Abstract
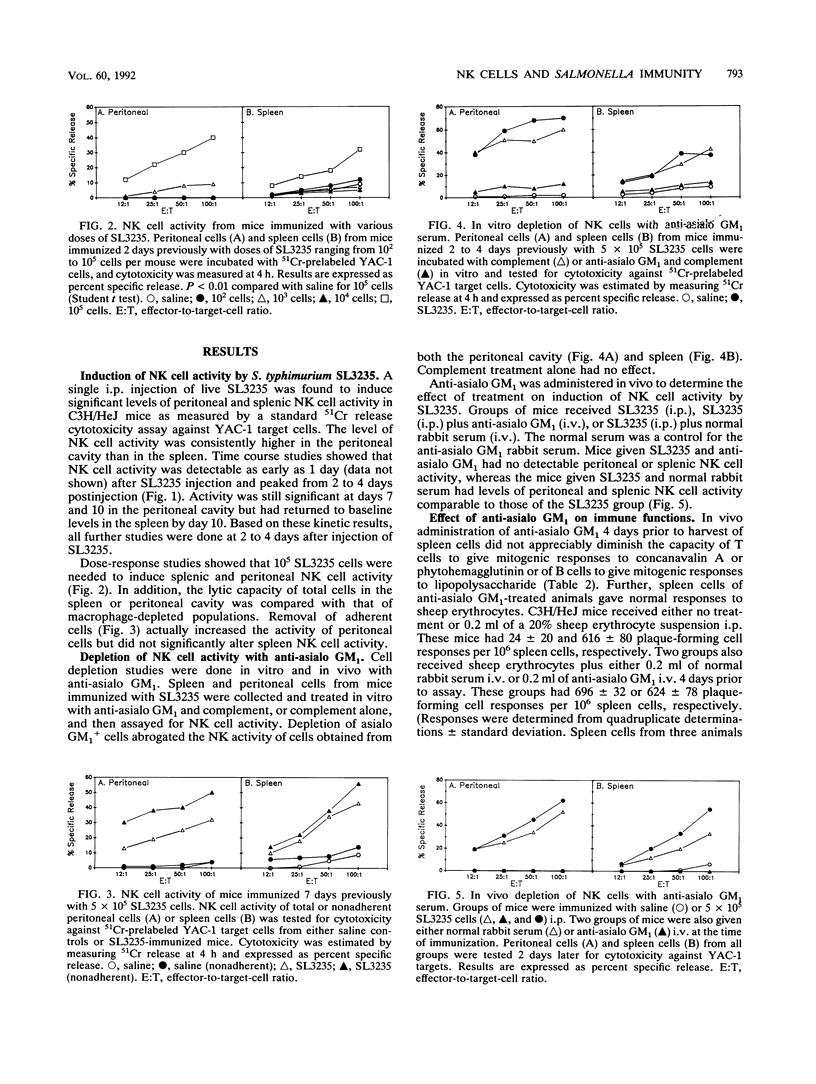
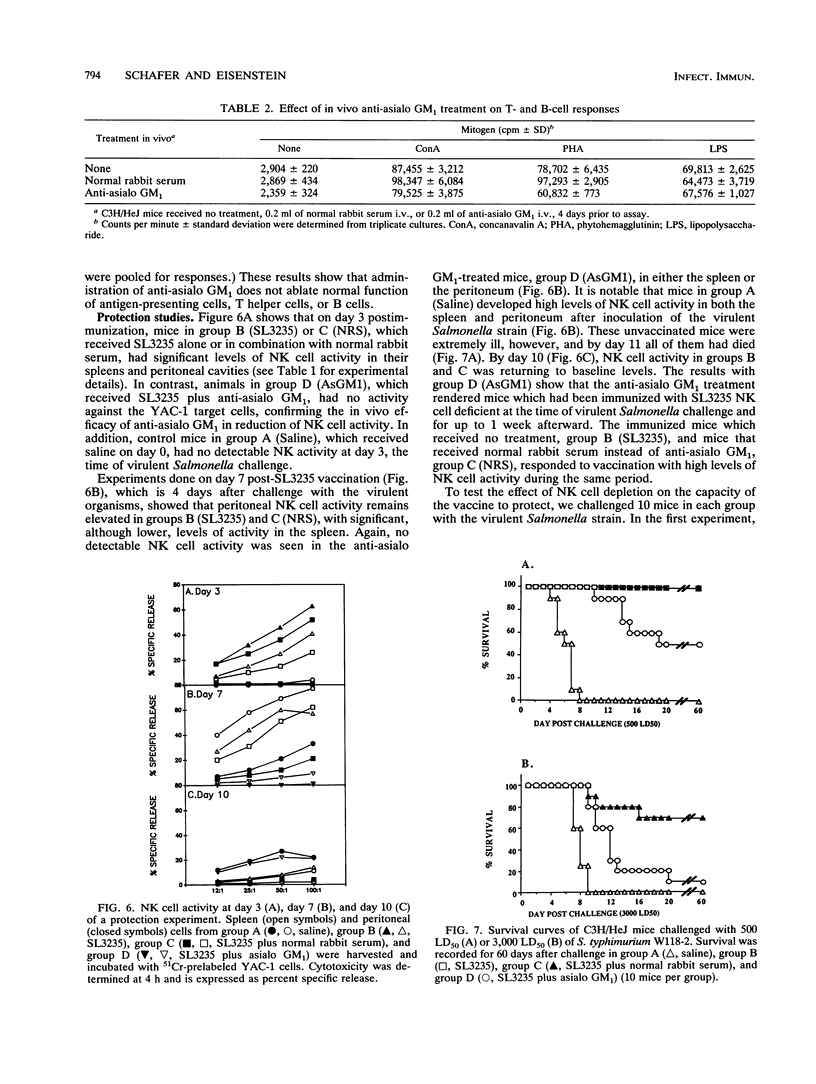
We have previously shown that an avirulent strain of Salmonella typhimurium, SL3235, blocked in aromatic synthesis, confers high levels of resistance to challenge with virulent Salmonella as early as 3 days postvaccination. In the present studies, it was found that immunization with SL3235 resulted in high levels of natural killer (NK) cell activity in the spleens and peritoneal cavities of C3H/HeJ mice, as measured by cytotoxicity against YAC-1 targets. NK cell activity was at its maximum 2 to 4 days after immunization and was ablated by in vivo or in vitro treatment with anti-asialo GM1. In vivo treatment with anti-asialo GM1 during the first week after immunization with SL3235 depleted NK cell activity and markedly increased mortality in mice challenged with a virulent Salmonella strain. These results are compatible with a role for NK cells as one important component in the resistance against virulent Salmonella infection induced by a live, attenuated vaccine.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baccarini M., Hao L., Decker T., Lohmann-Matthes M. L. Macrophage precursors as natural killer cells against tumor cells and microorganisms. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul. 1988;7(5-6):316–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard D. K., Stewart W. E., 2nd, Klein T. W., Friedman H., Djeu J. Y. Cytolytic activity of human peripheral blood leukocytes against Legionella pneumophila-infected monocytes: characterization of the effector cell and augmentation by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):551–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., Hormaeche C. E., Demarco de Hormaeche R., Winther M., Dougan G., Maskell D. J., Stocker B. A. An attenuated aroA Salmonella typhimurium vaccine elicits humoral and cellular immunity to cloned beta-galactosidase in mice. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):86–92. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunda M. J., Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Inhibition of murine natural killer cell activity by prostaglandins. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2682–2687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Lyon F. L., Lowe K. L., Farrand A. L., el-Morshidy S. Oral immunization of mice with attenuated Salmonella enteritidis containing a recombinant plasmid which codes for production of the B subunit of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):685–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.685-692.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K., Killar L. M., Stocker B. A., Sultzer B. M. Cellular immunity induced by avirulent Salmonella in LPS-defective C3H/HeJ mice. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):958–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Peñarrubia P., Koster F. T., Kelley R. O., McDowell T. D., Bankhurst A. D. Antibacterial activity of human natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):99–113. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman Z., Herberman R. B. Natural killer cells and their relationship to T-cells: hypothesis on the role of T-cell receptor gene rearrangement on the course of adaptive differentiation. Cancer Res. 1986 Jun;46(6):2651–2658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatcher F. M., Kuhn R. E. Destruction of Trypanosoma cruzi by Natural killer cells. Science. 1982 Oct 15;218(4569):295–296. doi: 10.1126/science.6812218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser W. E., Jr, Tsai V. Acute toxoplasma infection of mice induces spleen NK cells that are cytotoxic for T. gondii in vitro. