Abstract
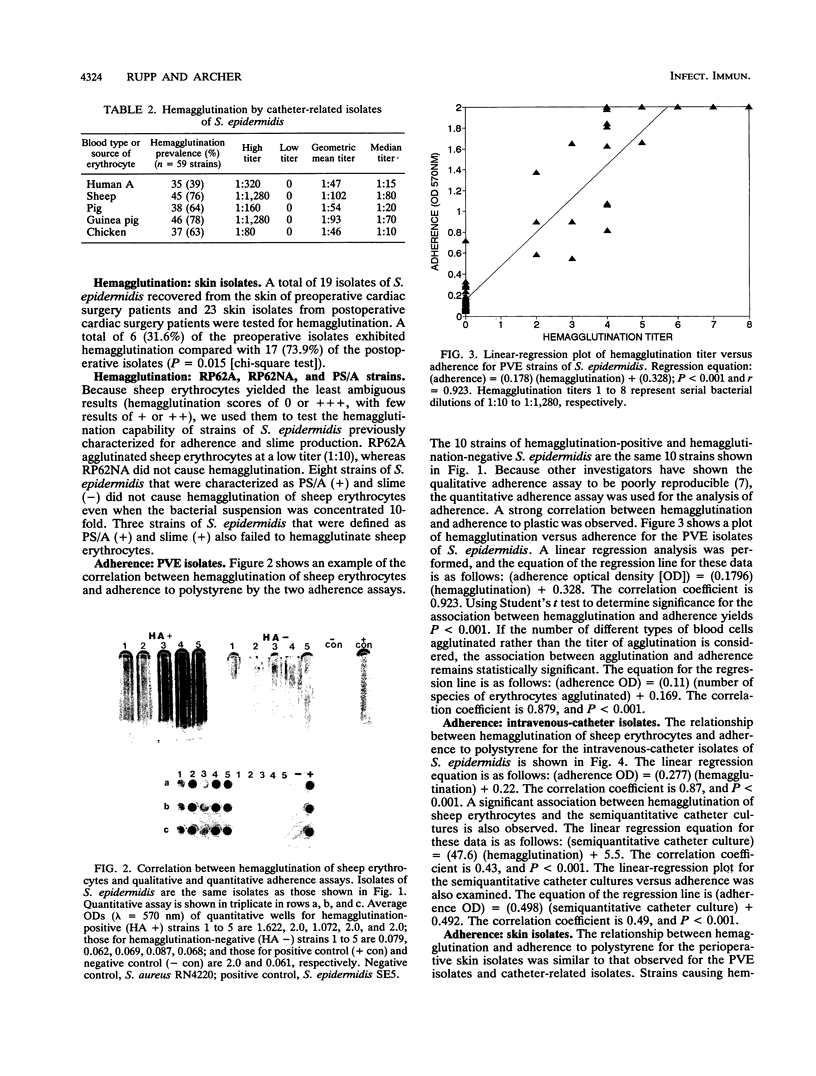
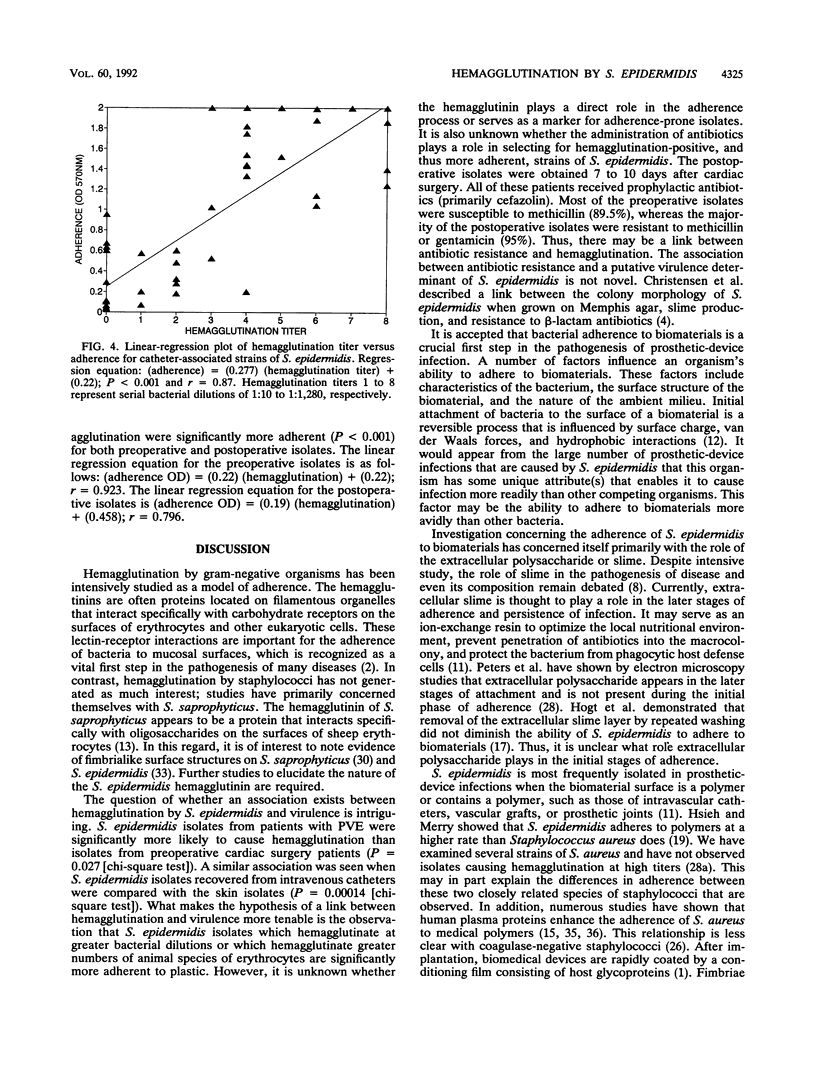
Staphylococcus epidermidis is an important nosocomial pathogen responsible for intravenous catheter-related bacteremia and infections of other prosthetic medical devices. We found that the ability of S. epidermidis to hemagglutinate erythrocytes correlated with the adherence of bacteria to plastic and to intravenous catheters. S. epidermidis isolates responsible for prosthetic-valve endocarditis (n = 61) and isolates from intravenous catheters (n = 59) were significantly more likely to cause hemagglutination than isolates from the skin of preoperative cardiac surgery patients (n = 19) (P = 0.027). S. epidermidis isolates (n = 23) recovered from the skin of patients 7 to 10 days after cardiac surgery were significantly more likely to exhibit hemagglutination than the preoperative isolates (P = 0.015). By a quantitative adherence assay, we also observed that the hemagglutination titer and number of species of erythrocytes agglutinated correlated directly with adherence to polystyrene (P less than 0.001). In addition, hemagglutinating isolates were significantly more likely to be recovered in high number from intravenous catheters when semiquantitative catheter culture techniques were used (P less than 0.001). We speculate that hemagglutinin(s) either plays a direct role in adherence to polymers and thus prosthetic-device infection or serves as an easily demonstrable marker for adherence-prone isolates.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baier R. E., Meyer A. E., Natiella J. R., Natiella R. R., Carter J. M. Surface properties determine bioadhesive outcomes: methods and results. J Biomed Mater Res. 1984 Apr;18(4):337–355. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820180404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuth J., Ko H. L., Schumacher-Perdreau F., Peters G., Heczko P., Pulverer G. Hemagglutination by Staphylococcus saprophyticus and other coagulase-negative staphylococci. Microb Pathog. 1988 May;4(5):379–383. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Baddour L. M., Madison B. M., Parisi J. T., Abraham S. N., Hasty D. L., Lowrance J. H., Josephs J. A., Simpson W. A. Colonial morphology of staphylococci on Memphis agar: phase variation of slime production, resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics, and virulence. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1153–1169. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Baddour L. M., Simpson W. A. Phenotypic variation of Staphylococcus epidermidis slime production in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2870–2877. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2870-2877.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):318–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.318-326.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Younger J. J., Baddour L. M., Barrett F. F., Melton D. M., Beachey E. H. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: a quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):996–1006. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.996-1006.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewry D. T., Galbraith L., Wilkinson B. J., Wilkinson S. G. Staphylococcal slime: a cautionary tale. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1292–1296. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1292-1296.