Abstract
Mice infected with LP-BM5 murine leukemia viruses develop a syndrome, termed mouse AIDS (MAIDS), characterized by increasingly severe immunodeficiency and progressive lymphoproliferation. Virus-infected mice were examined for the ability to resist acute infection and to control chronic infection with the protozoan Toxoplasma gondii, a major opportunistic pathogen of individuals infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Mice infected with the retroviruses for 2 or 4 weeks responded normally to challenge with the parasite, but mice inoculated with the protozoan 8 or 12 weeks after viral infection died with acute disease due to T. gondii. Increased sensitivity to acute infection was associated with a reduced ability to produce gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and with established changes in CD4+ T-cell function. Mice latently infected with T. gondii and then inoculated with the retrovirus mixture were found to reactivate the parasite infection, with 30 to 40% of dually infected animals dying between 5 and 16 weeks after viral infection. Reactivation was associated with reduced proliferation and impaired production of IFN-gamma in response to stimulation with soluble T. gondii antigens or to concanavalin A. Continuing resistance to lethal reactivation in the remaining mice was shown to require CD8+ T cells and expression of IFN-gamma. In addition, it was found that chronic infection with T. gondii altered the course of MAIDS by inhibiting the progression of splenomegaly and immunodeficiency and reducing the expression of both the helper and etiologic defective viruses. These results support previous studies which indicate that infection with T. gondii is controlled by synergistic interactions between CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, the functions of which are progressively impaired during the course of MAIDS.
Full text
PDF

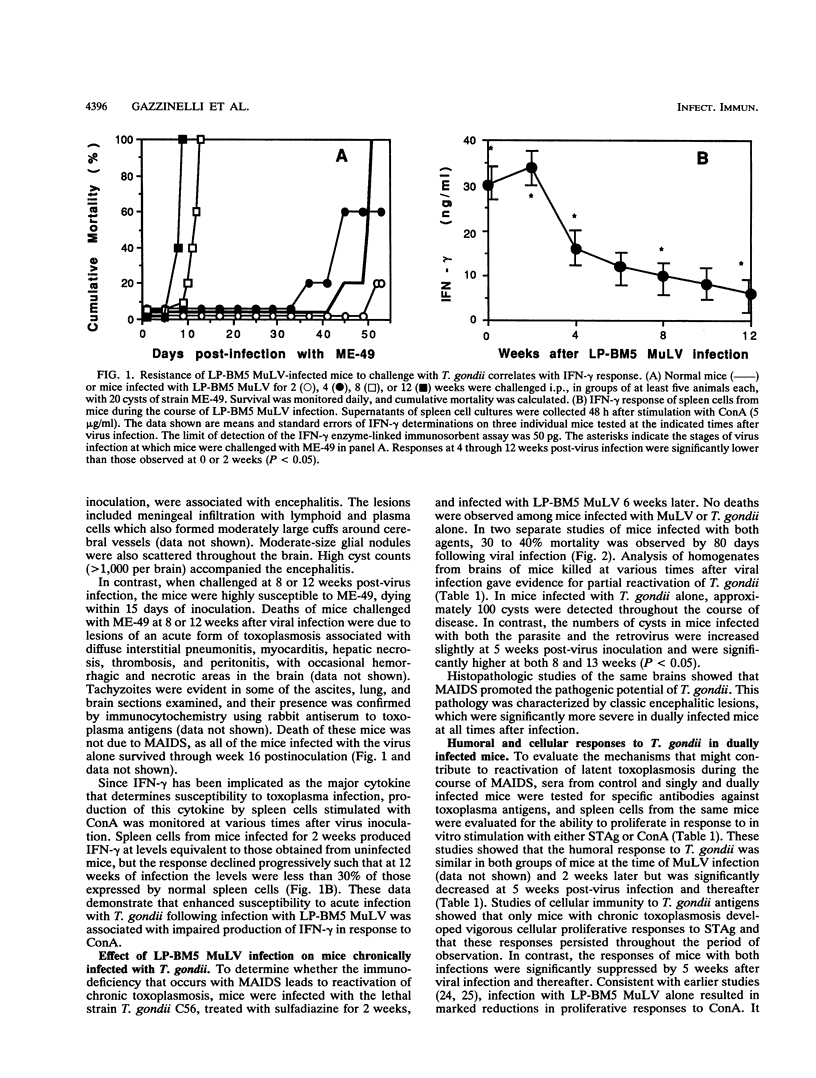
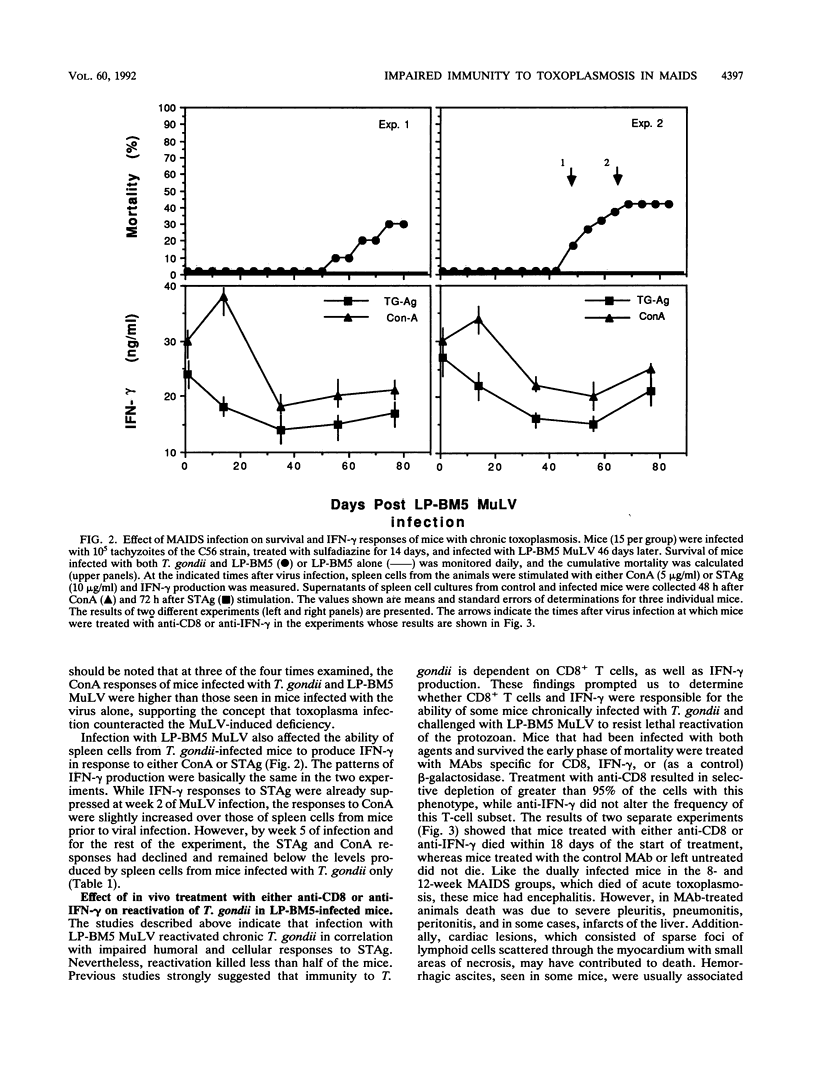
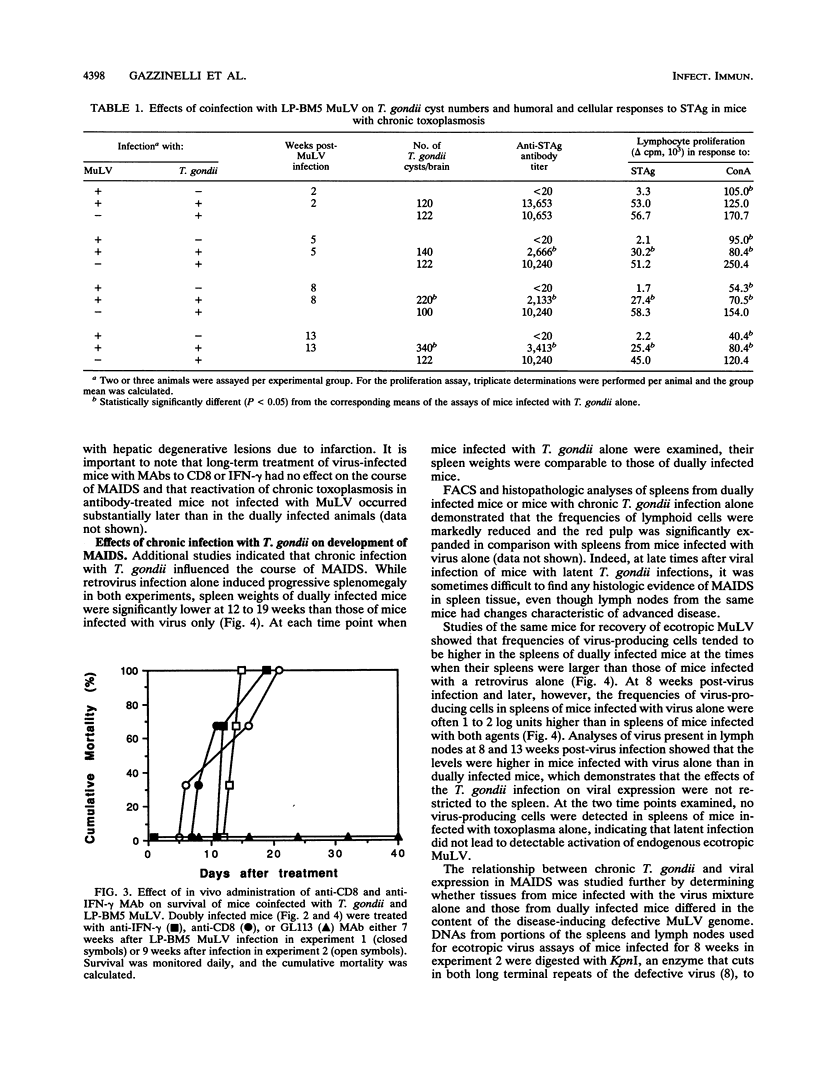


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araujo F. G. Depletion of L3T4+ (CD4+) T lymphocytes prevents development of resistance to Toxoplasma gondii in mice. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1614–1619. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1614-1619.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aziz D. C., Hanna Z., Jolicoeur P. Severe immunodeficiency disease induced by a defective murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):505–508. doi: 10.1038/338505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. R., McLeod R. Class I MHC genes and CD8+ T cells determine cyst number in Toxoplasma gondii infection. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3438–3441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. M., Holmes K. L., Hügin A., Frederickson T. N., Morse H. C., 3rd Induction of cytotoxic T-cell responses in vivo in the absence of CD4 helper cells. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):77–79. doi: 10.1038/328077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. M., Yetter R. A., Fredrickson T. N., Morse H. C., 3rd Abrogation of resistance to severe mousepox in C57BL/6 mice infected with LP-BM5 murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):383–387. