Abstract
The ability to adhere to salivary agglutinin-coated hydroxyapatite beads and to aggregate in the presence of fluid-phase salivary agglutinin was tested by using 25 isolates of mutants streptococci representing eight serotypes. Both adherence and aggregation activity correlated with expression of the Mr-185,000 cell surface antigen P1 on Streptococcus mutans serotype c, e, and f strains. In addition, it was shown that the P1 molecule itself served as the adhesin of S. mutans serotype c, since adherence was significantly inhibited by the presence of recombinant-specified Mr-150,000 P1. The ability of S. sobrinus strains to adhere or aggregate did not correlate with expression of the P1 cross-reactive antigen SpaA. There was also evidence for interaction with salivary agglutinin, as manifested by aggregation but not adherence of S. rattus serotype b, which does not express a P1 cross-reactive antigen. To understand the interaction of P1 with salivary agglutinin at the molecular level, a panel of 11 anti-P1 monoclonal antibodies was tested for inhibitory activity in adherence and aggregation inhibition assays. Overlapping, but not identical, subsets of monoclonal antibodies were found to inhibit adherence and aggregation, indicating that the interactions of P1 with salivary agglutinin which mediate these two phenomena are different. The localization of functional domains of P1 which may mediate the aggregation and adherence reactions is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abiko Y., Hayakawa M., Aoki H., Saito S., Takiguchi H. Cloning of the gene for cell-surface protein antigen A from Streptococcus sobrinus (serotype d). Arch Oral Biol. 1989;34(7):571–575. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(89)90096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackermans F., Klein J. P., Ogier J., Bazin H., Cormont F., Frank R. M. Purification and characterization of a saliva-interacting cell-wall protein from Streptococcus mutans serotype f by using monoclonal-antibody immunoaffinity chromatography. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):211–217. doi: 10.1042/bj2280211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayakawa G. Y., Boushell L. W., Crowley P. J., Erdos G. W., McArthur W. P., Bleiweis A. S. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for antigen P1, a major surface protein of mutans streptococci. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2759–2767. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2759-2767.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babu J. P., Dabbous M. K. Interaction of salivary fibronectin with oral streptococci. J Dent Res. 1986 Aug;65(8):1094–1100. doi: 10.1177/00220345860650081001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
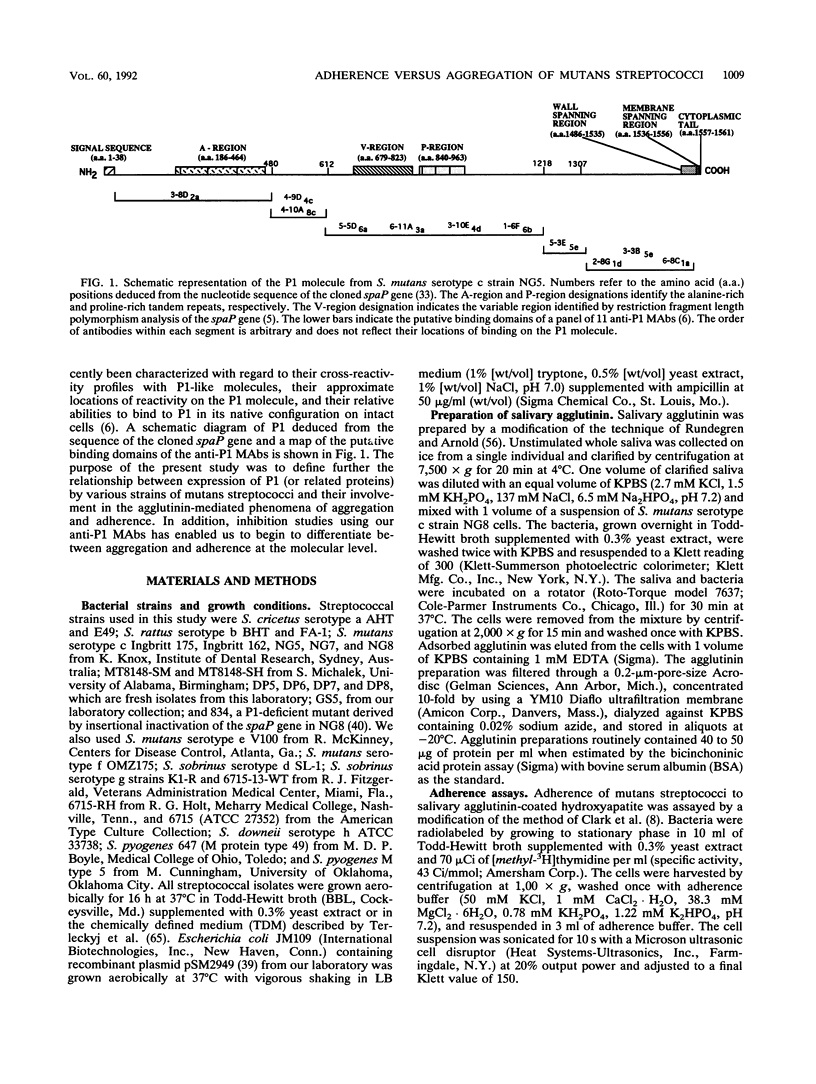
- Brady L. J., Crowley P. J., Ma J. K., Kelly C., Lee S. F., Lehner T., Bleiweis A. S. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms and sequence variation within the spaP gene of Streptococcus mutans serotype c isolates. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1803–1810. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1803-1810.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady L. J., Piacentini D. A., Crowley P. J., Bleiweis A. S. Identification of monoclonal antibody-binding domains within antigen P1 of Streptococcus mutans and cross-reactivity with related surface antigens of oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4425–4435. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4425-4435.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caparon M. G., Stephens D. S., Olsén A., Scott J. R. Role of M protein in adherence of group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1811–1817. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1811-1817.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
