Abstract
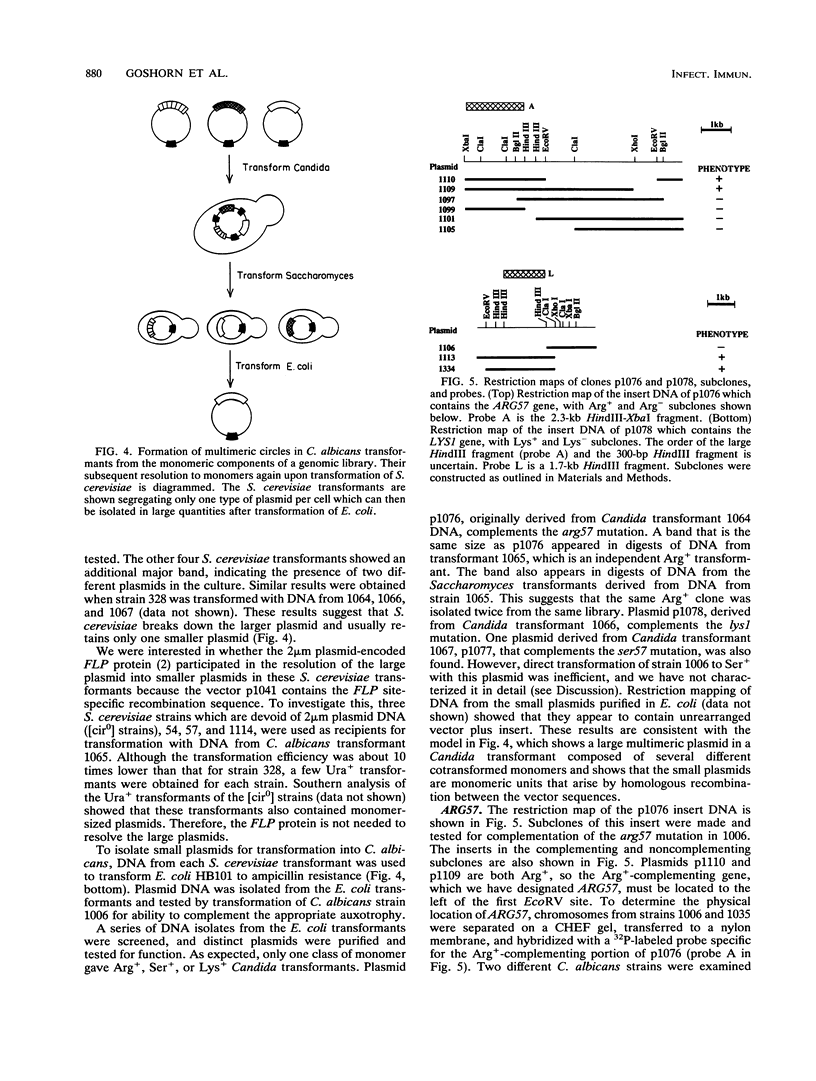
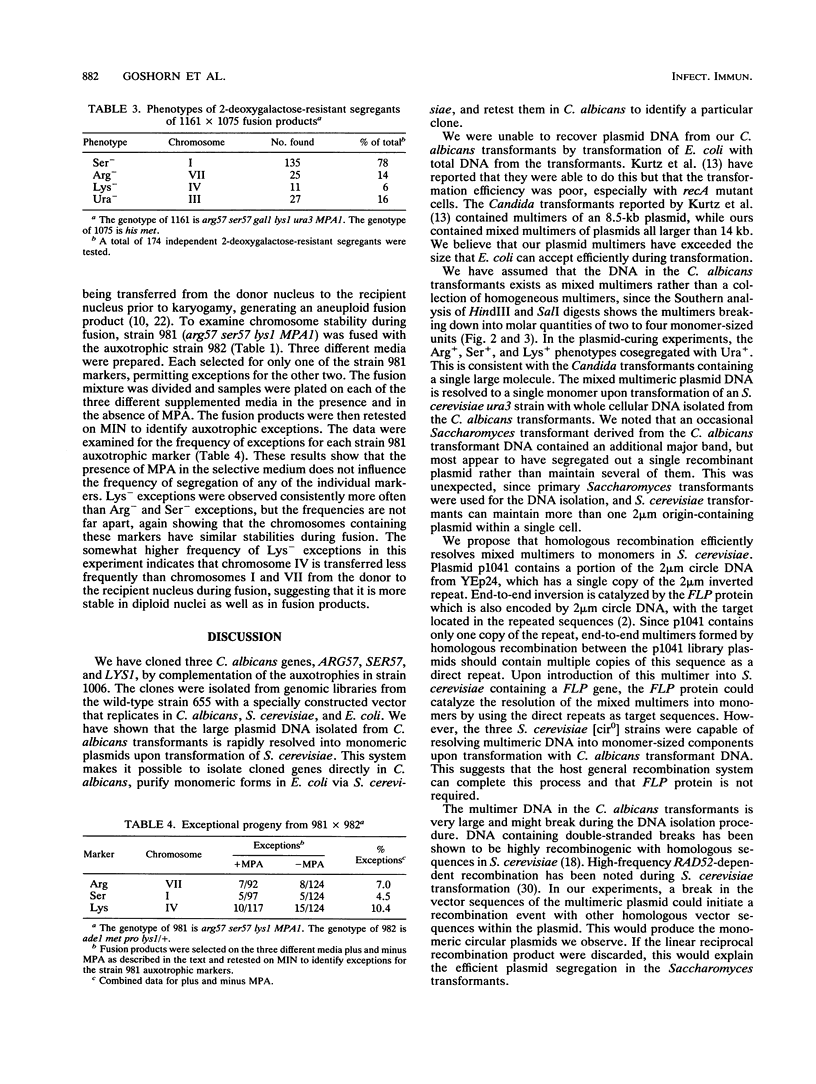
We have isolated three genes, ARG57, SER57, and LYS1, on the basis of their function in Candida albicans. A C. albicans transformation vector containing the C. albicans URA3 gene, a Candida ARS sequence, and a portion of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae 2 microns circle containing the replication origin was constructed. Clones from genomic libraries in this vector were isolated by direct complementation of the auxotrophies in strain 1006 (arg57 ser57 lys1 ura3 MPA1). Transformants typically contain two to four plasmids in a mixed tandem multimer. A scheme to resolve mixed multimers into monomers in vivo by transformation of S. cerevisiae with Candida transformant DNA selecting Ura+ transformants was devised. Monomeric plasmids were then isolated by transformation of Escherichia coli with the S. cerevisiae transformant DNA. These were retested by transformation of strain 1006 to identify the specific plasmid that complemented the auxotrophy. The chromosomal locations of the genes were determined by hybridization to C. albicans chromosomes separated on contour-clamped homogenous electric field gels. We used these locations to assess the stability of individual C. albicans chromosomes in parasexual genetic analysis. The Lys(+)-complementing clone was shown to be LYS1 by complementation of S. cerevisiae lys1 mutants. These cloned genes help to align the Candida physical and genetic maps and provide additional markers for the transformation system.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botstein D., Falco S. C., Stewart S. E., Brennan M., Scherer S., Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Sterile host yeasts (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutcher S. K. Internuclear transfer of genetic information in kar1-1/KAR1 heterokaryons in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):245–253. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum A. M., Tsay E. Y., Kirsch D. R. Isolation of the Candida albicans gene for orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase by complementation of S. cerevisiae ura3 and E. coli pyrF mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;198(2):179–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00328721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goshorn A. K., Scherer S. Genetic analysis of prototrophic natural variants of Candida albicans. Genetics. 1989 Dec;123(4):667–673. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.4.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton C., Markie D., Corner B., Rikkerink E., Poulter R. Heat shock induces chromosome loss in the yeast Candida albicans. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(1):162–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00383330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakar S. N., Partridge R. M., Magee P. T. A genetic analysis of Candida albicans: isolation of a wide variety of auxotrophs and demonstration of linkage and complementation. Genetics. 1983 Jun;104(2):241–255. doi: 10.1093/genetics/104.2.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R., Miller S. M., Kurtz M. B., Kirsch D. R. Directed mutagenesis in Candida albicans: one-step gene disruption to isolate ura3 mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):199–208. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz M. B., Cortelyou M. W., Kirsch D. R. Integrative transformation of Candida albicans, using a cloned Candida ADE2 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):142–149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz M. B., Cortelyou M. W., Miller S. M., Lai M., Kirsch D. R. Development of autonomously replicating plasmids for Candida albicans. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):209–217. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lott T. J., Page L. S., Boiron P., Benson J., Reiss E. Nucleotide sequence of the Candida albicans aspartyl proteinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1779–1779. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason M. M., Lasker B. A., Riggsby W. S. Molecular probe for identification of medically important Candida species and Torulopsis glabrata. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):563–566. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.563-566.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter R. T., Rikkerink E. H. Genetic analysis of red, adenine-requiring mutants of Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1066–1077. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1066-1077.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter R., Jeffery K., Hubbard M. J., Shepherd M. G., Sullivan P. A. Parasexual genetic analysis of Candida albicans by spheroplast fusion. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):833–840. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.833-840.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Davis R. W. Replacement of chromosome segments with altered DNA sequences constructed in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4951–4955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Magee P. T. Genetics of Candida albicans. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Sep;54(3):226–241. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.3.226-241.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Stevens D. A. A Candida albicans dispersed, repeated gene family and its epidemiologic applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1452–1456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Stevens D. A. Application of DNA typing methods to epidemiology and taxonomy of Candida species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):675–679. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.675-679.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd M. G., Poulter R. T., Sullivan P. A. Candida albicans: biology, genetics, and pathogenicity. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:579–614. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. A., Allaudeen H. S., Whitman M. H., Koltin Y., Gorman J. A. Isolation and characterization of a beta-tubulin gene from Candida albicans. Gene. 1988;63(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90545-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Rogers A. L., Magee P. T. Inter- and intra-species crosses between Candida albicans and Candida guilliermondii. Yeast. 1986 Mar;2(1):53–58. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. High frequency excision of Ty elements during transformation of yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2989–3001. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Resolution of DNA molecules greater than 5 megabases by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7865–7876. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan W. L., Markie D. M., Simpkin K. G., Poulter R. M. Instability of Candida albicans hybrids. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1131–1136. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1131-1136.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickes B., Staudinger J., Magee B. B., Kwon-Chung K. J., Magee P. T., Scherer S. Physical and genetic mapping of Candida albicans: several genes previously assigned to chromosome 1 map to chromosome R, the rDNA-containing linkage group. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2480–2484. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2480-2484.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]