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.383-387.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall J. R., Hofflin J. M., Remington J. S. Pulmonary toxoplasmosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Apr;133(4):704–705. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.4.704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerny A., Hügin A. W., Holmes K. L., Morse H. C., 3rd CD4+ T cells in murine acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: evidence for an intrinsic defect in the proliferative response to soluble antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jul;20(7):1577–1581. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Morse H. C., 3rd, Makino M., Ruscetti S. K., Hartley J. W. Defective virus is associated with induction of murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3862–3866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Sengupta D. N., Fredrickson T. N., Morse H. C., 3rd, Hartley J. W. Characteristics and contributions of defective, ecotropic, and mink cell focus-inducing viruses involved in a retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome of mice. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4232–4241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4232-4241.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Genetic study of lymphoma induction by AKR mink cell focus-inducing virus in AKR x NFS crosses. J Exp Med. 1981 Aug 1;154(2):450–457. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.2.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Lymphomagenicity of recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):542–552. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darban H., Enriquez J., Sterling C. R., Lopez M. C., Chen G., Abbaszadegan M., Watson R. R. Cryptosporidiosis facilitated by murine retroviral infection with LP-BM5. J Infect Dis. 1991 Oct;164(4):741–745. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.4.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzinelli R. T., Hakim F. T., Hieny S., Shearer G. M., Sher A. Synergistic role of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes in IFN-gamma production and protective immunity induced by an attenuated Toxoplasma gondii vaccine. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):286–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzinelli R. T., Makino M., Chattopadhyay S. K., Snapper C. M., Sher A., Hügin A. W., Morse H. C., 3rd CD4+ subset regulation in viral infection. Preferential activation of Th2 cells during progression of retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency in mice. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):182–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzinelli R., Xu Y., Hieny S., Cheever A., Sher A. Simultaneous depletion of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes is required to reactivate chronic infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 1;149(1):175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Fredrickson T. N., Yetter R. A., Makino M., Morse H. C., 3rd Retrovirus-induced murine acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: natural history of infection and differing susceptibility of inbred mouse strains. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1223–1231. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1223-1231.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israelski D. M., Araujo F. G., Conley F. K., Suzuki Y., Sharma S., Remington J. S. Treatment with anti-L3T4 (CD4) monoclonal antibody reduces the inflammatory response in toxoplasmic encephalitis. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):954–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israelski D. M., Skowron G., Leventhal J. P., Long I., Blankenship C. F., Barrio G. W., Prince J. B., Araujo F. G., Remington J. S. Toxoplasma peritonitis in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Jul;148(7):1655–1657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinken S. P., Fredrickson T. N., Hartley J. W., Yetter R. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Evolution of B cell lineage lymphomas in mice with a retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome, MAIDS. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1123–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman D. M., Morse H. C., 3rd Characteristics of B cell proliferation and activation in murine AIDS. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1144–1149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft B. J., Brooks R. G., Conley F. K., McCabe R. E., Remington J. S. Toxoplasmic encephalitis in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. JAMA. 1984 Aug 17;252(7):913–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuochi T., Hügin A. W., Morse H. C., 3rd, Singer A., Buller R. M. Role of lymphokine-secreting CD8+ T cells in cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses against vaccinia virus. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):270–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. C., 3rd, Yetter R. A., Via C. S., Hardy R. R., Cerny A., Hayakawa K., Hugin A. W., Miller M. W., Holmes K. L., Shearer G. M. Functional and phenotypic alterations in T cell subsets during the course of MAIDS, a murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):844–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Yetter R. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Retroviral induction of acute lymphoproliferative disease and profound immunosuppression in adult C57BL/6 mice. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):766–784. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Fong T. A. Specific assays for cytokine production by T cells. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Jan 17;116(2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Petito C. K., Gold J. W., Cho E. S., Jordan B. D., Price R. W. Cerebral toxoplasmosis complicating the acquired immune deficiency syndrome: clinical and neuropathological findings in 27 patients. Ann Neurol. 1986 Mar;19(3):224–238. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parke D. W., 2nd, Font R. L. Diffuse toxoplasmic retinochoroiditis in a patient with AIDS. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986 Apr;104(4):571–575. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1986.01050160127028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattengale P. K., Taylor C. R., Twomey P., Hill S., Jonasson J., Beardsley T., Haas M. Immunopathology of B-cell lymphomas induced in C57BL/6 mice by dualtropic murine leukemia virus (MuLV). Am J Pathol. 1982 Jun;107(3):362–377. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomeroy C., Kline S., Jordan M. C., Filice G. A. Reactivation of Toxoplasma gondii by cytomegalovirus disease in mice: antimicrobial activities of macrophages. J Infect Dis. 1989 Aug;160(2):305–311. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.2.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. S., Maniero T. G., Morse H. C., 3rd In vivo immunologic deficits in mice with murine acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and the effect of LP-BM5 infection on rejection of skin from infected mice. Transplant Proc. 1991 Feb;23(1 Pt 1):167–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. IgG or IgM monoclonal antibodies reactive with different determinants on the molecular complex bearing Lyt 2 antigen block T cell-mediated cytolysis in the absence of complement. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2665–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer G. M., Singer A., Mizuochi T., Buller M., Hugin A., Morse H. C., 3rd Importance of CD8+ T helper cell function in AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):893–893. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Conley F. K., Remington J. S. Importance of endogenous IFN-gamma for prevention of toxoplasmic encephalitis in mice. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):2045–2050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Orellana M. A., Schreiber R. D., Remington J. S. Interferon-gamma: the major mediator of resistance against Toxoplasma gondii. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):516–518. doi: 10.1126/science.3128869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Remington J. S. The effect of anti-IFN-gamma antibody on the protective effect of Lyt-2+ immune T cells against toxoplasmosis in mice. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1954–1956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Via C. S., Morse H. C., 3rd, Shearer G. M. Altered immunoregulation and autoimmune aspects of HIV infection: relevant murine models. Immunol Today. 1990 Jul;11(7):250–255. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90099-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollmer T. L., Waldor M. K., Steinman L., Conley F. K. Depletion of T-4+ lymphocytes with monoclonal antibody reactivates toxoplasmosis in the central nervous system: a model of superinfection in AIDS. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3737–3741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yetter R. A., Buller R. M., Lee J. S., Elkins K. L., Mosier D. E., Fredrickson T. N., Morse H. C., 3rd CD4+ T cells are required for development of a murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome (MAIDS). J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):623–635. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]