Abstract
Background. Pancreatic cancer is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the world. Operative resection is the only therapeutic option with curative potential for this disease. Objective. The aim of the present study was to correlate clinical and pathologic parameters with survival in patients submitted to pancreatic resection for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Methods. Surgical resection with curative intent (R0 and R1 resections) was performed in 65 pancreatic cancer patients between 1990 and 2006. The overall results of surgical treatment were retrospectively analyzed and compared with the clinicopathologic features of these patients. Results. Pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy was performed in 37 patients (56.9%), classic resection in 35.4%, distal pancreatectomy in 4.6% and total pancreatectomy in 3.6%. The inhospital mortality was 5% (three patients). Postoperative complications occurred in 28 patients (43%). Mean survival and five-year survival rate after curative resection were 27 months and 9.0%, respectively. Sex, TNM stage, tumor differentiation, neural invasion, tumor size and involvement of resection margin were significant prognostic factors on univariate analysis. Multivariate analysis showed tumor differentiation and neural invasion as prognostic factors. Conclusion. Patients with pancreatic cancer, even those with poor prognostic factors should be given the opportunity of surgical resection with curative intent.
Keywords: adenocarcinoma, survival, prognosis, surgery, surgical pathology, pancreatoduodenectomy, pancreatectomy, pancreatic neoplasms
Introduction
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most fatal malignant diseases and ranks fifth in cancer mortality worldwide. Survival after resection remains disappointing, with five-year survival rates ranging from 10 to 29% 1,2,3. Advances in operative techniques and in perioperative care have increased the resecability of pancreatic cancer, and have decreased rates of operative morbidity and mortality 4,5,6,7. Despite these improvements long-term outcomes still remain disappointing because early recurrence still represents the main challenge for surgeons dealing with pancreatic cancer patients. Although some reports show five-year survival rates of 25–30% 1,8,9,10,11 in the great majority of the reported series patient survival for more than five years is rare 12,13,14,15,16.
The incidence of pancreatic cancer in the USA approaches 32,000 cases each year 16,17. And less than half of patients in the USA with Stage 1 disease are offered resection because of the persisting perception that resection is not worthwhile 18. In Brazil, 4% of cancer-related deaths are due to pancreatic cancer and the incidence is about six cases per 100,000 habitants 19.
Objective
The aim of the present study is to correlate clinical and pathologic findings with survival after attempted curative resection for pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Materials and methods
In the period between January of 1990 and December of 2006, 336 patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma were admitted at the Pancreatobiliary Surgical Unit of the São Paulo University Medical School Hospital. From this patient population 65 were submitted to surgical treatment with curative intention. The retrospective review of the medical records of these patients consists the basis of the present report. Patients with neuroendocrine and cystic pancreatic neoplasms, and those undergoing R2 resections were excluded. Patient demographics, clinical presentation and findings, and pathologic factors were evaluated to determine the prognostic factors after resection. Variables studied included: sex, age, portal vein resection, blood transfusion, type of pancreatic resection (Whipple, pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy, distal pancreatectomy, DP and total pancreatectomy, TP), postoperative complications (bleeding, pancreatic fistula and infection) 20,21,22, tumor size, tumor differentiation, lymph node status, neural invasion, margin status and Tumor, Nodal status and Metastaasis (TNM) staging (according to UICC-2002) 23.
Neoplasms were classified microscopically as well, moderate, or poorly differentiated tumors according to Kloppel 23.
Statistical analysis
Continuos variables were compared using either the two-sample t test or the Wilcox rank sum test depending on normally or non-normally distributed data, respectively. Nominal variables were compared using either the χ2 test or the Fisher's exact test. All calculated p values were two-sided and p value of less than or equal to 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Cumulative survival data were calculated using the Kaplan–Meier method. Cox regression model was used to calculate multivariate analysis and variables with significance at univariate model were included.