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):313–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidore M. R., Murphy J. W. Correlation of natural killer cell activity and clearance of Cryptococcus neoformans from mice after adoptive transfer of splenic nylon wool-nonadherent cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):547–555. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.547-555.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):238–239. doi: 10.1038/291238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez B. E., Murphy J. W. In vitro effects of natural killer cells against Paracoccidioides brasiliensis yeast phase. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):552–558. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.552-558.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai M., Iwamori M., Nagai Y., Okumura K., Tada T. A glycolipid on the surface of mouse natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Mar;10(3):175–180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawase I., Urdal D. L., Brooks C. G., Henney C. S. Selective depletion of NK cell activity in vivo and its effect on the growth of NK-sensitive and NK-resistant tumor cell variants. Int J Cancer. 1982 May 15;29(5):567–574. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910290513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killar L. M., Eisenstein T. K. Immunity to Salmonella typhimurium infection in C3H/HeJ and C3H/HeNCrlBR mice: studies with an aromatic-dependent live S. typhimurium strain as a vaccine. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):605–612. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.605-612.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel G. R., Niesel D. W., Asuncion M., Klimpel K. D. Natural killer cell activation and interferon production by peripheral blood lymphocytes after exposure to bacteria. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1436–1441. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1436-1441.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langermans J. A., van der Hulst M. E., Nibbering P. H., van Furth R. Activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages during infection with Salmonella typhimurium does not result in enhanced intracellular killing. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4340–4346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Gibson C. W., Eisenstein T. K. Macrophage-mediated mitogenic suppression induced in mice of the C3H lineage by a vaccine strain of Salmonella typhimurium. Cell Immunol. 1985 Mar;91(1):75–91. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Herrington D., Murphy J. R., Morris J. G., Losonsky G., Tall B., Lindberg A. A., Svenson S., Baqar S., Edwards M. F. Safety, infectivity, immunogenicity, and in vivo stability of two attenuated auxotrophic mutant strains of Salmonella typhi, 541Ty and 543Ty, as live oral vaccines in humans. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):888–902. doi: 10.1172/JCI112899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowell G. H., Smith L. F., Artenstein M. S., Nash G. S., MacDermott R. P., Jr Antibody-dependent cell-mediated antibacterial activity of human mononuclear cells. I. K lymphocytes and monocytes are effective against meningococi in cooperation with human imune sera. J Exp Med. 1979 Jul 1;150(1):127–137. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merluzzi V. J. Comparison of murine lymphokine-activated killer cells, natural killer cells, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1985 Oct 1;95(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. R., DuPont H. L., Gonik B., Kohl S. Cytotoxicity of human peripheral blood and colostral leukocytes against Shigella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):25–33. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.25-33.