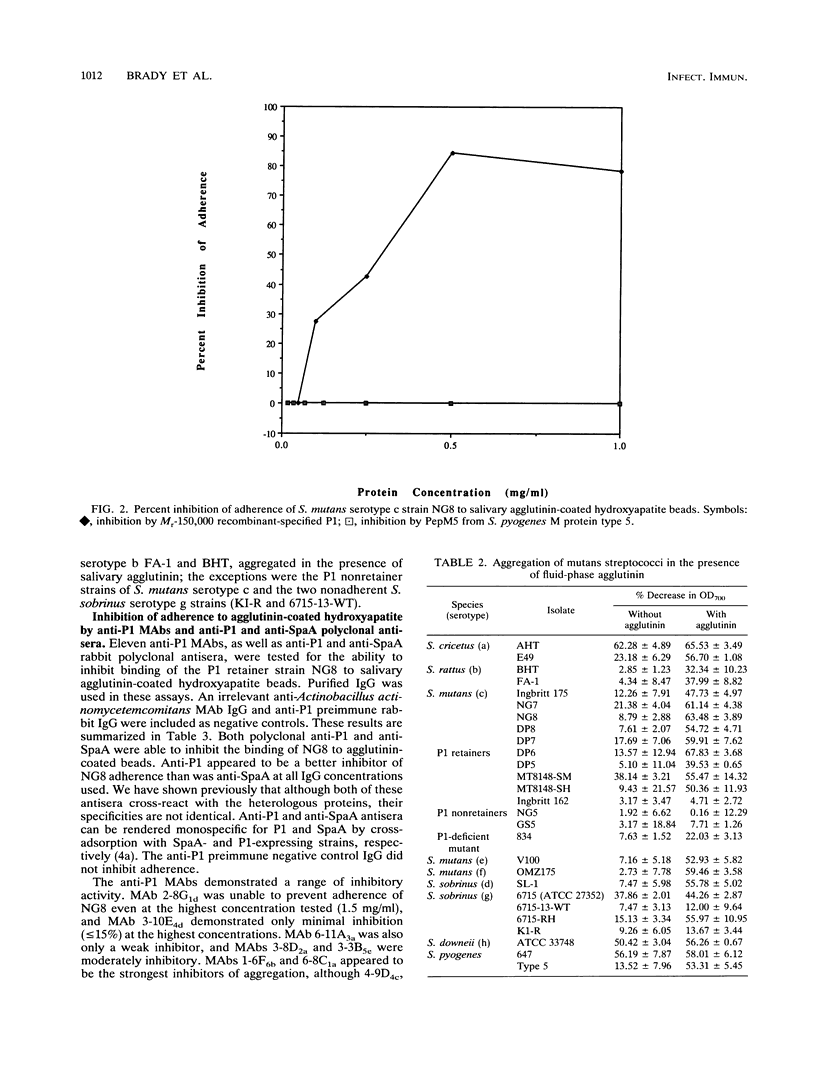
- Clark W. B., Bammann L. L., Gibbons R. J. Comparative estimates of bacterial affinities and adsorption sites on hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):846–853. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.846-853.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
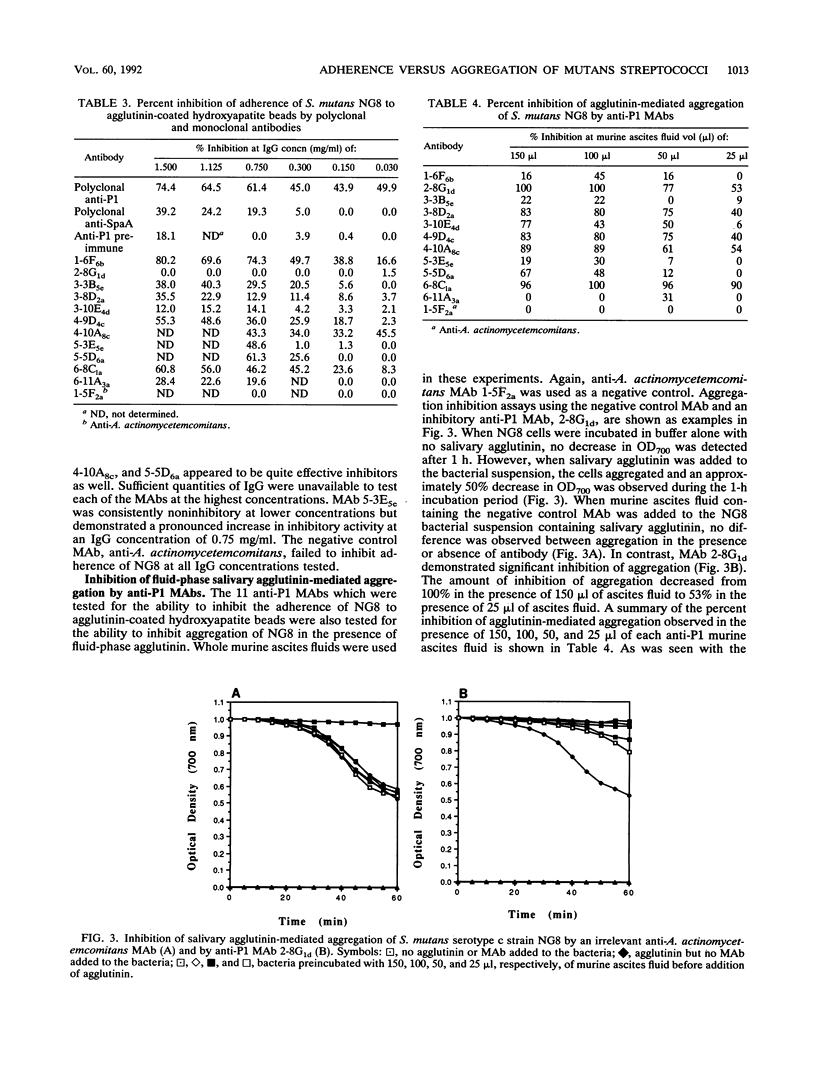
- Courtney H. S., Hasty D. L. Aggregation of group A streptococci by human saliva and effect of saliva on streptococcal adherence to host cells. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1661–1666. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1661-1666.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley P. J., Fischlschweiger W., Coleman S. E., Bleiweis A. S. Intergeneric bacterial coaggregations involving mutans streptococci and oral actinomyces. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2695–2700. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2695-2700.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham M. W., Beachey E. H. Peptic digestion of streptococcal M protein. I. Effect of digestion at suboptimal pH upon the biological and immunochemical properties of purified M protein extracts. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):244–248. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.244-248.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demuth D. R., Berthold P., Leboy P. S., Golub E. E., Davis C. A., Malamud D. Saliva-mediated aggregation of Enterococcus faecalis transformed with a Streptococcus sanguis gene encoding the SSP-5 surface antigen. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1470–1475. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1470-1475.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demuth D. R., Davis C. A., Corner A. M., Lamont R. J., Leboy P. S., Malamud D. Cloning and expression of a Streptococcus sanguis surface antigen that interacts with a human salivary agglutinin. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2484–2490. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2484-2490.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demuth D. R., Golub E. E., Malamud D. Streptococcal-host interactions. Structural and functional analysis of a Streptococcus sanguis receptor for a human salivary glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7120–7126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demuth D. R., Lammey M. S., Huck M., Lally E. T., Malamud D. Comparison of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis receptors for human salivary agglutinin. Microb Pathog. 1990 Sep;9(3):199–211. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90022-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson T., Rundegren J. Characterization of a salivary agglutinin reacting with a serotype c strain of Streptococcus mutans. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 15;133(2):255–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A. Streptococcal M protein: molecular design and biological behavior. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jul;2(3):285–314. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forester H., Hunter N., Knox K. W. Characteristics of a high molecular weight extracellular protein of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2779–2788. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J. Bacterial adhesion to oral tissues: a model for infectious diseases. J Dent Res. 1989 May;68(5):750–760. doi: 10.1177/00220345890680050101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Cohen L., Hay D. I. Strains of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus attach to different pellicle receptors. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):555–561. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.555-561.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I. Albumin as a blocking agent in studies of streptococcal adsorption to experimental salivary pellicles. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):592–594. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.592-594.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Hay D. I. Adsorbed salivary acidic proline-rich proteins contribute to the adhesion of Streptococcus mutans JBP to apatitic surfaces. J Dent Res. 1989 Sep;68(9):1303–1307. doi: 10.1177/00220345890680090201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt R. M., Curtiss R., 3rd Cross-reactivity between the immunodominant determinant of the antigen I component of Streptococcus sobrinus SpaA protein and surface antigens from other members of the Streptococcus mutans group. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2276–2282. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2276-2282.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley P. S., Carter P. L., Wyatt J. E., Hesketh L. M. Surface structures (peritrichous fibrils and tufts of fibrils) found on Streptococcus sanguis strains may be related to their ability to coaggregate with other oral genera. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):217–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.217-227.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt R. G., Abiko Y., Saito S., Smorawinska M., Hansen J. B., Curtiss R., 3rd Streptococcus mutans genes that code for extracellular proteins in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):147–156. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.147-156.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M., Machardy S. M., Sheppard A. J., Woods N. C. Evidence for an immunological relationship between Streptococcus mutans and human cardiac tissue. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):576–588. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.576-588.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwaki M., Okahashi N., Takahashi I., Kanamoto T., Sugita-Konishi Y., Aibara K., Koga T. Oral immunization with recombinant Streptococcus lactis carrying the Streptococcus mutans surface protein antigen gene. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2929–2934. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2929-2934.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly C., Evans P., Bergmeier L., Lee S. F., Progulske-Fox A., Harris A. C., Aitken A., Bleiweis A. S., Lehner T. Sequence analysis of the cloned streptococcal cell surface antigen I/II. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 20;258(1):127–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81632-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto E., Hay D. I., Gibbons R. J. A human salivary protein which promotes adhesion of Streptococcus mutans serotype c strains to hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3702–3707. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3702-3707.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Asakawa H., Okahashi N., Takahashi I. Effect of subculturing on expression of a cell-surface protein antigen by Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Dec;135(12):3199–3207. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-12-3199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E. Intergeneric coaggregation among human oral bacteria and ecology of dental plaque. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:627–656. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.003211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPolla R. J., Haron J. A., Kelly C. G., Taylor W. R., Bohart C., Hendricks M., Pyati J. P., Graff R. T., Ma J. K., Lehner T. Sequence and structural analysis of surface protein antigen I/II (SpaA) of Streptococcus sobrinus. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2677–2685. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2677-2685.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont R. J., Rosan B. Adherence of mutans streptococci to other oral bacteria. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1738–1743. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1738-1743.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. F., Progulske-Fox A., Bleiweis A. S. Molecular cloning and expression of a Streptococcus mutans major surface protein antigen, P1 (I/II), in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2114–2119. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2114-2119.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. F., Progulske-Fox A., Erdos G. W., Piacentini D. A., Ayakawa G. Y., Crowley P. J., Bleiweis A. S. Construction and characterization of isogenic mutants of Streptococcus mutans deficient in major surface protein antigen P1 (I/II). Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3306–3313. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3306-3313.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Caldwell J., Smith R. Local passive immunization by monoclonal antibodies against streptococcal antigen I/II in the prevention of dental caries. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):796–799. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.796-799.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T. Immunization against dental caries. Vaccine. 1985 Mar;3(1):65–68. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(85)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Russell M. W., Caldwell J., Smith R. Immunization with purified protein antigens from Streptococcus mutans against dental caries in rhesus monkeys. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):407–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.407-415.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J. K., Hunjan M., Smith R., Kelly C., Lehner T. An investigation into the mechanism of protection by local passive immunization with monoclonal antibodies against Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3407–3414. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3407-3414.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J. K., Kelly C. G., Munro G., Whiley R. A., Lehner T. Conservation of the gene encoding streptococcal antigen I/II in oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2686–2694. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2686-2694.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J. K., Smith R., Lehner T. Use of monoclonal antibodies in local passive immunization to prevent colonization of human teeth by Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1274–1278. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1274-1278.