Abstract
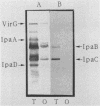
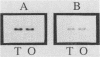
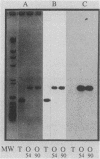
Colonial variation of Shigella flexneri serotype 2a from the translucent (2457T) to the opaque form (2457O) occurs spontaneously once in 10(4) cell divisions, with concomitant loss of ipa gene expression and virulence. The appearance of 2457O was associated with the insertional inactivation of virF, an invasion plasmid-encoded positive regulator of ipa gene expression. Plasmid pWR110, a Tn5-tagged invasion plasmid that restores the invasive phenotype to plasmid-cured Shigella derivatives, was conjugally transferred into 2457O. Synthesis of the invasion-associated IpaB and IpaC polypeptides, normally present on the surface of virulent shigellae, and the invasive phenotype were restored in 2457O(pWR110) transconjugants. Plasmid DNA restriction endonuclease patterns of 2457T and 2457O, along with hybridization analysis, showed that a SalI fragment carrying the virF gene in 2457O had increased in size relative to its counterpart in 2457T. Analysis of virF DNA sequences amplified by the polymerase chain reaction revealed that the virF sequence from 2457O was 780 bp larger than that amplified from 2457T. Moreover, the virF sequence amplified from 2457O hybridized to an IS1 DNA probe whereas the amplified 2457T virF sequence did not. DNA sequence analysis mapped the insertion element, designated IS1SFO, within an A.T-rich region of the virF open reading frame and identified a 9-bp virF target sequence that was duplicated at the insertion site of IS1SFO. The DNA sequence of IS1SFO was greater than 99% homologous to IS1F. Plasmid pWR600, carrying a 1,260-bp HpaII fragment encoding a wild-type virF gene, was able to restore the virulent phenotype and translucent colonial morphology to nine independently isolated 2457O hosts.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernardini M. L., Mounier J., d'Hauteville H., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Identification of icsA, a plasmid locus of Shigella flexneri that governs bacterial intra- and intercellular spread through interaction with F-actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3867–3871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C. A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:243–255. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buysse J. M., Stover C. K., Oaks E. V., Venkatesan M., Kopecko D. J. Molecular cloning of invasion plasmid antigen (ipa) genes from Shigella flexneri: analysis of ipa gene products and genetic mapping. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2561–2569. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2561-2569.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buysse J. M., Venkatesan M., Mills J. A., Oaks E. V. Molecular characterization of a trans-acting, positive effector (ipaR) of invasion plasmid antigen synthesis in Shigella flexneri serotype 5. Microb Pathog. 1990 Mar;8(3):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90047-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chosa H., Makino S., Sasakawa C., Okada N., Yamada M., Komatsu K., Suk J. S., Yoshikawa M. Loss of virulence in Shigella strains preserved in culture collections due to molecular alteration of the invasion plasmid. Microb Pathog. 1989 May;6(5):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daskaleros P. A., Payne S. M. Characterization of Shigella flexneri sequences encoding congo red binding (crb): conservation of multiple crb sequences and role of IS1 in loss of the Crb+ phenotype. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.435-443.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daskaleros P. A., Payne S. M. Cloning the gene for Congo red binding in Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):165–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.165-168.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Formal S. B., Gangarosa E. J. Immunity in shigellosis. I. Response of man to attenuated strains of Shigella. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jan;125(1):5–11. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsinghorst E. A., Baron L. S., Kopecko D. J. Penetration of human intestinal epithelial cells by Salmonella: molecular cloning and expression of Salmonella typhi invasion determinants in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., DAMMIN G. J., LABREC E. H., SCHNEIDER H. Experimental Shigella infections: characteristics of a fatal infection produced in guinea pigs. J Bacteriol. 1958 May;75(5):604–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.5.604-610.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Gemski P., Baron L. S., Labrec E. H. A Chromosomal Locus Which Controls the Ability of Shigella flexneri to Evoke Keratoconjunctivitis. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):73–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.73-79.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Labrec E. H., Palmer A., Falkow S. Protection of Monkeys Against Experimental Shigellosis with Attenuated Vaccines. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):63–68. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.63-68.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Calos M. P., Miller J. H. Sequence analysis of Tn9 insertions in the lacZ gene. J Mol Biol. 1980 Nov 25;144(1):19–41. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L. Genetic basis of virulence in Shigella species. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jun;55(2):206–224. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.2.206-224.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Oaks E. V., Formal S. B. Identification and antigenic characterization of virulence-associated, plasmid-coded proteins of Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):620–629. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.620-629.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan E., Saedler H., Starlinger P. O0 and strong-polar mutations in the gal operon are insertions. Mol Gen Genet. 1968;102(4):353–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00433726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Ito K., Nakamura A., Watanabe H. Cloning of regions required for contact hemolysis and entry into LLC-MK2 cells from Shigella sonnei form I plasmid: virF is a positive regulator gene for these phenotypes. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1391–1398. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1391-1398.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim R., Corwin L. M. Mutation in Shigella flexneri resulting in loss of ability to penetrate HeLa cells and loss of glycerol kinase activity. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):916–923. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.916-923.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecko D. J., Holcombe J., Formal S. B. Molecular characterization of plasmids from virulent and spontaneously occurring avirulent colonial variants of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):580–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.580-582.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Sasakawa C., Kamata K., Kurata T., Yoshikawa M. A genetic determinant required for continuous reinfection of adjacent cells on large plasmid in S. flexneri 2a. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90880-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Blackmon B., Curtiss R., 3rd Loss of pigmentation in Shigella flexneri 2a is correlated with loss of virulence and virulence-associated plasmid. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):397–401. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.397-401.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Sansonetti P. J. Identification of a chromosomal gene controlling temperature-regulated expression of Shigella virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2820–2824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. A., Buysse J. M., Oaks E. V. Shigella flexneri invasion plasmid antigens B and C: epitope location and characterization with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2933–2941. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2933-2941.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyman K., Nakamura K., Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. Distribution of the insertion sequence IS1 in gram-negative bacteria. Nature. 1981 Feb 12;289(5798):609–612. doi: 10.1038/289609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks E. V., Wingfield M. E., Formal S. B. Plaque formation by virulent Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.124-129.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