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabavi N., Murphy J. W. Antibody-dependent natural killer cell-mediated growth inhibition of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):556–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.556-562.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nencioni L., Villa L., Boraschi D., Berti B., Tagliabue A. Natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated activity against Salmonella typhimurium by peripheral and intestinal lymphoid cells in mice. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):903–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Metcalf E. S., Rosenstreich D. L. Defect in macrophage effector function confers Salmonella typhimurium susceptibility on C3H/HeJ mice. Cell Immunol. 1982 Mar 1;67(2):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Reynolds C. W. Natural killer activity: definition of a function rather than a cell type. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4545–4546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier T. P., Kehoe M. A., Beachey E. H. Protective immunity evoked by oral administration of attenuated aroA Salmonella typhimurium expressing cloned streptococcal M protein. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):25–32. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer R., Nacy C. A., Eisenstein T. K. Induction of activated macrophages in C3H/HeJ mice by avirulent Salmonella. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1638–1644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. P., Reina-Guerra M., Stocker B. A., Hoiseth S. K., Johnson E. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella dublin as a parenteral modified live vaccine for calves. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Nov;45(11):2231–2235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitz L., Baenziger J., Pircher H., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M. Effect of rabbit anti-asialo GM1 treatment in vivo or with anti-asialo GM1 plus complement in vitro on cytotoxic T cell activities. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4674–4680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttles J., Schwarting G. A., Stout R. D. Flow cytometric analysis reveals the presence of asialo GM1 on the surface membrane of alloimmune cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1586–1591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkkanen J., Saksela E., Lanier L. L. Bacterial activation of human natural killer cells. Characteristics of the activation process and identification of the effector cell. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2428–2433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkkanen J., Saxén H., Nurminen M., Mäkelä P. H., Saksela E. Bacterial induction of human activated lymphocyte killing and its inhibition by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2662–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigent D. A., Baron S., Stanton G. J. Streptococcus pneumoniae cocultured with fibroblasts enhances both interferon production and cytotoxic activity by lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):593–597. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.593-597.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiltrout R. H., Santoni A., Peterson E. S., Knott D. C., Overton W. R., Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Reactivity of anti-asialo GM1 serum with tumoricidal and non-tumoricidal mouse macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 May;37(5):597–614. doi: 10.1002/jlb.37.5.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Ramadi B. K., Brodkin M. A., Mosser D. M., Eisenstein T. K. Immunosuppression induced by attenuated Salmonella. Evidence for mediation by macrophage precursors. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2737–2746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



