Abstract
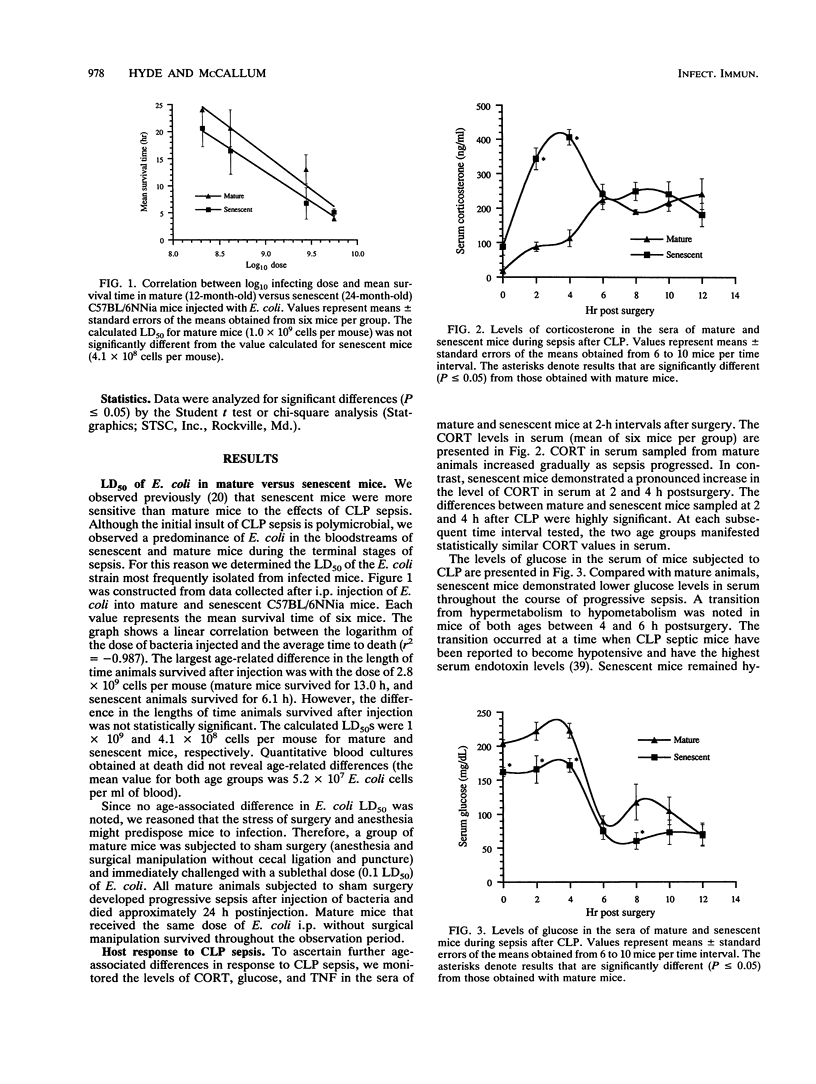
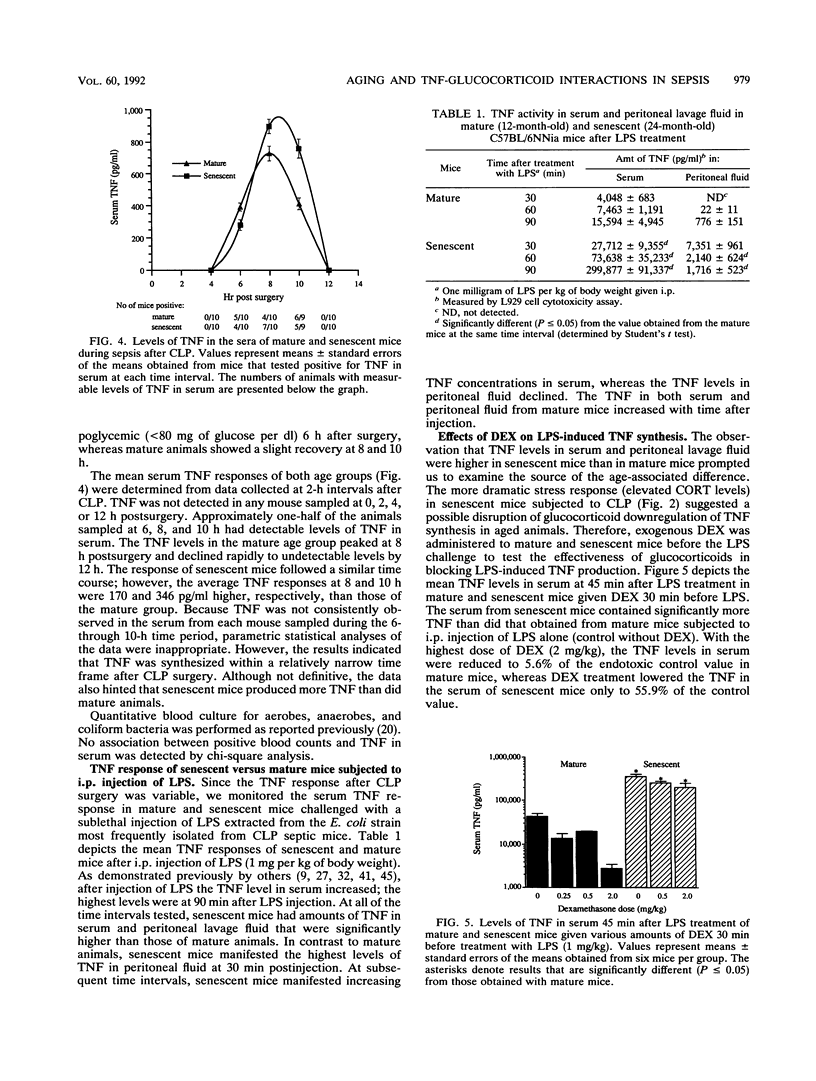
Previous work in our laboratory demonstrated increased sensitivity of senescent (24-month-old) mice to cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) sepsis compared with that of mature (12-month-old) mice. In this study the median lethal dose of the strain of Escherichia coli most frequently isolated during CLP sepsis was determined. No significant age-associated difference in the mean lethal dose or the mean survival time was noted; however, sham surgery before injection of E. coli decreased the mean lethal dose by at least 100-fold. With surgical manipulation, the average time to death after bacterial injection simulated more closely that observed after CLP surgery. Host responses to CLP sepsis were investigated by measuring the levels of corticosterone, glucose, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in the sera of mature and senescent mice at 2-h intervals after surgery. Corticosterone levels increased gradually during the course of sepsis in mature mice; however, senescent mice demonstrated a pronounced elevation in hormone levels at 2 and 4 h after surgery. At subsequent sampling intervals the corticosterone levels remained elevated, although they were similar for both ages. At all sampling intervals, the glucose levels in serum were lower in senescent mice than in mature mice. Pronounced hypoglycemia (less than 80 mg/dl) was observed in senescent mice at 8 h postsurgery. TNF was detected in serum within a narrow time frame in both age groups at 6, 8, and 10 h postsurgery. Although elevated TNF levels in serum were not seen in every mouse in each group (approximately 50%), the data hinted that senescent animals produced larger quantities of TNF during CLP sepsis than did mature animals. E. coli lipopolysaccharide (1 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally, and the TNF levels in serum and peritoneal lavage fluid were measured at 30, 60, and 90 min. Senescent mice demonstrated a level of TNF in serum at 90 min after lipopolysaccharide treatment that was 20-fold higher than that of mature mice (299,877 pg/ml versus 15,594 pg/ml). The amount of TNF produced locally in the peritoneum was also substantially higher in senescent mice than in mature animals (1,716 pg/ml versus 776 pg/ml). The increased production of TNF in senescent animals, despite elevated circulating corticosterone levels, suggested an age-related defect in glucocorticoid-directed downregulation of TNF production. This was confirmed in lipopolysaccharide-treated animals given exogenous dexamethasone.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagby G. J., Plessala K. J., Wilson L. A., Thompson J. J., Nelson S. Divergent efficacy of antibody to tumor necrosis factor-alpha in intravascular and peritonitis models of sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):83–88. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Chaudry I. H., Gaines H. O., Baue A. E. Evaluation of factors affecting mortality rate after sepsis in a murine cecal ligation and puncture model. Surgery. 1983 Aug;94(2):331–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauss F., Dröge W., Männel D. N. Tumor necrosis factor mediates endotoxic effects in mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1622–1625. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1622-1625.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Brown T. A CAT reporter construct allows ultrasensitive estimation of TNF synthesis, and suggests that the TNF gene has been silenced in non-macrophage cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1336–1344. doi: 10.1172/JCI115137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor: an endogenous mediator of shock and inflammation. Immunol Res. 1986;5(4):281–293. doi: 10.1007/BF02935501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B. Regulation of cachectin biosynthesis occurs at multiple levels. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;349:229–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Tompkins R. G., Gelfand J. A., Michie H. R., Stanford G. G., van der Meer J. W., Endres S., Lonnemann G., Corsetti J., Chernow B. Circulating interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor in septic shock and experimental endotoxin fever. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):79–84. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling G., Goldstein D. S., Stull R., Gorschboth C. M., Norton J. A. Tumor necrosis factor: immune endocrine interaction. Surgery. 1989 Dec;106(6):1155–1160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echtenacher B., Falk W., Männel D. N., Krammer P. H. Requirement of endogenous tumor necrosis factor/cachectin for recovery from experimental peritonitis. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3762–3766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertel W., Morrison M. H., Wang P., Ba Z. F., Ayala A., Chaudry I. H. The complex pattern of cytokines in sepsis. Association between prostaglandins, cachectin, and interleukins. Ann Surg. 1991 Aug;214(2):141–148. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199108000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. F., Snyder Y. M., Butler L. D., Zuckerman S. H. Differential expression of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor in murine septic shock models. Circ Shock. 1989 Dec;29(4):279–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardin E., Grau G. E., Dayer J. M., Roux-Lombard P., Lambert P. H. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in the serum of children with severe infectious purpura. N Engl J Med. 1988 Aug 18;319(7):397–400. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198808183190703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Brown T., Beutler B. Endotoxin-responsive sequences control cachectin/tumor necrosis factor biosynthesis at the translational level. J Exp Med. 1990 Feb 1;171(2):465–475. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.2.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Huez G., Beutler B. Interactive effects of the tumor necrosis factor promoter and 3'-untranslated regions. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 15;146(6):1843–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Thompson P., Beutler B. Dexamethasone and pentoxifylline inhibit endotoxin-induced cachectin/tumor necrosis factor synthesis at separate points in the signaling pathway. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):391–394. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw L. B., Tekamp-Olson P., Chang A. C., Lee P. A., Taylor F. B., Jr, Murray C. K., Peer G. T., Emerson T. E., Jr, Passey R. B., Kuo G. C. Survival of primates in LD100 septic shock following therapy with antibody to tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha). Circ Shock. 1990 Mar;30(3):279–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde S. R., Stith R. D., McCallum R. E. Mortality and bacteriology of sepsis following cecal ligation and puncture in aged mice. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):619–624. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.619-624.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalimi M., Hubbard J., Gupta S. Modulation of glucocorticoid receptor from development to aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;521:149–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb35273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger B. E., Craven D. E., Carling P. C., McCabe W. R. Gram-negative bacteremia. III. Reassessment of etiology, epidemiology and ecology in 612 patients. Am J Med. 1980 Mar;68(3):332–343. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90101-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H., Premdas F., Harrison D. E., Lipson L. G. Aging and glucose homeostasis in C57BL/6J male mice. FASEB J. 1988 Sep;2(12):2807–2811. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.12.3044905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayoral J. L., Schweich C. J., Dunn D. L. Decreased tumor necrosis factor production during the initial stages of infection correlates with survival during murine gram-negative sepsis. Arch Surg. 1990 Jan;125(1):24–28. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1990.01410130026003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldawer L. L., Gelin J., Scherstén T., Lundholm K. G. Circulating interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor during inflammation. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 2):R922–R928. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1987.253.6.R922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. L., Smith J. W., Klein D. B., Trunkey D. D., Cooper R. H., Adinolfi M. F., Mills J. Risk of infection after penetrating abdominal trauma. N Engl J Med. 1984 Oct 25;311(17):1065–1070. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198410253111701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks W. W., Cohen H. E. Endotoxin shock in the geriatric patient. Geriatrics. 1967 Mar;22(3):120–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remick D. G., Strieter R. M., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Nguyen D., Eskandari M., Kunkel S. L. In vivo dynamics of murine tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression. Kinetics of dexamethasone-induced suppression. Lab Invest. 1989 Jun;60(6):766–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapolsky R. M., Krey L. C., McEwen B. S. The neuroendocrinology of stress and aging: the glucocorticoid cascade hypothesis. Endocr Rev. 1986 Aug;7(3):284–301. doi: 10.1210/edrv-7-3-284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaccianoce S., Di Sciullo A., Angelucci L. Age-related changes in hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis activity in the rat. In vitro studies. Neuroendocrinology. 1990 Aug;52(2):150–155. doi: 10.1159/000125566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stith R. D., McCallum R. E. Effects of aging and endotoxin on hepatic glucocorticoid action and glucose metabolism in mice. Mech Ageing Dev. 1985 Apr;30(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(85)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbaschek B., Ditter B., Becker K. P., Urbaschek R. Protective effects and role of endotoxin in experimental septicemia. Circ Shock. 1984;14(4):209–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Havell E. A. Differential inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced phenomena by anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2397–2400. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2397-2400.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Bakke O. Glucocorticoids suppress the production of tumour necrosis factor by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes. Immunology. 1988 Feb;63(2):299–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Halstensen A., Espevik T. Association between tumour necrosis factor in serum and fatal outcome in patients with meningococcal disease. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A. Production and clearance of tumor necrosis factor in rats exposed to endotoxin and dexamethasone. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Dec;45(3):348–355. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wichterman K. A., Baue A. E., Chaudry I. H. Sepsis and septic shock--a review of laboratory models and a proposal. J Surg Res. 1980 Aug;29(2):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(80)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman S. H., Shellhaas J., Butler L. D. Differential regulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor synthesis: effects of endogenous and exogenous glucocorticoids and the role of the pituitary-adrenal axis. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Feb;19(2):301–305. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



