Abstract
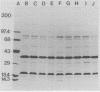
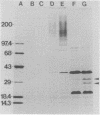
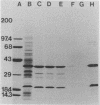
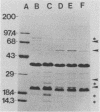
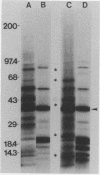
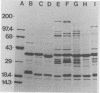
The outer membrane proteins of Bordetella avium were examined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Sarkosyl-insoluble outer membrane protein-enriched profiles from 50 virulent B. avium isolates, containing major 21,000- and 37,000-molecular-weight proteins (21K and 37K proteins, respectively) and at least 13 less intensely stained proteins with molecular weights ranging from 13,500 to 143,000, were very similar. The 21K, 27K, 31K, and 37K outer membrane proteins were shown to be associated noncovalently with the underlying peptidoglycan layer. It was necessary to treat cell envelopes with 2% sodium dodecyl sulfate and at temperatures in excess of 60 degrees C for 15 min to release these proteins. Exposure of proteins on the cell surface of B. avium was assessed by labeling with 125I followed by electrophoresis. As many as 13 bands were present in profiles from labeled whole cells. Of the surface-labeled bands, eight corresponded to bands in a radiolabeled outer membrane preparation. The outer membrane protein profile of B. avium was compared with profiles from other Bordetella spp., including 20 B. avium-like and 16 B. bronchiseptica strains isolated from turkeys. The outer membrane protein profile of B. avium was distinctly different from those of the other bordetella. The effect of variations in the growth medium on the expression of outer membrane proteins of B. avium was examined. Expression of 22K, 26K, 56K, and 73K proteins was decreased or eliminated by addition of 50 mM MgSO4 to the medium.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aricó B., Miller J. F., Roy C., Stibitz S., Monack D., Falkow S., Gross R., Rappuoli R. Sequences required for expression of Bordetella pertussis virulence factors share homology with prokaryotic signal transduction proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6671–6675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong S. K., Parker C. D. Heat-modifiable envelope proteins of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):109–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.109-117.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong S. K., Parker C. D. Surface proteins of Bordetella pertussis: comparison of virulent and avirulent strains and effects of phenotypic modulation. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):308–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.308-314.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong S. K., Parr T. R., Jr, Parker C. D., Hancock R. E. Bordetella pertussis major outer membrane porin protein forms small, anion-selective channels in lipid bilayer membranes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):212–216. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.212-216.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arp L. H., Cheville N. F. Tracheal lesions in young turkeys infected with Bordetella avium. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Oct;45(10):2196–2200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arp L. H., Fagerland J. A. Ultrastructural pathology of Bordetella avium infection in turkeys. Vet Pathol. 1987 Sep;24(5):411–418. doi: 10.1177/030098588702400508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arp L. H., Hellwig D. H. Passive immunization versus adhesion of Bordetella avium to the tracheal mucosa of turkeys. Avian Dis. 1988 Jul-Sep;32(3):494–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arp L. H., Leyh R. D., Griffith R. W. Adherence of Bordetella avium to tracheal mucosa of turkeys: correlation with hemagglutination. Am J Vet Res. 1988 May;49(5):693–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Subtyping isolates of Haemophilus influenzae type b by outer-membrane protein profiles. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):668–676. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes H. J., Hofstad M. S. Susceptibility of turkey poults from vaccinated and unvaccinated hens to alcaligenes rhinotracheitis (turkey coryza). Avian Dis. 1983 Apr-Jun;27(2):378–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R. Structure and function of porins from gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:359–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhoff H. A., Riddle G. D. Differentiation of Alcaligenes-like bacteria of avian origin and comparison with Alcaligenes spp. reference strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;19(4):477–481. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.4.477-481.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. S., Jensen M. M. Immunization against turkey coryza by colonization with mutants of Alcaligenes faecalis. Avian Dis. 1980 Jul-Sep;24(3):726–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezzell J. W., Dobrogosz W. J., Kloos W. E., Manclark C. R. Phase-shift markers in Bordetella: alterations in envelope proteins. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):562–569. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry-Weeks C. R., Cookson B. T., Goldman W. E., Rimler R. B., Porter S. B., Curtiss R., 3rd Dermonecrotic toxin and tracheal cytotoxin, putative virulence factors of Bordetella avium. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1698–1707. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1698-1707.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry-Weeks C. R., Provence D. L., Keith J. M., Curtiss R., 3rd Isolation and characterization of Bordetella avium phase variants. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4026–4033. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4026-4033.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. G., Roberts J. F., Dillman R. C., Simmons D. G. Pathogenesis of change in the upper respiratory tracts of turkeys experimentally infected with an Alcaligenes faecalis isolate. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):350–355. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.350-355.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R., Rappuoli R. Positive regulation of pertussis toxin expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3913–3917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Carey A. M. Outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: heat- 2-mercaptoethanol-modifiable proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):902–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.902-910.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellwig D. H., Arp L. H., Fagerland J. A. A comparison of outer membrane proteins and surface characteristics of adhesive and non-adhesive phenotypes of Bordetella avium. Avian Dis. 1988 Oct-Dec;32(4):787–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellwig D. H., Arp L. H. Identification of Bordetella avium antigens recognized after experimental inoculation in turkeys. Am J Vet Res. 1990 Aug;51(8):1188–1191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackwood M. W., Saif Y. M., Moorhead P. D., Dearth R. N. Further characterization of the agent causing coryza in turkeys. Avian Dis. 1985 Jul-Sep;29(3):690–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackwood M. W., Saif Y. M. Pili of Bordetella avium: expression, characterization, and role in in vitro adherence. Avian Dis. 1987 Apr-Jun;31(2):277–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackwood M. W., Sasser M., Saif Y. M. Contribution to the taxonomy of the turkey coryza agent: cellular fatty acid analysis of the bacterium. Avian Dis. 1986 Jan-Mar;30(1):172–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACEY B. W. Antigenic modulation of Bordetella pertussis. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Mar;58:57–93. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luginbuhl G. H., Rader J. M., Simmons D. G. Evidence for plasmid DNA in Alcaligenes faecalis. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Aug;45(8):1679–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton A. R., Weiss A. A. Environmental regulation of expression of virulence determinants in Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6206–6212. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6206-6212.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parton R., Wardlaw A. C. Cell-envelope proteins of Bordetella pertussis. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):47–57. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp V. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Ross R. F. Outer membrane protein profiles of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):414–420. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.414-420.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redinbaugh M. G., Turley R. B. Adaptation of the bicinchoninic acid protein assay for use with microtiter plates and sucrose gradient fractions. Anal Biochem. 1986 Mar;153(2):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D. A., Domenighini M., Tuomanen E., Rappuoli R., Falkow S. Filamentous hemagglutinin of Bordetella pertussis: nucleotide sequence and crucial role in adherence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2637–2641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson K., Parker C. D. Identification and characterization of Vibrio cholerae surface proteins by radioiodination. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):87–93. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.87-93.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A., Hawkins D. C. Structure and biological properties of solubilized envelope proteins of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):590–598. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.590-598.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif Y. M., Moorhead P. D., Dearth R. N., Jackwood D. J. Observations on Alcaligenes faecalis infection in turkeys. Avian Dis. 1980 Jul-Sep;24(3):665–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. G., Gray J. G., Rose L. P., Dillman R. C., Miller S. E. Isolation of an etiologic agent of acute respiratory disease (rhinotracheitis) of turkey poults. Avian Dis. 1979 Jan-Mar;23(1):194–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. G., Rose L. P., Brogden K. A., Rimler R. B. Partial characterization of the hemagglutinin of Alcaligenes faecalis. Avian Dis. 1984 Jul-Sep;28(3):700–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavik M. F., Skeeles J. K., Beasley J. N., Harris G. C., Roblee P., Hellwig D. Effect of humidity on infection of turkeys with Alcaligenes faecalis. Avian Dis. 1981 Oct-Dec;25(4):936–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Aaronson W., Monack D., Falkow S. Phase variation in Bordetella pertussis by frameshift mutation in a gene for a novel two-component system. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):266–269. doi: 10.1038/338266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of phase change in Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):263–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.263-269.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]