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Wheat L. J., Bemis A. T., White A., Bayer A. S., Hooper D. C. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay for IgG antibodies to Staphylococcus epidermidis. Use in serious coagulase-negative staphylococcal infections. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Apr;147(4):689–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gristina A. G. Biomaterial-centered infection: microbial adhesion versus tissue integration. Science. 1987 Sep 25;237(4822):1588–1595. doi: 10.1126/science.3629258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gristina A. G., Oga M., Webb L. X., Hobgood C. D. Adherent bacterial colonization in the pathogenesis of osteomyelitis. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):990–993. doi: 10.1126/science.4001933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson A., Mårdh P. A., Lundblad A., Svensson S. Oligosaccharide structures mediating agglutination of sheep erythrocytes by Staphylococcus saprophyticus. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):41–46. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.41-46.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann M., Vaudaux P. E., Pittet D., Auckenthaler R., Lew P. D., Schumacher-Perdreau F., Peters G., Waldvogel F. A. Fibronectin, fibrinogen, and laminin act as mediators of adherence of clinical staphylococcal isolates to foreign material. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):693–701. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogt A. H., Dankert J., de Vries J. A., Feijen J. Adhesion of coagulase-negative staphylococci to biomaterials. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2959–2968. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovelius B., Mårdh P. A. Haemagglutination by Staphylococcus saprophyticus and other staphylococcal species. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Feb;87B(1):45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh Y. L., Merry J. The adherence of Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis and Escherichia coli on cotton, polyester and their blends. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;60(6):535–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb01093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karchmer A. W., Archer G. L., Dismukes W. E. Staphylococcus epidermidis causing prosthetic valve endocarditis: microbiologic and clinical observations as guides to therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Apr;98(4):447–455. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-4-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhoff L. V., Sheagren J. N. Epidemiology and clinical significance of blood cultures positive for coagulase-negative staphylococcus. Infect Control. 1985 Dec;6(12):479–486. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700063591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Schleifer K. H. Simplified scheme for routine identification of human Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.82-88.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koransky J. R., Scales R. W., Kraus S. J. Bacterial hemagglutination by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):495–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.495-498.