawa Y., Wagner R. D., Czuprynski C. J. Administration of anti-IL-4 monoclonal antibody 11B11 increases the resistance of mice to Listeria monocytogenes infection. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):3978–3985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. H., Vitti G. F., Burgess D. R., Whitty G. A., Piccoli D. S., Hamilton J. A. Potential antiinflammatory effects of interleukin 4: suppression of human monocyte tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1, and prostaglandin E2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3803–3807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Production of tumor necrosis factor during murine listeriosis. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4225–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Sehgal P. B. Tumor necrosis factor-independent IL-6 production during murine listeriosis. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):756–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P., Sadick M. D., Holaday B. J., Coffman R. L., Locksley R. M. Reciprocal expression of interferon gamma or interleukin 4 during the resolution or progression of murine leishmaniasis. Evidence for expansion of distinct helper T cell subsets. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):59–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P., Sadick M. D., Mutha S. S., Locksley R. M. Production of interferon gamma, interleukin 2, interleukin 4, and interleukin 10 by CD4+ lymphocytes in vivo during healing and progressive murine leishmaniasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7011–7015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G. S., Conary J. T., Summar M., McCurley T. L., Colley D. G. In vivo molecular analysis of lymphokines involved in the murine immune response during Schistosoma mansoni infection. I. IL-4 mRNA, not IL-2 mRNA, is abundant in the granulomatous livers, mesenteric lymph nodes, and spleens of infected mice. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):992–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratz S. S., Kurlander R. J. Characterization of the pattern of inflammatory cell influx and cytokine production during the murine host response to Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):598–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane F. C., Unanue E. R. Requirement of thymus (T) lymphocytes for resistance to listeriosis. J Exp Med. 1972 May 1;135(5):1104–1112. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.5.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehn M., Weiser W. Y., Engelhorn S., Gillis S., Remold H. G. IL-4 inhibits H2O2 production and antileishmanial capacity of human cultured monocytes mediated by IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):3020–3024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kohanawa M., Chen Y., Sato H., Moriyama M., Tsuruoka N. Interactions between endogenous gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor in host resistance against primary and secondary Listeria monocytogenes infections. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3331–3337. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3331-3337.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Numata A., Asano M., Kohanawa M., Chen Y., Minagawa T. Evidence that endogenous gamma interferon is produced early in Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2386–2388. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2386-2388.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Numata A., Chen Y., Minagawa T. Endogenous gamma interferon-independent host resistance against Listeria monocytogenes infection in CD4+ T cell- and asialo GM1+ cell-depleted mice. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3439–3445. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3439-3445.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poston R. M., Kurlander R. J. Analysis of the time course of IFN-gamma mRNA and protein production during primary murine listeriosis. The immune phase of bacterial elimination is not temporally linked to IFN production in vivo. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4333–4337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P., Kaufmann S. H. The role of T-cell subsets and cytokines in the regulation of infection. Immunol Today. 1991 Oct;12(10):346–348. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90063-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada H., Kawamura I., Arakawa M., Nomoto K., Mitsuyama M. Dissociated development of T cells mediating delayed-type hypersensitivity and protective T cells against Listeria monocytogenes and their functional difference in lymphokine production. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3589–3595. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3589-3595.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youdim S., Stutman O., Good R. A. Studies of delayed hypersensitivity to L. Monocytogenes in mice: nature of cells involved in passive transfers. Cell Immunol. 1973 Jan;6(1):98–109. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubiaga A. M., Munoz E., Merrow M., Huber B. T. Regulation of interleukin 6 production in T helper cells. Int Immunol. 1990;2(11):1047–1054. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.11.1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]