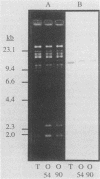
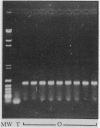
- Oaks E. V., Wingfield M. E., Formal S. B. Plaque formation by virulent Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.124-129.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. Detection and differentiation of iron-responsive avirulent mutants on Congo red agar. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):94–98. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.94-98.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson B. C., Hashimoto H., Rownd R. H. Cointegrate formation between homologous plasmids in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1086–1094. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1086-1094.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pál T., Newland J. W., Tall B. D., Formal S. B., Hale T. L. Intracellular spread of Shigella flexneri associated with the kcpA locus and a 140-kilodalton protein. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):477–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.477-486.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental shigella keratoconjunctivitis; a preliminary report. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;2(3):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Sasakawa C., Makino S., Kamata K., Yoshikawa M. Molecular cloning of a genetic determinant for Congo red binding ability which is essential for the virulence of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):476–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.476-482.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Sasakawa C., Makino S., Yoshikawa M. DNA sequence and product analysis of the virF locus responsible for congo red binding and cell invasion in Shigella flexneri 2a. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):395–402. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.395-402.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Sasakawa C., Yoshikawa M. Expression of four virulence antigens of Shigella flexneri is positively regulated at the transcriptional level by the 30 kiloDalton virF protein. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):589–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Hale T. L., Dammin G. J., Kapfer C., Collins H. H., Jr, Formal S. B. Alterations in the pathogenicity of Escherichia coli K-12 after transfer of plasmid and chromosomal genes from Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1392–1402. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1392-1402.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Involvement of a plasmid in the invasive ability of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.852-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Ryter A., Clerc P., Maurelli A. T., Mounier J. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri within HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):461–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.461-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Adler B., Tobe T., Okada N., Nagai S., Komatsu K., Yoshikawa M. Functional organization and nucleotide sequence of virulence Region-2 on the large virulence plasmid in Shigella flexneri 2a. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1191–1201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Kamata K., Sakai T., Murayama S. Y., Makino S., Yoshikawa M. Molecular alteration of the 140-megadalton plasmid associated with loss of virulence and Congo red binding activity in Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):470–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.470-475.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Makino S., Kamata K., Yoshikawa M. Isolation, characterization, and mapping of Tn5 insertions into the 140-megadalton invasion plasmid defective in the mouse Sereny test in Shigella flexneri 2a. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):32–36. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.32-36.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. A. Mutations caused by the insertion of genetic material into the galactose operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Feb 28;40(1):93–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler J., Adelberg E. A. Temperature dependence of sex-factor maintenance in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):447–449. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.447-449.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe T., Nagai S., Okada N., Adler B., Yoshikawa M., Sasakawa C. Temperature-regulated expression of invasion genes in Shigella flexneri is controlled through the transcriptional activation of the virB gene on the large plasmid. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Apr;5(4):887–893. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomoeda M., Inuzuka M., Kubo N., Nakamura S. Effective elimination of drug resistance and sex factors in Escherichia coli by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1078–1089. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1078-1089.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeda M., Ohtsubo E. Four types of IS1 with differences in nucleotide sequence reside in the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome. Gene. 1991 Feb 1;98(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90096-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan M. M., Buysse J. M., Kopecko D. J. Characterization of invasion plasmid antigen genes (ipaBCD) from Shigella flexneri. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9317–9321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan M., Buysse J. M., Vandendries E., Kopecko D. J. Development and testing of invasion-associated DNA probes for detection of Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):261–266. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.261-266.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATKINS H. M. Some attributes of virulence in Shigella. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Nov 21;88:1167–1186. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Sasakawa C., Okada N., Makino S. I., Yoshikawa M. Molecular cloning and characterization of chromosomal virulence region kcpA of Shigella flexneri. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Feb;3(2):207–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb01809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerbib D., Gamas P., Chandler M., Prentki P., Bass S., Galas D. Specificity of insertion of IS1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 5;185(3):517–524. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]