Abstract
Serologic evidence of anti-I and anti-Fl cold agglutinins occurring in mycoplasma infections led to the isolation of I/Fl glycoprotein from human erythrocyte membranes. Mycoplasma pneumoniae bound to purified I/Fl glycoprotein in a dose-dependent fashion depending on sialylated carbohydrate determinants. This was shown by the decreased binding of mycoplasmas to either sialidase-treated I/Fl glycoprotein (dot blot analysis) or sialidase-treated erythrocytes (hemagglutination test). Structural properties of the receptor for optimal binding could be explored by hemagglutination inhibition assays. Glycophorins were excluded as receptors. These results indicate that Fl (and I) antigens are receptors for M. pneumoniae.
Full text
PDF
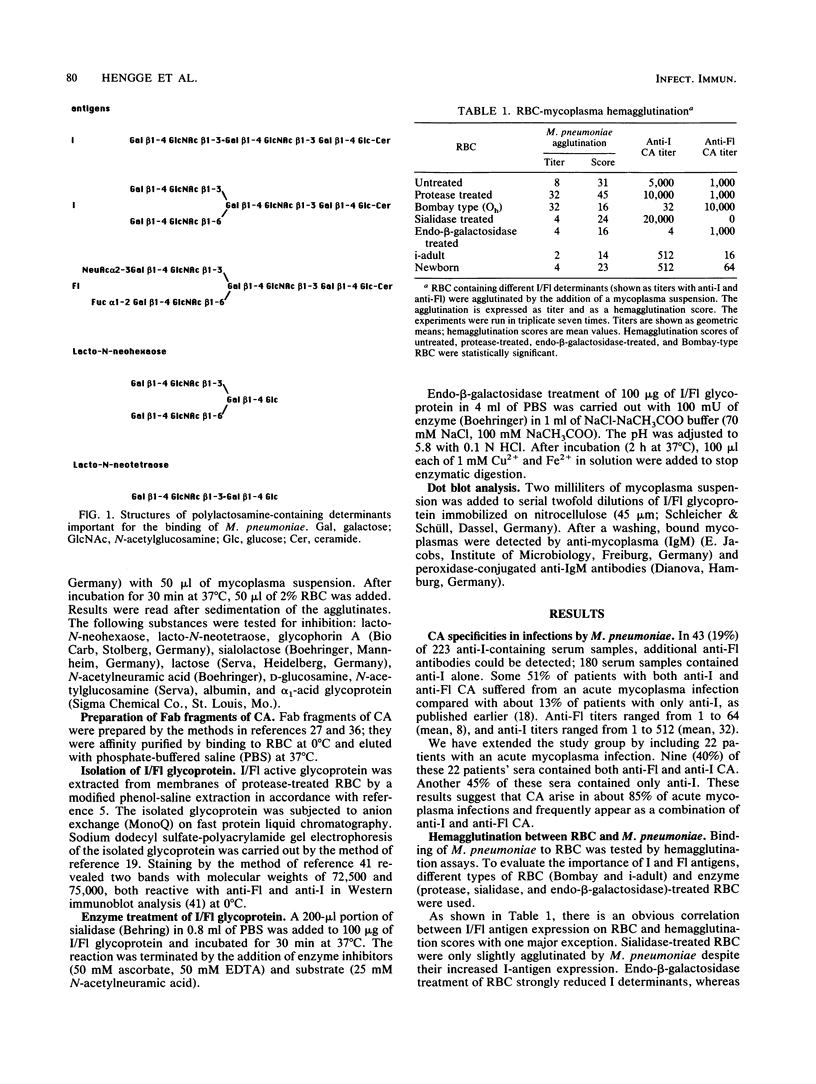



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunner H., Feldner J., Bredt W. Effect of monoclonal antibodies to the attachment-tip on experimental Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection of hamsters. A preliminary report. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Sep;20(9):878–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Rothstein A. Membrane proteins related to anion permeability of human red blood cells. II. Effects of proteolytic enzymes on disulfonic stilbene sites of surface proteins. J Membr Biol. 1974;15(3):227–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01870089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. K., Grabowski M. W., Barile M. F. Mycoplasma pneumoniae attachment: competitive inhibition by mycoplasmal binding component and by sialic acid-containing glycoconjugates. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):598–603. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.598-603.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert W., Roelcke D., Weicker H. The I antigen of human red cell membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May 6;53(2):505–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T., Gooi H. C., Loomes L. M., Suzuki Y., Suzuki T., Matsumoto M. Cryptic I antigen activity and Mycoplasma pneumoniae-receptor activity associated with sialoglycoprotein GP-2 of bovine erythrocyte membranes. Biosci Rep. 1984 Sep;4(9):743–749. doi: 10.1007/BF01128815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T., Taylor-Robinson D. Cold agglutinin anti-I and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Immunology. 1967 Oct;13(4):405–409. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T., Taylor-Robinson D., Shields M. D., Carter R. A. Production of cold agglutinins in rabbits immunized with human erythrocytes treated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Nature. 1969 Jun 28;222(5200):1253–1256. doi: 10.1038/2221253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda M. N., Fukuda M., Hakomori S. Cell surface modification by endo-beta-galactosidase. Change of blood group activities and release of oligosaccharides from glycoproteins and glycosphingolipids of human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5458–5465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabridge M. G. Respiratory tract organ cultures to assay attachment and pathogenicity of mycoplasmas. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1984 Jan-Feb;135A(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(84)80056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabridge M. G., Taylor-Robinson D., Davies H. A., Dourmashkin R. R. Interaction of Mycoplasma pneumoniae with human lung fibroblasts: characterization of the in vitro model. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):446–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.446-454.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisen H. P., Roelcke D., Rehn K., Konrad G. Hochtitrige Kälteagglutinine der Spezilfität Anti-Pr nach Rötelninfektion. Klin Wochenschr. 1975 Aug 15;53(16):767–772. doi: 10.1007/BF01614858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Wilson R. M., Baseman J. B. Two-dimensional gel electrophoretic comparison of proteins from virulent and avirulent strains of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):468–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.468-475.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINS W. J., KOSTER H. G., MARSH W. L., CARTER R. L. INFECTIOUS MONONUCLEOSIS: AN UNSUSPECTED SOURCE ON ANTI-I. Br J Haematol. 1965 Jul;11:480–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb06611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Tucker S., Leith D. K., Morrison-Plummer J., Baseman J. B. Detection of the major adhesin P1 in triton shells of virulent Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):944–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.944-946.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannagi R., Roelcke D., Peterson K. A., Okada Y., Levery S. B., Hakomori S. Characterization of an epitope (determinant) structure in a developmentally regulated glycolipid antigen defined by a cold agglutinin Fl, recognition of alpha-sialosyl and alpha-L-fucosyl groups in a branched structure. Carbohydr Res. 1983 Aug 16;120:143–157. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(83)88013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König A. L., Kreft H., Hengge U., Braun R. W., Roelcke D. Coexisting anti-I and anti-F1/Gd cold agglutinins in infections by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Vox Sang. 1988;55(3):176–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1988.tb05088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamblin G., Boersma A., Klein A., Roussel P., van Halbeek H., Vliegenthart J. F. Primary structure determination of five sialylated oligosaccharides derived from bronchial mucus glycoproteins of patients suffering from cystic fibrosis. The occurrence of the NeuAc alpha(2----3)Gal beta(1----4)[Fuc alpha(1----3)] GlcNAc beta(1----.) structural element revealed by 500-MHz 1H NMR spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9051–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K. Production of cold agglutinins in rabbits induced by Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Listeria monocytogenes or Streptococcus MG. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Aug;81(4):487–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomes L. M., Uemura K., Childs R. A., Paulson J. C., Rogers G. N., Scudder P. R., Michalski J. C., Hounsell E. F., Taylor-Robinson D., Feizi T. Erythrocyte receptors for Mycoplasma pneumoniae are sialylated oligosaccharides of Ii antigen type. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):560–563. doi: 10.1038/307560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomes L. M., Uemura K., Feizi T. Interaction of Mycoplasma pneumoniae with erythrocyte glycolipids of I and i antigen types. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):15–20. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.15-20.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loveless R. W., Feizi T. Sialo-oligosaccharide receptors for Mycoplasma pneumoniae and related oligosaccharides of poly-N-acetyllactosamine series are polarized at the cilia and apical-microvillar domains of the ciliated cells in human bronchial epithelium. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1285–1289. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1285-1289.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manchee R. J., Taylor-Robinson D. Utilization of neuraminic acid receptors by mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):914–919. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.914-919.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newkirk M. M., Edmundson A., Wistar R., Jr, Klapper D. G., Capra J. D. A new protocol to digest human IgM with papain that results in homogeneous Fab preparations that can be routinely crystallized. Hybridoma. 1987 Oct;6(5):453–460. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1987.6.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Kannagi R., Levery S. B., Hakomori S. Glycolipid antigens with blood group I and i specificities from human adult and umbilical cord erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):835–842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelcke D. A further cold agglutinin, F1, recognizing a N-acetylneuraminic acid-determined antigen. Vox Sang. 1981;41(2):98–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1981.tb01021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelcke D., Ebert W., Anstee D. J. Demonstration of low-titer anti-Pr cold agglutinins. Vox Sang. 1974;27(5):429–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1974.tb02439.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelcke D., Ebert W., Feizi T. Studies on the specificities of two IgM lambda cold agglutinins. Immunology. 1974 Nov;27(5):879–886. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelcke D., Hengge U., Kirschfink M. Neolacto (type-2 chain)-sialoautoantigens recognized by human cold agglutinins. Vox Sang. 1990;59(4):235–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1990.tb00244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfield R. E., Schmidt P. J., Calvo R. C., McGinniss M. H. Anti-i, a frequent cold agglutinin in infectious mononucleosis. Vox Sang. 1965 Sep-Oct;10(5):631–634. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1965.tb01418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseaux J., Rousseaux-Prévost R., Bazin H. Optimal conditions for the preparation of Fab and F(ab')2 fragments from monoclonal IgG of different rat IgG subclasses. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Nov 11;64(1-2):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90392-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scudder P., Hanfland P., Uemura K., Feizi T. Endo-beta-D-galactosidases of Bacteroides fragilis and Escherichia freundii hydrolyze linear but not branched oligosaccharide domains of glycolipids of the neolacto series. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6586–6592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su C. J., Tryon V. V., Baseman J. B. Cloning and sequence analysis of cytadhesin P1 gene from Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3023–3029. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3023-3029.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Hirabayashi Y., Suzuki T., Matsumoto M. Occurrence of O-glycosidically peptide-linked oligosaccharides of poly-N-acetyllactosamine type (erythroglycan II) in the I-antigenically active Sendai virus receptor sialoglycoprotein GP-2. J Biochem. 1985 Dec;98(6):1653–1659. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu M., Epstein R. L., Weiner H. L. Interaction of viruses with cell surface receptors. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;80:27–61. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(08)60366-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