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki D. G., Weise C. E., Sarafin H. W. A semiquantitative culture method for identifying intravenous-catheter-related infection. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 9;296(23):1305–1309. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706092962301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Pfaller M. A., Massanari R. M., Wenzel R. P. Use of cellular hydrophobicity, slime production, and species identification markers for the clinical significance of coagulase-negative staphylococcal isolates. Am J Infect Control. 1989 Jun;17(3):130–135. doi: 10.1016/0196-6553(89)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller E., Takeda S., Goldmann D. A., Pier G. B. Blood proteins do not promote adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to biomaterials. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3323–3326. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3323-3326.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Birch-Andersen A., Kanamori M., Svanborg-Edén C. O, K, H and fimbrial antigens in Escherichia coli serotypes associated with pyelonephritis and cystitis. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;33:18–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Locci R., Pulverer G. Adherence and growth of coagulase-negative staphylococci on surfaces of intravenous catheters. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):479–482. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H., Naumann G., Putzke H. P. Detection of different fimbriae-like structures on the surface of Staphylococcus saprophyticus. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Apr;268(2):228–237. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Lis H. Lectins as cell recognition molecules. Science. 1989 Oct 13;246(4927):227–234. doi: 10.1126/science.2552581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenström T. A., Kjelleberg S. Fimbriae mediated nonspecific adhesion of Salmonella typhimurium to mineral particles. Arch Microbiol. 1985 Oct;143(1):6–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00414759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmerman C. P., Fleer A., Besnier J. M., De Graaf L., Cremers F., Verhoef J. Characterization of a proteinaceous adhesin of Staphylococcus epidermidis which mediates attachment to polystyrene. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4187–4192. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4187-4192.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo M., Yamashita N., Goldmann D. A., Pier G. B. Isolation and characterization of a capsular polysaccharide adhesin from Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):713–722. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toy P. T., Lai L. W., Drake T. A., Sande M. A. Effect of fibronectin on adherence of Staphylococcus aureus to fibrin thrombi in vitro. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):83–86. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.83-86.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudaux P., Pittet D., Haeberli A., Huggler E., Nydegger U. E., Lew D. P., Waldvogel F. A. Host factors selectively increase staphylococcal adherence on inserted catheters: a role for fibronectin and fibrinogen or fibrin. J Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;160(5):865–875. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.5.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]