Results
Patient demographics, clinical factors
Sixty-five patients with the diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma underwent R0 or R1 resections. There were 37 females (57%) and 28 males (43%) with a mean age of 58 years (range 39–85 years). Weight loss was present in 79%, jaundice in 82.4% and nausea or vomiting in 25.4%. Thirty-eight percent of patients had new-onset diabetes mellitus.
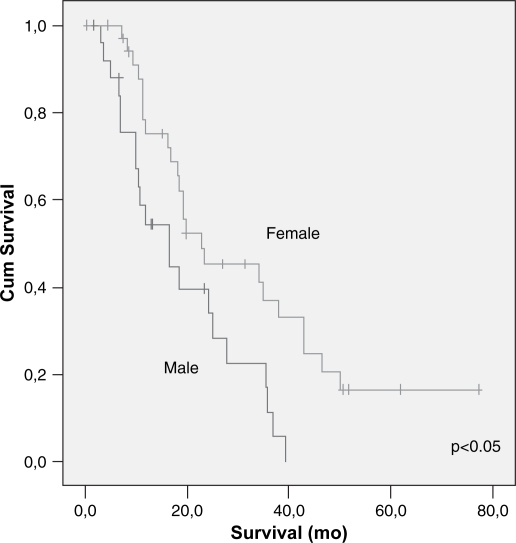
Race, age, weight loss, symptoms of upper Gastrointestinal (GI) obstruction, diabetes, jaundice, Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA), Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 (CA 19-9) levels were not identified as prognostic factors after resection for pancreatic cancer. Sex was the only parameter that showed statistical significance on univariate analysis (p<0.05) (Table I).
Table I. Demographic and pre-operative data.
| Variable | n | Median survival (mo) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Race | 0.28 | ||
| White | 43 | 26.3 | |
| Black | 12 | 17.8 | |
| Oriental | 7 | 32.5 | |
| Age (years) | 0.55 | ||
| < 60 | 36 | 24.5 | |
| > 60 | 26 | 29.2 | |
| Sex | 0.008 | ||
| Male | 26 | 18.2 | |
| Female | 36 | 33.0 | |
| Weight loss | 0.46 | ||
| No | 13 | 28.9 | |
| Yes | 47 | 26.6 | |
| Upper GI obstruction symptoms | 0.19 | ||
| No | 46 | 28.2 | |
| Yes | 15 | 19.9 | |
| Diabetes | 0.67 | ||
| No | 36 | 25.5 | |
| Yes | 24 | 26.3 | |
| Jaundice (TB > 3 mg/dl) | 0.56 | ||
| No | 21 | 30.5 | |
| Yes | 39 | 24.2 | |
| CEA (>5 ug/ml) | 0.25 | ||
| No | 20 | 24.8 | |
| Yes | 13 | 41.5 | |
| CA 19–9 (>200 ng/ml) | 0.09 | ||
| No | 22 | 33.2 | |
| Yes | 19 | 19.8 |
Operative procedures
Types of pancreatic resection were: pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy (PPPD) 37 (57%), classic Whipple (PD) 23 (35%), DP 3 (5%) and TP 2 (3%). Portal vein (PV) resection was performed on 10 patients (15%) in order to obtain an R0 resection. Mean operative time was 600 minutes. Intra-operative blood transfusion was needed in 32 patients (49%), with a median of two units. Pancreatic and bilioenteric anastomosis were externally drained through two separate abdominal stab incisions.
Morbidity and mortality
Postoperative complications occurred in 28 patients (43%), delayed gastric emptying (DGE) (33%) (16 Grade A, five Grade B and one Grade C) being the most common, followed by, pancreatic fistula (all Grade A) (25%), bleeding (12%) and infection (11%) 21,22,24. Four patients (6%) were re-operated because of bleeding (one Grade C and three Grade B) 21, three (one Grade C and two Grade B) of whom died because of systemic complications (in-hospital mortality of 5%). The median duration stay postoperatively was 15 days (range 7–46 days).
