Abstract
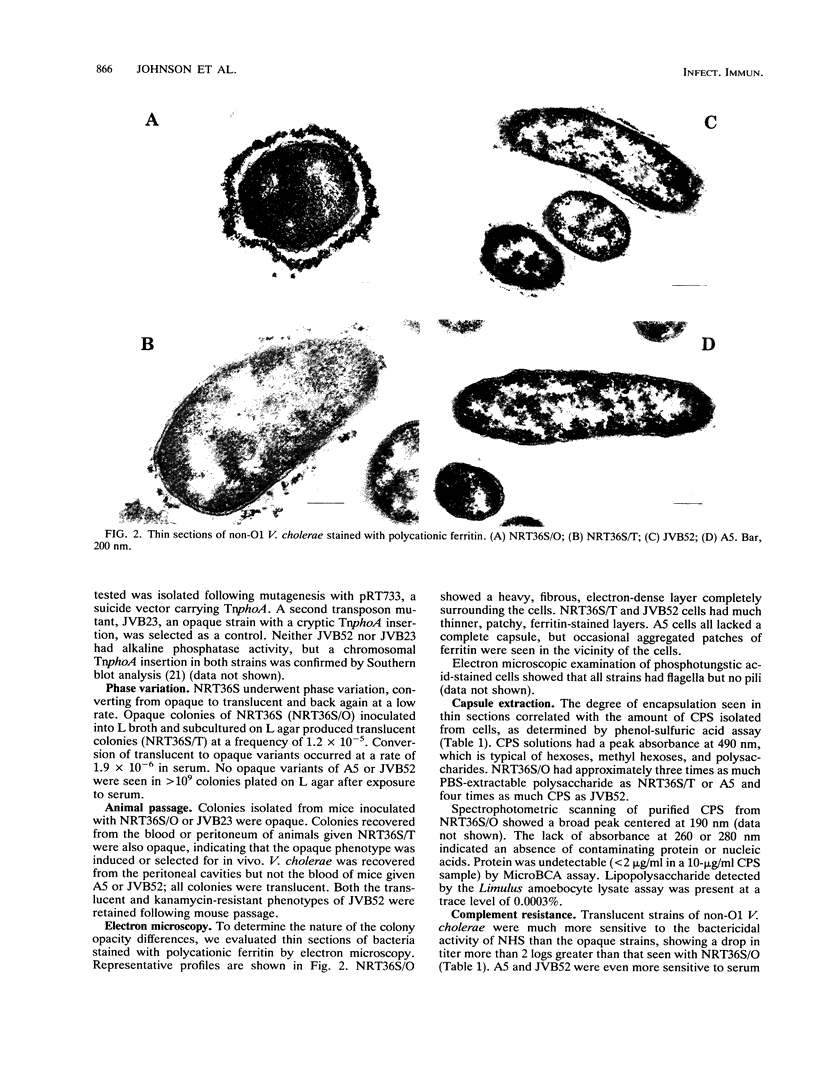
Non-O1 Vibrio cholerae produced two distinct colony types, designated as opaque and translucent. NRT36S, a clinical isolate shown to be virulent in volunteers, produced predominantly opaque colonies, but translucent colonies appeared on subculture. Opaque variants were recovered exclusively following exposure to normal human serum or animal passage. A nonreverting translucent mutant of NRT36S, JVB52, was isolated following mutagenesis with the transposon Tn5 IS50L::phoA (TnphoA). Only translucent colonies were produced by a nonpathogenic environmental isolate, A5. Electron microscopic examination of the opaque form of NRT36S revealed thick, electron-dense, fibrous capsules surrounding polycationic ferritin-stained cells. The ferritin-stained material around translucent NRT36S or A5 was patchy or absent. JVB52 had a thin but contiguous capsular layer. The amount of ferritin-stained capsular material correlated with the amount of surface polysaccharide determined by phenol-sulfuric acid assay: opaque NRT36S had approximately three times as much polysaccharide as translucent NRT36S or A5 and four times as much as JVB52. The encapsulated, opaque variant of NRT36S was protected from serum bactericidal activity, while translucent non-O1 V. cholerae was readily killed. The encapsulated form also had increased virulence in mice. Our data provide the first indication that non-O1 V. cholerae strains can have a polysaccharide capsule. This capsule may be important in protecting the organism from host defenses and may contribute to the ability of some non-O1 V. cholerae strains to cause septicemia in susceptible hosts.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldová E., Láznicková K., Stepánková E., Lietava J. Isolation of nonagglutinable vibrios from an enteritis outbreak in Czechoslovakia. J Infect Dis. 1968 Feb;118(1):25–31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arita M., Takeda T., Honda T., Miwatani T. Purification and characterization of Vibrio cholerae non-O1 heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):45–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.45-49.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G. Diseases of humans (other than cholera) caused by vibrios. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:341–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. R., Coker A. S., Berryman C. R., Pollock H. M. Spectrum of Vibrio infections in a Gulf Coast community. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Oct;99(4):464–469. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-4-464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulnois G. J., Roberts I. S. Genetics of capsular polysaccharide production in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:1–18. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovre K., Froholm L. O. Variation of colony morphology reflecting fimbriation in Moraxella bovis and two reference strains of M. nonliquefaciens. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(5):629–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäck E., Ljunggren A., Smith H., Jr Non-cholera Vibrios in Sweden. Lancet. 1974 Apr 20;1(7860):723–724. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92921-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers M. M., Kabat W. J. Vibrio vulnificus (lactose-positive vibrio) and Vibrio parahaemolyticus differ in their susceptibilities to human serum. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):964–966. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.964-966.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Irvin R. T., Cheng K. J. The bacterial glycocalyx in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:299–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S. The biologic significance of bacterial encapsulation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:87–95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fierer J., Finley F. Deficient serum bactericidal activity against Escherichia coli in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):912–921. doi: 10.1172/JCI109391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch M. J., Valdespino J. L., Wells J. G., Perez-Perez G., Arjona F., Sepulveda A., Bessudo D., Blake P. A. Non-01 Vibrio cholerae infections in Cancun, Mexico. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Mar;36(2):393–397. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques M., Gottschalk M., Foiry B., Higgins R. Ultrastructural study of surface components of Streptococcus suis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):2833–2838. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.2833-2838.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Calia F. M., Musher D. M., Goree A. Resistance of Vibrio vulnificus to serum bactericidal and opsonizing factors: relation to virulence in suckling mice and humans. J Infect Dis. 1984 Sep;150(3):413–418. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Black R. E. Cholera and other vibrioses in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 7;312(6):343–350. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502073120604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr Non-O group 1 Vibrio cholerae: a look at the epidemiology of an occasional pathogen. Epidemiol Rev. 1990;12:179–191. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Takeda T., Tall B. D., Losonsky G. A., Bhattacharya S. K., Forrest B. D., Kay B. A., Nishibuchi M. Experimental non-O group 1 Vibrio cholerae gastroenteritis in humans. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):697–705. doi: 10.1172/JCI114494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Wilson R., Davis B. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Riddle C. F., Wathen H. G., Pollard R. A., Blake P. A. Non-O group 1 Vibrio cholerae gastroenteritis in the United States: clinical, epidemiologic, and laboratory characteristics of sporadic cases. Ann Intern Med. 1981 May;94(5):656–658. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-5-656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Kroll J. S. The role of bacterial polysaccharide capsules as virulence factors. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:65–85. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. T., Baron L. S., Rubin F. A., Kopecko D. J. Specific insertion and deletion of insertion sequence 1-like DNA element causes the reversible expression of the virulence capsular antigen Vi of Citrobacter freundii in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4402–4405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panigrahi P., Tall B. D., Russell R. G., Detolla L. J., Morris J. G., Jr Development of an in vitro model for study of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae virulence using Caco-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3415–3424. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3415-3424.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roantree R. J., Rantz L. A. A STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP OF THE NORMAL BACTERICIDAL ACTIVITY OF HUMAN SERUM TO BACTERIAL INFECTION. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39(1):72–81. doi: 10.1172/JCI104029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safrin S., Morris J. G., Jr, Adams M., Pons V., Jacobs R., Conte J. E., Jr Non-O:1 Vibrio cholerae bacteremia: case report and review. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Sep-Oct;10(5):1012–1017. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.5.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert H. S., So M. Genetic mechanisms of bacterial antigenic variation. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Sep;52(3):327–336. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.3.327-336.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. M., White V. K., Zane S. F., Oliver J. D. Correlation between virulence and colony morphology in Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):269–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.269-272.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snellings N. J., Johnson E. M., Kopecko D. J., Collins H. H., Baron L. S. Genetic regulation of variable Vi antigen expression in a strain of Citrobacter freundii. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1010–1017. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1010-1017.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern A., Nickel P., Meyer T. F., So M. Opacity determinants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: gene expression and chromosomal linkage to the gonococcal pilus gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):447–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamplin M. L., Specter S., Rodrick G. E., Friedman H. Differential complement activation and susceptibility to human serum bactericidal action by Vibrio species. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1187–1190. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1187-1190.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Manoil C., Mekalanos J. J. Broad-host-range vectors for delivery of TnphoA: use in genetic analysis of secreted virulence determinants of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1870–1878. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1870-1878.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L. Virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:661–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. C., Simpson L. M., Oliver J. D., Morris J. G., Jr Phenotypic evaluation of acapsular transposon mutants of Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1769–1773. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1769-1773.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Ogawa M., Mizuguchi Y. Relation of capsular materials and colony opacity to virulence of Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):446–451. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.446-451.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Shawi N., Thewaini A. J. Non-agglutinable vibrios isolated in the 1966 epidemic of cholera in Irag. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;40(1):163–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]