Abstract
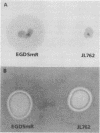
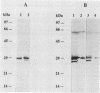
A phospholipase-deficient mutant, termed JL762, was obtained from a virulent strain of Listeria monocytogenes by screening a bank of 5,000 Tn1545 transposon-induced mutants on 2.5% egg yolk brain heart infusion agar. As previously shown (J. Mengaud, C. Geoffroy, and P. Cossart, Infect. Immun. 59:1043-1049, 1991), the transposon insertion took place inside the gene mpl, which encodes a zinc metalloprotease. By Western blot (immunoblot) analysis, we showed that loss of phospholipase activity was associated with loss of a 29-kDa zinc-dependent phosphatidylcholine-phospholipase C (PC-PLC) in culture supernatant of JL762 and of EGD-SmR incubated with ion chelator. As the parental strain, JL762 still produced in supernatants approximately 33-kDa proteins antigenically closely related to the 29-kDa PC-PLC. These results strongly suggest that the zinc metalloprotease of L. monocytogenes might play a role in the maturation of the 29-kDa PC-PLC. Although the uptake and the intracellular growth of bacteria were not affected in vitro, we found that the virulence of mutant JL762 was strongly impaired in the mouse.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alouf J. E. Streptococcal toxins (streptolysin O, streptolysin S, erythrogenic toxin). Pharmacol Ther. 1980;11(3):661–717. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielecki J., Youngman P., Connelly P., Portnoy D. A. Bacillus subtilis expressing a haemolysin gene from Listeria monocytogenes can grow in mammalian cells. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):175–176. doi: 10.1038/345175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Vicente M. F., Mengaud J., Baquero F., Perez-Diaz J. C., Berche P. Listeriolysin O is essential for virulence of Listeria monocytogenes: direct evidence obtained by gene complementation. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3629–3636. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3629-3636.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domann E., Leimeister-Wächter M., Goebel W., Chakraborty T. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and identification of a metalloprotease gene from Listeria monocytogenes that is species specific and physically linked to the listeriolysin gene. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):65–72. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.65-72.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Sansonetti P. Transposon mutagenesis as a tool to study the role of hemolysin in the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.50-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy C., Gaillard J. L., Alouf J. E., Berche P. Purification, characterization, and toxicity of the sulfhydryl-activated hemolysin listeriolysin O from Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1641–1646. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1641-1646.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy C., Raveneau J., Beretti J. L., Lecroisey A., Vazquez-Boland J. A., Alouf J. E., Berche P. Purification and characterization of an extracellular 29-kilodalton phospholipase C from Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2382–2388. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2382-2388.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Synthesis and secretion of interferon by murine fibroblasts in response to intracellular Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):787–792. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.787-792.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins E. M., Watson B. B. Extracellular Antigens from Listeria monocytogenes I. Purification and Resolution of Hemolytic and Lipolytic Antigens from Culture Filtrates of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):589–594. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.589-594.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kathariou S., Metz P., Hof H., Goebel W. Tn916-induced mutations in the hemolysin determinant affecting virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1291–1297. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1291-1297.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. A., Seaman T. A., Woodbine M. Listeria monocytogenes-haemolysin: lecithinase. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1973 Oct;225(1):66–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Domann E., Chakraborty T. Detection of a gene encoding a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C that is co-ordinately expressed with listeriolysin in Listeria monocytogenes. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):361–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Braun-Breton C., Cossart P. Identification of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity in Listeria monocytogenes: a novel type of virulence factor? Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Dramsi S., Gouin E., Vazquez-Boland J. A., Milon G., Cossart P. Pleiotropic control of Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors by a gene that is autoregulated. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2273–2283. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Geoffroy C., Cossart P. Identification of a new operon involved in Listeria monocytogenes virulence: its first gene encodes a protein homologous to bacterial metalloproteases. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1043–1049. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1043-1049.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel E., Reich K. A., Favier R., Berche P., Cossart P. Attenuated mutants of the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes obtained by single amino acid substitutions in listeriolysin O. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2167–2178. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier J., Ryter A., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular and cell-to-cell spread of Listeria monocytogenes involves interaction with F-actin in the enterocytelike cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1048–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1048-1058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möllby R., Holme T., Nord C. E., Smyth C. J., Wadström T. Production of phospholipase C (alpha-toxin), haemolysins and lethal toxins by Clostridium perfringens types A to D. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Sep;96(1):137–144. doi: 10.1099/00221287-96-1-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NJOKU-OBI A. N., JENKINS E. M., NJOKU-OBI J. C., ADAMS J., COVINGTON V. PRODUCTION AND NATURE OF LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES HEMOLYSINS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:1–8. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.1-8.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rácz P., Tenner K., Mérö E. Experimental Listeria enteritis. I. An electron microscopic study of the epithelial phase in experimental listeria infection. Lab Invest. 1972 Jun;26(6):694–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rácz P., Tenner K., Szivessy K. Electron microscopic studies in experimental keratoconjunctivitis listeriosa. I. Penetration of Listeria monocytogenes into corneal epithelial cells. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1970;17(3):221–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddique I. H., Lin I. F., Chung R. A. Purification and characterization of hemolysin produced by Listeria monocytogenes. Am J Vet Res. 1974 Feb;35(2):289–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUBENECK U. Susceptibility of Proteus mirabilis and its stable L-forms to erythromycin and other macrolides. Nature. 1962 Oct 13;196:195–196. doi: 10.1038/196195b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Connelly P. S., Portnoy D. A. Actin filament nucleation by the bacterial pathogen, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2979–2988. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Boland J. A., Kocks C., Dramsi S., Ohayon H., Geoffroy C., Mengaud J., Cossart P. Nucleotide sequence of the lecithinase operon of Listeria monocytogenes and possible role of lecithinase in cell-to-cell spread. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):219–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.219-230.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson B. B., Lavizzo J. C. Extracellular antigens from Listeria monocytogenes. II. Cytotoxicity of hemolytic and lipolytic antigens of Listeria for cultured mouse macrophages. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):753–758. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.753-758.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]