Prognostic factors
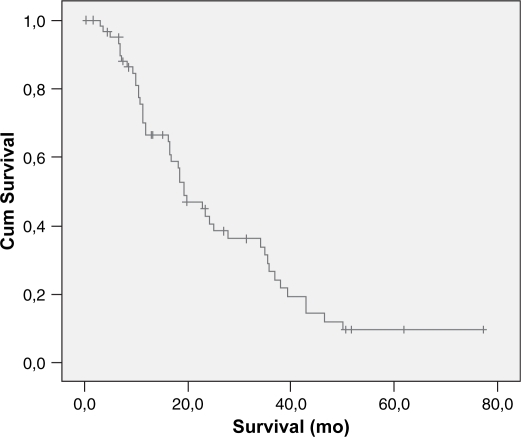
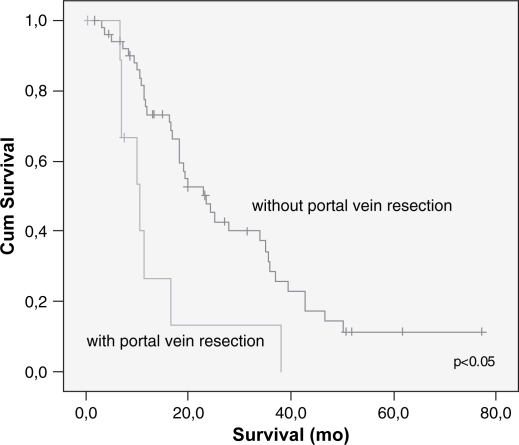
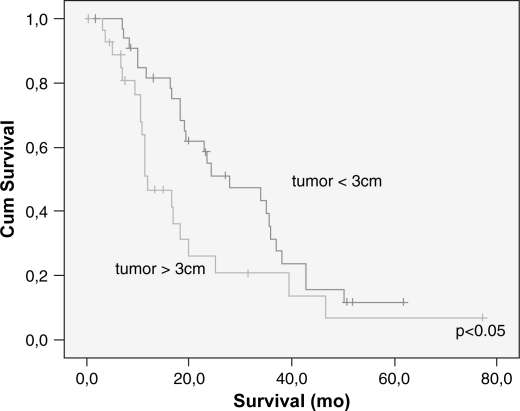
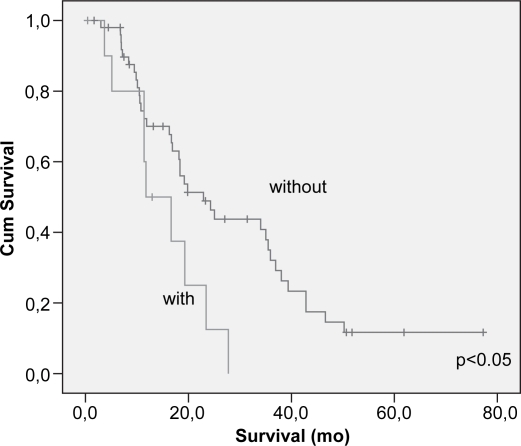
Overall cumulative survival is shown in Figure 1 and the five years survival rate was 9%. The type of pancreatic resection, amount of intra-operative bleeding, need for blood transfusion, DGE and the occurrence of postoperative complications did not correlate with the long-term survival. Patients submitted to PV resection had lesser survival than patients whose PV was not resected (14 vs. 29 months) (p<0.025) (Table II). Mean tumor size was 3.3 cm and most of them had moderate differentiation (68%). Vascular and neural invasion were present in 38 and 85%, respectively. A positive histologic margin (R1) was present in 20 patients (31%). Five (8%) patients were Stage IA, nine (14%) Stage IB, 13 (20%) Stage IIA, 36 (55%) Stage IIB and three (3%) Stage III. Mean follow-up and survival times were 21 and 27 months, respectively. Poorly differentiated tumors or those with neural invasion or a positive margin status also had lower survival rates (p<0.03 each).
Figure 1. .
Overall cumulative survival of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma submitted to surgical resection.
