Abstract
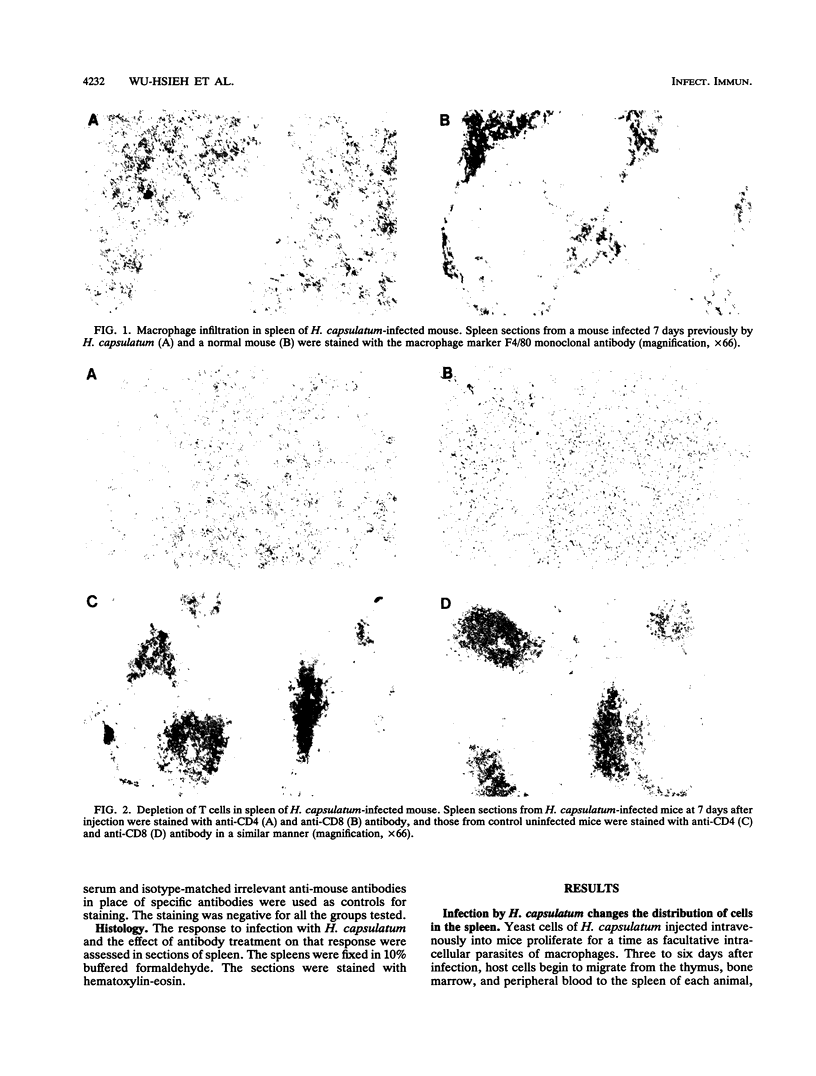
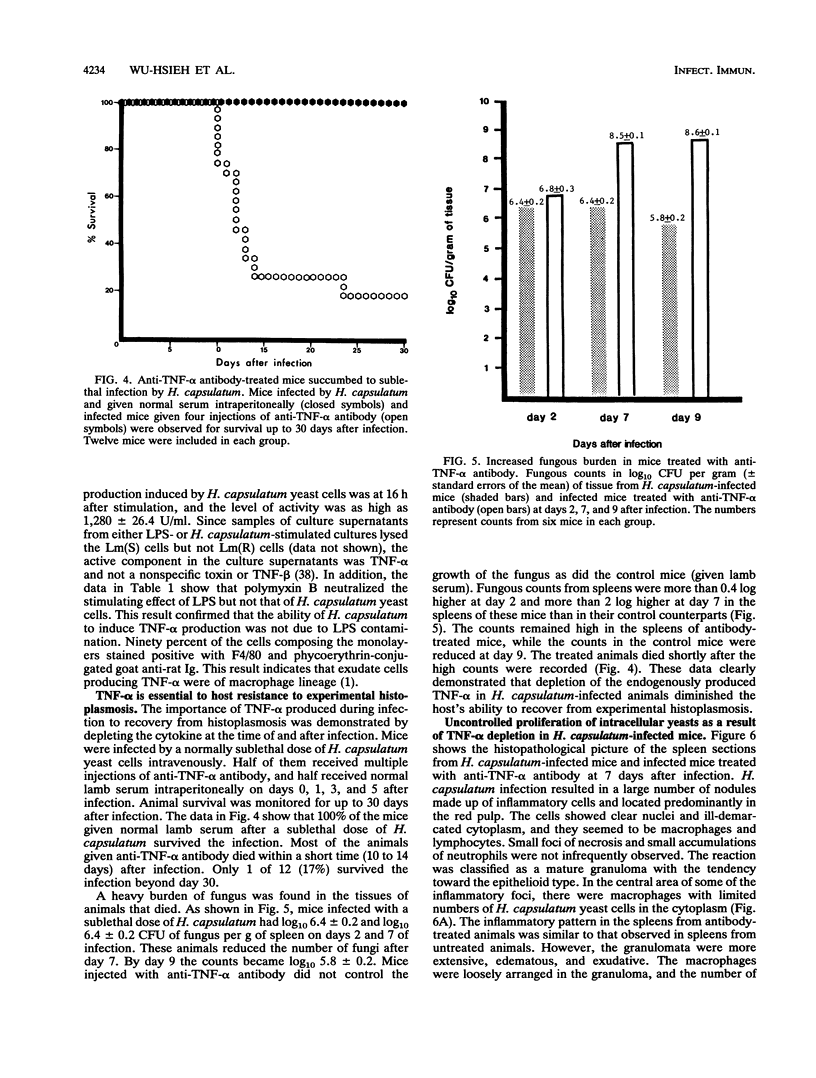
Experimental infection of animals with Histoplasma capsulatum caused a massive macrophage infiltration into the spleen and induced the production of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) locally. The cytokine was also produced in vitro by peritoneal exudate macrophages exposed to a large inoculum of yeast cells. Depletion of the cytokine by injection of polyclonal sheep anti-TNF-alpha antibody was detrimental to sublethally infected mice. Fungous burdens in the spleens of TNF-alpha-depleted mice were higher than they were in the infected control mice at days 2, 7, and 9 after infection, and the antibody-treated animals succumbed to the infection. Histopathological study of spleen sections revealed that splenic macrophages were not able to control proliferation of intracellular yeasts as a result of TNF-alpha depletion. It seems that TNF-alpha plays a role in early activation of splenic macrophages which is important in controlling the outcome of an infection.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austyn J. M., Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Oct;11(10):805–815. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft G. J., Sheehan K. C., Schreiber R. D., Unanue E. R. Tumor necrosis factor is involved in the T cell-independent pathway of macrophage activation in scid mice. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):127–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L. Effects of recombinant gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor on in vitro interactions of human mononuclear phagocytes with Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4227–4229. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4227-4229.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belosevic M., Finbloom D. S., Meltzer M. S., Nacy C. A. IL-2. A cofactor for induction of activated macrophage resistance to infection. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 1;145(3):831–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis, cachexia, shock, and inflammation: a common mediator. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:505–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard D. K., Djeu J. Y., Klein T. W., Friedman H., Stewart W. E., 2nd Protective effects of tumor necrosis factor in experimental Legionella pneumophila infections of mice via activation of PMN function. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 May;43(5):429–435. doi: 10.1002/jlb.43.5.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuturi M. C., Murphy M., Costa-Giomi M. P., Weinmann R., Perussia B., Trinchieri G. Independent regulation of tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin production by human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1581–1594. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Titto E. H., Catterall J. R., Remington J. S. Activity of recombinant tumor necrosis factor on Toxoplasma gondii and Trypanosoma cruzi. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1342–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Gifford G. E. Cell-associated tumor necrosis factor (TNF) as a killing mechanism of activated cytotoxic macrophages. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):957–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degliantoni G., Murphy M., Kobayashi M., Francis M. K., Perussia B., Trinchieri G. Natural killer (NK) cell-derived hematopoietic colony-inhibiting activity and NK cytotoxic factor. Relationship with tumor necrosis factor and synergism with immune interferon. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1512–1530. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faccioli L. H., Souza G. E., Cunha F. Q., Poole S., Ferreira S. H. Recombinant interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor induce neutrophil migration "in vivo" by indirect mechanisms. Agents Actions. 1990 Jun;30(3-4):344–349. doi: 10.1007/BF01966298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Fajardo L. F., Piguet P. F., Allet B., Lambert P. H., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) as an essential mediator in murine cerebral malaria. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1210–1212. doi: 10.1126/science.3306918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Heremans H., Piguet P. F., Pointaire P., Lambert P. H., Billiau A., Vassalli P. Monoclonal antibody against interferon gamma can prevent experimental cerebral malaria and its associated overproduction of tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5572–5574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Taylor T. E., Molyneux M. E., Wirima J. J., Vassalli P., Hommel M., Lambert P. H. Tumor necrosis factor and disease severity in children with falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 15;320(24):1586–1591. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906153202404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser T., Frei K., Zinkernagel R. M., Leist T. P. Role of tumor necrosis factor in Listeria resistance of nude mice. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1990;179(2):95–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00198530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Evidence that tumor necrosis factor has an important role in antibacterial resistance. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2894–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Hinton D. R., Baemayr J., Weil M., Merrill J. E. Lymphokines and immunoregulatory molecules in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Mar;58(3):331–342. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90124-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Hinton D. R., Johnson K., Merrill J. E. Tumor necrosis factor identified in multiple sclerosis brain. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):607–612. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard D. H., Otto V., Gupta R. K. Lymphocyte-mediated cellular immunity in histoplasmosis. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):605–610. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.605-610.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara K., Kobayashi K., Shikama Y., Yoneya I., Kaga S., Hashimoto M., Odagiri T., Soejima K., Ide H., Takahashi T. The role of monokines in granuloma formation in mice: the ability of interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha to induce lung granulomas. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Jun;51(3):419–425. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kasai N., Yamamoto K., Sato N., Tsuruoka N. Human tumor necrosis factor increases the resistance against Listeria infection in mice. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1989;178(6):337–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00197452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern P., Hemmer C. J., Van Damme J., Gruss H. J., Dietrich M. Elevated tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 serum levels as markers for complicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Am J Med. 1989 Aug;87(2):139–143. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(89)80688-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurlander R. J., Hoffman M., Kratz S. S., Gates J. Comparison of the effects of IL-1 alpha and TNF-alpha on phagocyte accumulation and murine antibacterial immunity. Cell Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;123(1):9–22. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90264-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Parkinson C., Millott S., Severn A., Carrier M. Tumour necrosis factor (TNF alpha) in leishmaniasis. I. TNF alpha mediates host protection against cutaneous leishmaniasis. Immunology. 1990 Apr;69(4):570–573. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kato K. Endogenous tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is essential to host resistance against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2563–2569. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2563-2569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusrat A. R., Wright S. D., Aderem A. A., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Properties of isolated red pulp macrophages from mouse spleen. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1505–1510. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Ng W., Wilson C. B., McMaster W. R., Burchett S. K. Modulation of in vitro monocyte cytokine responses to Leishmania donovani. Interferon-gamma prevents parasite-induced inhibition of interleukin 1 production and primes monocytes to respond to Leishmania by producing both tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1914–1924. doi: 10.1172/JCI114654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slagle D. C., Cox R. A., Kuruganti U. Induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha by spherules of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1916–1921. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1916-1921.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. G., Magee D. M., Williams D. M., Graybill J. R. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha plays a role in host defense against Histoplasma capsulatum. J Infect Dis. 1990 Dec;162(6):1349–1353. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.6.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima T., Ueta C., Tsuyuguchi I., Kishimoto S. Production of tumor necrosis factor alpha by monocytes from patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3286–3292. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3286-3292.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarleton R. L. Tumour necrosis factor (cachectin) production during experimental Chagas' disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Aug;73(2):186–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari R. P., Sharma D., Solotorovsky M., Lafemina R., Balint J. Adoptive transfer of immunity from mice immunized with ribosomes or live yeast cells of Histoplasma capsulatum. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):789–795. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.789-795.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Sherry B., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis factor plays a protective role in experimental murine cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2097–2104. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wankowicz Z., Megyeri P., Issekutz A. Synergy between tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 in the induction of polymorphonuclear leukocyte migration during inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Apr;43(4):349–356. doi: 10.1002/jlb.43.4.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. R., Miller T. B., Redington T. J., Bullock W. E. Immunoregulation in experimental disseminated histoplasmosis: flow microfluorometry (FMF) studies of the Thy and Lyt phenotypes of T lymphocytes from infected mice. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):984–990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Graybill J. R., Drutz D. J. Adoptive transfer of immunity to Histoplasma capsulatum in athymic nude mice. Sabouraudia. 1981 Mar;19(1):39–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson B. D., Carswell E. A., Rubin B. Y., Prendergast J. S., Old L. J. Human tumor necrosis factor produced by human B-cell lines: synergistic cytotoxic interaction with human interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5397–5401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worsham P. L., Goldman W. E. Quantitative plating of Histoplasma capsulatum without addition of conditioned medium or siderophores. J Med Vet Mycol. 1988 Jun;26(3):137–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu-Hsieh B. A., Howard D. H. Inhibition of the intracellular growth of Histoplasma capsulatum by recombinant murine gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):1014–1016. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.1014-1016.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu-Hsieh B., Howard D. H., Ahmed R. Virus-induced immunosuppression: a murine model of susceptibility to opportunistic infection. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):232–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu-Hsieh B. Relative susceptibilities of inbred mouse strains C57BL/6 and A/J to infection with Histoplasma capsulatum. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3788–3792. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3788-3792.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]