Abstract
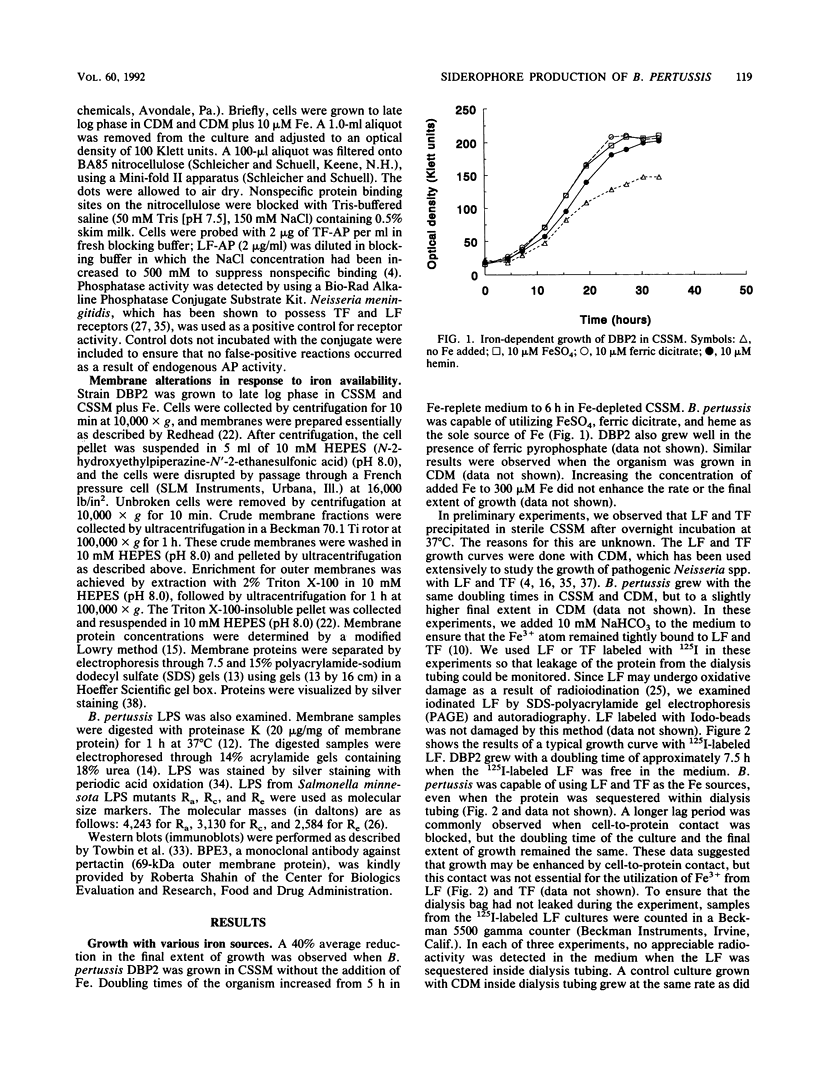
Bordetella pertussis was grown in iron (Fe)-free defined medium to limit the growth of the organism. Doubling times of the Fe-starved organism increased by approximately 1 h, and a 40% reduction in the final extent of growth in Fe-depleted medium was observed. Under these conditions, a hydroxamate siderophore named bordetellin was secreted by B. pertussis. Lactoferrin and transferrin supported growth of B. pertussis even when the protein was sequestered inside dialysis tubing. This suggested that binding of lactoferrin and transferrin to B. pertussis was not essential and that bordetellin production plays a major role in Fe uptake. Solid-phase dot blot assays indicated weak binding of lactoferrin to the cell surface, consistent with previous reports of a lactoferrin receptor. Three new proteins of 97, 77, and 63 kDa were synthesized in response to Fe starvation. Fe-inducible proteins of 103, 72, 24, 21, and 18 kDa were also observed. The synthesis of lipopolysaccharide was also altered by Fe availability.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisen P., Leibman A. Lactoferrin and transferrin: a comparative study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 29;257(2):314–323. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90283-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkin C. L., Neilands J. B. Rhodotorulic acid, a diketopiperazine dihydroxamic acid with growth-factor activity. I. Isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3734–3739. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton K. J., Biswas G. D., Tsai J., Adams J., Dyer D. W., Davis S. M., Koch G. G., Sen P. K., Sparling P. F. Genetic evidence that Neisseria gonorrhoeae produces specific receptors for transferrin and lactoferrin. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5225–5235. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5225-5235.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. J., Li Z. M., Cowell J. L., Bisher M. E., Steven A. C., Novotny P., Manclark C. R. Identification of a 69-kilodalton nonfimbrial protein as an agglutinogen of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3189–3195. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3189-3195.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B. R., Powell M. V., Lankford C. E. Iron-chelating hydroxamic acid (schizokinen) active in initiation of cell division in Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):286–294. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.286-294.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost G. E., Rosenberg H. The inducible citrate-dependent iron transport system in Escherichia coli K12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 30;330(1):90–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorringe A. R., Woods G., Robinson A. Growth and siderophore production by Bordetella pertussis under iron-restricted conditions. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jan 1;54(1-3):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90265-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Sparling P. F. Haemophilus influenzae can use human transferrin as a sole source for required iron. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):248–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.248-251.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna W. R., Mickelsen P. A., Sparling P. F., Dyer D. W. Iron uptake from lactoferrin and transferrin by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):785–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.785-791.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menozzi F. D., Gantiez C., Locht C. Identification and purification of transferrin- and lactoferrin-binding proteins of Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3982–3988. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3982-3988.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. J., Williams P. Siderophore-independent acquisition of transferrin-bound iron by Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 May;136(5):927–933. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-5-927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial envelope proteins related to iron. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial iron compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:715–731. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppler M. S. Two physically and serologically distinct lipopolysaccharide profiles in strains of Bordetella pertussis and their phenotype variants. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):224–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.224-232.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redhead K., Hill T. Acquisition of iron from transferrin by Bordetella pertussis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jan 15;61(2-3):303–307. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90570-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redhead K., Hill T., Chart H. Interaction of lactoferrin and transferrins with the outer membrane of Bordetella pertussis. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Apr;133(4):891–898. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-4-891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenmund A., Kuyas C., Haeberli A. Oxidative radioiodination damage to human lactoferrin. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):239–245. doi: 10.1042/bj2400239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEIFTER S., GALLOP P. M., MICHAELS S., MEILMAN E. Analysis of hydroxamic acids and hydrazides; preparation and properties of dinitrophenyl derivatives of hydroxamic acids, oximes, hydrazides, and hydrazones. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2613–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Hale T. L., Zollinger W. D., Seid R. C., Jr, Hammack C. A., Griffiss J. M. Heterogeneity of molecular size and antigenic expression within lipooligosaccharides of individual strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):544–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.544-549.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Morris L. J. Identification and characterization of the transferrin receptor from Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):281–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyn B., Neilands J. B. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jan;160(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stainer D. W., Scholte M. J. A simple chemically defined medium for the production of phase I Bordetella pertussis. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Oct;63(2):211–220. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-2-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. B., Bohling T., Payvandi F., Rennard S. I. Lower respiratory tract lactoferrin and lysozyme arise primarily in the airways and are elevated in association with chronic bronchitis. J Lab Clin Med. 1990 Feb;115(2):148–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J., Dyer D. W., Sparling P. F. Loss of transferrin receptor activity in Neisseria meningitidis correlates with inability to use transferrin as an iron source. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3132–3138. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3132-3138.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Sparling P. F. Aerobactin utilization by Neisseria gonorrhoeae and cloning of a genomic DNA fragment that complements Escherichia coli fhuB mutations. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3414–3421. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3414-3421.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]