Table II. Surgical and peri-operative data.
| Variable | n | Mean survival±SEM (mo) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of pancreatectomy | 0.89 | ||
| PD | 22 | 28.9 (3.9) | |
| PPPD | 35 | 24.2 (3.2) | |
| Distal | 3 | ||
| Total | 2 | ||
| Intra-operative blood transfusion | 0.81 | ||
| No | 28 | 26.5 (3.9) | |
| Yes | 32 | 26.8 (3.7) | |
| Portal vein resection | 0.004 | ||
| No | 52 | 29.4 (3.2) | |
| Yes | 10 | 13.8 (3.8) | |
| PO complicationa | 0.11 | ||
| No | 35 | 23.4 (4.0) | |
| Yes | 25 | 29.5 (3.2) | |
| Pancreatic fistulaa | 0.96 | ||
| No | 45 | 27.6 (3.3) | |
| Yes | 14 | 24.7 (4.5) | |
| Delayed gastric emptyinga | 0.29 | ||
| No | 47 | 25.7 (3.3) | |
| Yes | 12 | 29.6 (4.6) | |
| Infection | 0.49 | ||
| No | 53 | 26.3 (3.2) | |
| Yes | 7 | 34.4 (6.6) | |
| Bleeding | 0.61 | ||
| No | 55 | 28.1 (3.3) | |
| Yes | 5 | 23.2 (7.3) |
aData not available for all patients.
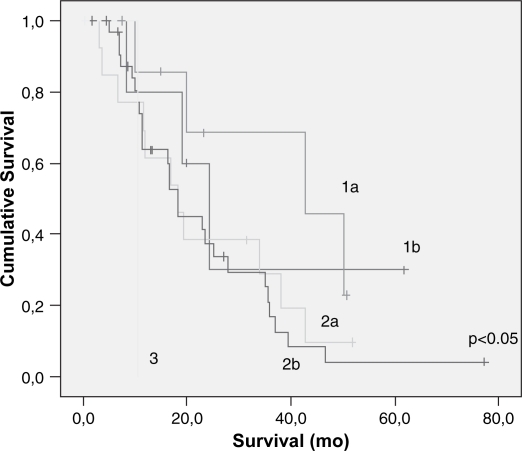
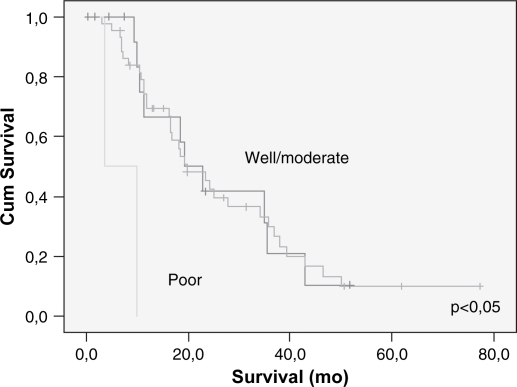
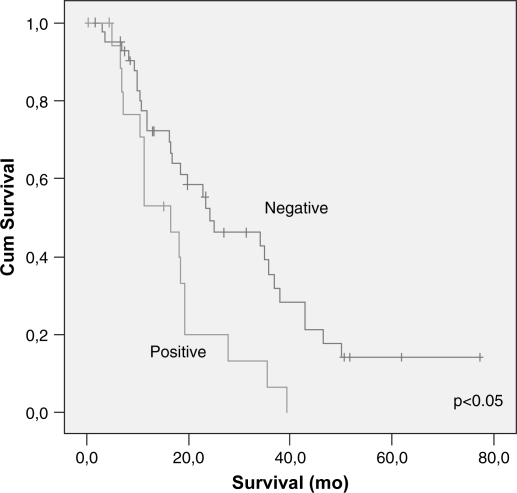
Lymph node metastasis and vascular invasion did not correlate with prolonged survival. In contrast, TNM stage, neural invasion, tumor differentiation, peri-pancreatic invasion, tumor size (>3 cm) and resection margin involvement all correlated with survival (p<0.05) (Table III) (Figures 23456789). On multivariate analysis, neural invasion and tumoral differentiation were significant (p<0.05) (Table IV).
