Abstract
The interaction of Glu-plasminogen with group A, C, and G streptococci and subsequent formation of surface-associated plasminogen by tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) were studied. Binding of 125I-Glu-plasminogen to streptococci greatly facilitated its activation to 125I-Glu-plasmin by exogenous t-PA, whereas activation in the absence of bacteria took place only slowly. Glu-plasmin formed on the streptococcal surface was further converted to the Lys form. Similar activation and modification took place also in the presence of plasminogen-depleted plasma, containing functional t-PA and plasmin inhibitors, indicating that the surface-associated enzymes were protected against these inhibitors. Lys-plasminogen was 10- to 30-fold more potent than Glu-plasminogen or Glu-plasmin in inhibiting the binding of 125I-Glu-plasminogen to streptococci. This indicated a higher affinity of the Lys form towards plasminogen-binding molecule(s) on the streptococcal surface. The surface-associated plasmin was also enzymically active as judged by digestion of chromogenic substrate S-2251. Surface-associated plasmin activity was observed only when the incubations were carried out in the presence of t-PA and Glu-plasminogen or human plasma as the source of plasminogen. Under these conditions, soluble enzymatic activity was also recovered in the supernatant of group A streptococci. This favors the idea that plasmin can be released from the bacterial surface. The findings provide a mechanism for streptococci to adopt proteolytic activity by binding a host-derived enzyme zymogen on their surface, where the subsequent activation then takes place. The results suggest a role for surface-associated plasmin activity in tissue tropism and tissue invasiveness of streptococci.
Full text
PDF

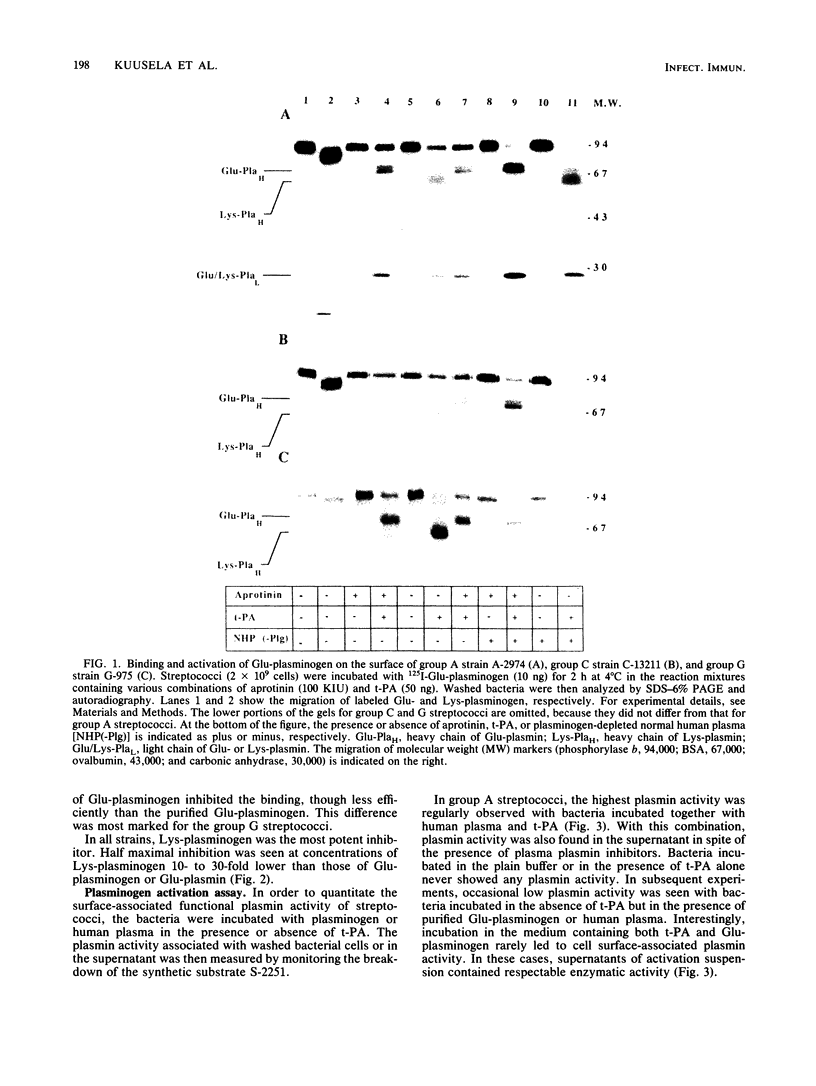


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bajaj A. P., Castellino F. J. Activation of human plasminogen by equimolar levels of streptokinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):492–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder C. C., Lottenberg R., Boyle M. D. Mapping of the human plasmin domain recognized by the unique plasmin receptor of group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2597–2605. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2597-2605.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder C. C., Lottenberg R., von Mering G. O., Johnston K. H., Boyle M. D. Isolation of a prokaryotic plasmin receptor. Relationship to a plasminogen activator produced by the same micro-organism. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4922–4928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broeseker T. A., Boyle M. D., Lottenberg R. Characterization of the interaction of human plasmin with its specific receptor on a group A streptococcus. Microb Pathog. 1988 Jul;5(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friberger P., Knös M., Gustavsson S., Aurell L., Claeson G. Methods for determination of plasmin, antiplasmin and plasminogen by means of substrate S-2251. Haemostasis. 1978;7(2-3):138–145. doi: 10.1159/000214252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Saksela O. Binding and activation of plasminogen at the surface of Staphylococcus aureus. Increase in affinity after conversion to the Lys form of the ligand. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):759–765. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19397.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottenberg R., Broder C. C., Boyle M. D. Identification of a specific receptor for plasmin on a group A streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1914–1918. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1914-1918.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus G., Evers J. L., Hobika G. H. Comparison of some properties of native (Glu) and modified (Lys) human plasminogen. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):733–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Hacker J., Korhonen T. K. Enhancement of tissue plasminogen activator-catalyzed plasminogen activation by Escherichia coli S fimbriae associated with neonatal septicaemia and meningitis. Thromb Haemost. 1991 May 6;65(5):483–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Korhonen T. K. Binding of plasminogen to Escherichia coli adhesion proteins. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):437–440. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80772-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy K. N., Markus G. Mechanism of activation of human plasminogen by streptokinase. Presence of active center in streptokinase-plasminogen complex. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1683–1691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Rifkin D. B. Cell-associated plasminogen activation: regulation and physiological functions. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:93–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöholm I. Studies on the conformational changes of plasminogen induced during activation to plasmin and by 6-aminohexanoic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 15;39(2):471–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullberg M., Kronvall G., Karlsson I., Wiman B. Receptors for human plasminogen on gram-negative bacteria. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):21–25. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.21-25.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullberg M., Kronvall G., Wiman B. New receptor for human plasminogen on gram positive cocci. APMIS. 1989 Nov;97(11):996–1002. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1989.tb00508.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]