Table III. Pathological data.
| Variable | n | Median survival±SEM (mo) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor size (>3 cm) | 0.04 | ||
| No | 34 | 29.9 (3.0) | |
| Yes | 28 | 21.0 (4.3) | |
| N stage | 0.09 | ||
| 0 | 27 | 30.0 (4.1) | |
| 1 | 35 | 22.9 (3.0) | |
| TNM | 0.05 | ||
| 1a | 58 | 31.3 (10.3) | |
| 1b | 13 | 37.6 (6.2) | |
| 2a | 34 | 23.0 (4.4) | |
| 2b | 2 | 23.3 (3.1) | |
| 3 | 10.5 (00) | ||
| Tumor differentiation | 0.001 | ||
| Well | 16 | 25.6 (4.2) | |
| Moderate | 44 | 27.8 (3.4) | |
| Poor | 2 | 6.8 (3.0) | |
| Neural invasion | 0.026 | ||
| No | 10 | 39.6 (5.5) | |
| Yes | 52 | 23.7 (2.8) | |
| Vascular invasion | 0.15 | ||
| No | 37 | 28.7 (3.3) | |
| Yes | 25 | 22.2 (3.7) | |
| Peri-pancreatic invasion | 0.023 | ||
| No | 51 | 26.6 (3.3) | |
| Yes | 11 | 15.2 (2.6) | |
| Tumor margin status | 0.006 | ||
| R0 | 43 | 31.6 (3.8) | |
| R1 | 19 | 17.1 (2.5) |
Figure 2. .
Cumulative survival according to TNM stages on univariate analysis.
Figure 3. .
Cumulative survival related to tumoral differentiation – univariate analysis.
Figure 4. .
Cumulative survival related to gender – univariate analysis.
Figure 5. .
Cumulative survival related to margin status – univariate analysis.
Figure 6. .
Cumulative survival related to perineural invasion on univariate analysis.
Figure 7. .
Cumulative survival related to portal vein resection on univariate analysis.
Figure 8. .
Cumulative survival related to tumor size on univariate analysis.
Figure 9. .
Cumulative survival related to peri-pancreatic tissue invasion on univariate analysis.
Table IV. Significant variables – multivariate analysis.
| Variable | P |
|---|---|
| Neural invasion | 0.03 |
| Tumor differentiation | 0.04 |
Discussion
In the early 1970s, pancreatoduodenectomy was not consistently performed for the management of pancreatic cancer, because according to some studies its results were similar to or even worse than bypass procedures 25,26. Nowadays, however, pancreatoduodenectomy can be performed in specialized centers for the surgical treatment of periampullary malignancies with a low operative mortality and morbidity 7,15,27,28. Many studies have demonstrated that this improvement was related to the concentration of this operation in high volume centers, specialized in pancreatic surgery 7,29. Furthermore, technical advances in operative technique and alternative methods for reconstruction of the alimentary tract after pancreatoduodenectomy 30,31,32,33,34 also contributed for these achievements and appear to be responsible for the good early results obtained in the present study. However, these improvements do not necessarily correlate with long-term postoperative survival 15,35, probably due to the heterogeneity of the clinicopathologic characteristics of pancreatic cancer 36,37. This diversity was also found in the present study and possibly counted for the poorer prognosis observed in male patients as there were more women than men with Stage I disease.
Although PV resection was undertaken in this series as an attempt to achieve an R0 resection, 31% of patients still had a positive surgical margin (R1 resection) despite the presumption of a “curative resection”. The finding of a worse prognosis in patients submitted to PV resection may be also attributed to the fact that these patients also presented with larger tumor sizes (p<0.05).
The present study demonstrated similar rates of R0 resection, lymph node involvement and status of surgical margin for both PPPD and PD procedures, in accordance with published randomized, controlled trials 38,39,40,41.
Although lymph node metastasis, poorly differentiated tumors and positive margins have been associated with a worse prognosis in some studies, 8,42,43, a few patients presenting some of these poor prognostic factors may live longer than expected 15,35, whereas other patients without bad prognostic factors will die early. In the present series, poorly differentiated tumors, neural invasion and the presence of positive resection margins were associated with a poor long-term outcome. In contrast, absence of lymph node metastasis was not a significant predictor of long-term survival. Schwarz and Smith demonstrated that an adequate assessment of lymph node involvement in pancreatic cancer depends on the number of nodes evaluated, what sometimes can occur when the surgeon dealing with this disease is not used to perform a reasonable amount of pancreaticoduodenectomies per year 44. The small number of retrieved lymph nodes and the variability of sampling in the present series may account for the lack of correlation observed between lymph node involvement and survival. Furthermore, occult tumor cells may be found in apparently tumor-free lymph nodes of pancreatic cancer patients and often overlooked in conventional histopathology 45. These micrometastases can, thus, impair prognosis, making it comparable to that of patients with true lymphatic metastases 46. Better methods such as molecular classification may improve patient selection and though stratifying the risk of occult metastatic disease. Current studies of our service are underway to evaluate the pathological specimen of this patients population looking for molecular markers (VEGF receptors, COX2, D2-40).
Long-term survival after pancreatoduodenectomy for pancreatic carcinoma is far from excellent. The five-year survival rate nears 10% and patients surviving more than five years are exceptional 15,35,47. The actual five-year survival rate of 9% reported herein is in accordance of other reports that could not show an improvement in long-term survival after operative resection of pancreatic cancer 3,35,47.
The results of the present study corroborates with the findings of other reports which point to the fact that surgical resection is the only hope for cure of patients with pancreatic cancer and, thus, this modality of treatment, followed by an effective adjuvant therapy, should always be offered to these patients.
References
- 1.Trede M, Schwall G, Saeger HD. Survival after pancreatoduodenectomy. 118 Consecutive resections without an operative mortality. Ann Surg. 1990;211(4):447–58. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199004000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Sohn TA, Lillemoe KD, Pitt HA, Talamini MA, et al. Six hundred fifty consecutive pancreaticoduodenectomies in the 1990s: pathology, complications, and outcomes. Ann Surg 1997;226(3):248–57; discussion 257–60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nitecki SS, Sarr MG, Colby TV, van Heerden JA. Long-term survival after resection for ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Is it really improving? Ann Surg. 1995;221(1):59–66. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199501000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Baumel H, Huguier M, Manderscheid JC, Fabre JM, Houry S, Fagot H. Results of resection for cancer of the exocrine pancreas: a study from the French Association of Surgery. Br J Surg. 1994;81(1):102–7. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800810138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Janes RH, Jr, Niederhuber JE, Chmiel JS, Winchester DP, Ocwieja KC, Karnell JH, et al. National patterns of care for pancreatic cancer. Results of a survey by the commission on cancer. Ann Surg. 1996;223(3):261–72. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199603000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yeo CJ, Cameron JL. Pancreatic cancer. Curr Probl Surg. 1999;36(2):59–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Buchler MW, Wagner M, Schmied BM, Uhl W, Friess H, Z'Graggen K. Changes in morbidity after pancreatic resection: toward the end of completion pancreatectomy. Arch Surg 2003;138(12):1310–4; discussion 1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Lillemoe KD, Sitzmann JV, Hruban RH, Goodman SN, et al. Pancreaticoduodenectomy for cancer of the head of the pancreas. 201 Patients. Ann Surg. 1995;221(6):721–31. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199506000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nagakawa T, Nagamori M, Futakami F, Tsukioka Y, Kayahara M, Ohta T, et al. Results of extensive surgery for pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer. 1996;77(4):640–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tsiotos GG, Farnell MB, Sarr MG. Are the results of pancreatectomy for pancreatic cancer improving? World J Surg. 1999;23(9):913–9. doi: 10.1007/s002689900599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Farnell MB, Nagorney DM, Sarr MG. The Mayo clinic approach to the surgical treatment of adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Surg Clin North Am. 2001;81(3):611–23. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(05)70147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Allema JH, Reinders ME, van Gulik TM, van Leeuwen DJ, Verbeek PC, de Wit LT, et al. Results of pancreaticoduodenectomy for ampullary carcinoma and analysis of prognostic factors for survival. Surgery. 1995;117(3):247–53. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6060(05)80197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Trede M, Richter A, Wendl K. Personal observations, opinions, and approaches to cancer of the pancreas and the periampullary area. Surg Clin North Am. 2001;81(3):595–610. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(05)70146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wagner M, Redaelli C, Lietz M, Seiler CA, Friess H, Buchler MW. Curative resection is the single most important factor determining outcome in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Br J Surg. 2004;91(5):586–94. doi: 10.1002/bjs.4484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Han SS, Jang JY, Kim SW, Kim WH, Lee KU, Park YH. Analysis of long-term survivors after surgical resection for pancreatic cancer. Pancreas. 2006;32(3):271–5. doi: 10.1097/01.mpa.0000202953.87740.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57(1):43–66. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.57.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C, et al. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56(2):106–30. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.56.2.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bilimoria KY, Bentrem DJ, Ko CY, Stewart AK, Winchester DP, Talamonti MS. National failure to operate on early stage pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg. 2007;246(2):173–80. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3180691579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Moraes VMD. Evolucäo do padräo alimentar e tendência da mortalidade por câncer de pâncreas nas capitais do Brasil, 1980–1997/Evolution of feeding behavior trends of the mortality the pancreatic neoplasms in Brazil states: 1980–1997, in Apresentada a Escola Nacional de Saúde Pública. 2002: Rio de Janeiro, Brasil. p. 106. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bassi C, Butturini G, Molinari E, Mascetta G, Salvia R, Falconi M, et al. Pancreatic fistula rate after pancreatic resection. The importance of definitions. Dig Surg. 2004;21(1):54–9. doi: 10.1159/000075943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wente MN, Veit JA, Bassi C, Dervenis C, Fingerhut A, Gouma DJ, et al. Postpancreatectomy hemorrhage (PPH): an International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS) definition. Surgery. 2007;142(1):20–5. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2007.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wente MN, Bassi C, Dervenis C, Fingerhut A, Gouma DJ, Izbicki JR, et al. Delayed gastric emptying (DGE) after pancreatic surgery: a suggested definition by the International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS) Surgery. 2007;142(5):761–8. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2007.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kloppel GEA. Hamilton SR, Aaeltonen LA. IARC Press; Lyon: 2000. Ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas, World Health Organization classification of tumours, pathology of tumours of the digestive tract; pp. 221–30. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bassi C, Dervenis C, Butturini G, Fingerhut A, Yeo C, Izbicki J, et al. Postoperative pancreatic fistula: an international study group (ISGPF) definition. Surgery. 2005;138(1):8–13. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2005.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Crile G., Jr The advantages of bypass operations over radical pancreatoduodenectomy in the treatment of pancreatic carcinoma. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1970;130(6):1049–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shapiro TM. Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: a statistical analysis of biliary bypass vs Whipple resection in good risk patients. Ann Surg. 1975;182(6):715–21. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197512000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Neoptolemos JP, Russell RC, Bramhall S, Theis B. Low mortality following resection for pancreatic and periampullary tumours in 1026 patients: UK survey of specialist pancreatic units. UK Pancreatic Cancer Group. Br J Surg. 1997;84(10):1370–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sosa JA, Bowman HM, Gordon TA, Bass EB, Yeo CJ, Lillemoe KD, et al. Importance of hospital volume in the overall management of pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg. 1998;228(3):429–38. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199809000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cameron JL, Riall TS, Coleman J, Belcher KA. One thousand consecutive pancreaticoduodenectomies. Ann Surg. 2006;244(1):10–5. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000217673.04165.ea. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Machado MC, da Cunha JE, Bacchella T, Bove P. A modified technique for the reconstruction of the alimentary tract after pancreatoduodenectomy. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1976;143(2):271–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Traverso LW, Longmire WP., Jr Preservation of the pylorus in pancreaticoduodenectomy. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1978;146(6):959–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Machado MC, Figueira ER, Machado MA, Jukemura J, Cunha JE, Perini MV, et al. Portal vein resection: a modified technique for reconstruction after pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Surg Oncol. 2004;88(1):52–4. doi: 10.1002/jso.20114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Varty PP, Yamamoto H, Farges O, Belghiti J, Sauvanet A. Early retropancreatic dissection during pancreaticoduodenectomy. Am J Surg. 2005;189(4):488–91. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2005.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jain S, Sacchi M, Vrachnos P, Lygidakis NJ. Carcinoma of the pancreas with portal vein involvement – our experience with a modified technique of resection. Hepatogastroenterology. 2005;52(65):1596–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cooperman AM. Pancreatic cancer: the bigger picture. Surg Clin North Am. 2001;81(3):557–74. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(05)70143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Youmans R, McGee JM, Lee J, Malnar K, Bellefeuille C, Berry B. Surgical treatment of cancer of the pancreas in large community hospitals. J Okla State Med Assoc. 1996;89(1):16–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Takai S, Satoi S, Toyokawa H, Yanagimoto H, Sugimoto N, Tsuji K, et al. Clinicopathologic evaluation after resection for ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: a retrospective, single-institution experience. Pancreas. 2003;26(3):243–9. doi: 10.1097/00006676-200304000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lin PW, Lin YJ. Prospective randomized comparison between pylorus-preserving and standard pancreaticoduodenectomy. Br J Surg. 1999;86(5):603–7. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2168.1999.01074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Seiler CA, Wagner M, Sadowski C, Kulli C, Buchler MW. Randomized prospective trial of pylorus-preserving vs. Classic duodenopancreatectomy (Whipple procedure): initial clinical results. J Gastrointest Surg. 2000;4(5):443–52. doi: 10.1016/s1091-255x(00)80084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tran KT, Smeenk HG, van Eijck CH, Kazemier G, Hop WC, Greve JW, et al. Pylorus preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy versus standard Whipple procedure: a prospective, randomized, multicenter analysis of 170 patients with pancreatic and periampullary tumors. Ann Surg. 2004;240(5):738–45. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000143248.71964.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lin PW, Shan YS, Lin YJ, Hung CJ. Pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic head cancer: PPPD versus Whipple procedure. Hepatogastroenterology. 2005;52(65):1601–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Allison DC, Piantadosi S, Hruban RH, Dooley WC, Fishman EK, Yeo CJ, et al. DNA content and other factors associated with ten-year survival after resection of pancreatic carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 1998;67(3):151–9. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9098(199803)67:3<151::aid-jso2>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Cleary SP, Gryfe R, Guindi M, Greig P, Smith L, Mackenzie R, et al. Prognostic factors in resected pancreatic adenocarcinoma: analysis of actual 5-year survivors. J Am Coll Surg. 2004;198(5):722–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2004.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Schwarz RE, Smith DD. Extent of lymph node retrieval and pancreatic cancer survival: information from a large US population database. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13(9):1189–200. doi: 10.1245/s10434-006-9016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Milsmann C, Fuzesi L, Werner C, Becker H, Horstmann O. Significance of occult lymphatic tumor spread in pancreatic cancer] Chirurg. 2005;76(11):1064–72. doi: 10.1007/s00104-005-1041-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Demeure MJ, Doffek KM, Komorowski RA, Wilson SD. Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: detection of occult metastases in regional lymph nodes by a polymerase chain reaction-based assay. Cancer. 1998;83(7):1328–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mosca F, Giulianotti PC, Balestracci T, Di Candio G, Pietrabissa A, Sbrana F, et al. Long-term survival in pancreatic cancer: pylorus-preserving versus Whipple pancreatoduodenectomy. Surgery. 1997;122(3):553–66. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6060(97)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]