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson I., Ericson T. Effect of salivary agglutinins of reactions between hydroxyapatite and a serotype c strain of Streptococcus mutans. Caries Res. 1976;10(4):273–286. doi: 10.1159/000260208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamud D., Appelbaum B., Kline R., Golub E. E. Bacterial aggregating activity in human saliva: comparisons of bacterial species and strains. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1003–1006. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1003-1006.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogier J. A., Wachsmann D., Schöller M., Lepoivre Y., Klein J. P. Molecular characterization of the gene sr of the saliva interacting protein from Streptococcus mutans OMZ175. Arch Oral Biol. 1990;35 (Suppl):25S–31S. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(90)90127-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okahashi N., Koga T., Hamada S. Purification and immunochemical properties of a protein antigen from serotype g Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(1):35–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb00919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okahashi N., Sasakawa C., Yoshikawa M., Hamada S., Koga T. Cloning of a surface protein antigen gene from serotype c Streptococcus mutans. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Feb;3(2):221–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb01811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okahashi N., Sasakawa C., Yoshikawa M., Hamada S., Koga T. Molecular characterization of a surface protein antigen gene from serotype c Streptococcus mutans, implicated in dental caries. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):673–678. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otake S., Nishihara Y., Makimura M., Hatta H., Kim M., Yamamoto T., Hirasawa M. Protection of rats against dental caries by passive immunization with hen-egg-yolk antibody (IgY). J Dent Res. 1991 Mar;70(3):162–166. doi: 10.1177/00220345910700030101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundegren J. L., Arnold R. R. Bacteria-agglutinating characteristics of secretory IgA and a salivary agglutinin. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1987;216B:1005–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundegren J. Calcium-dependent salivary agglutinin with reactivity to various oral bacterial species. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):173–178. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.173-178.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Lehner T. Characterisation of antigens extracted from cells and culture fluids of Streptococcus mutans serotype c. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(1):7–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Distribution of cross-reactive antigens A and B in Streptococcus mutans and other oral streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jun;118(2):383–388. doi: 10.1099/00221287-118-2-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R., Peach S. L., Colman G., Cohen B. Antibody responses to antigens of Streptococcus mutans in monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) immunized against dental caries. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Mar;129(3):865–875. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-3-865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):109–115. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer P., Bruyère T., Ogier J. A., Garnier J. M., Jeltsch J. M., Klein J. P. Cloning of the saliva-interacting protein gene from Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5167–5173. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5167-5173.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staffileno L. K., Hendricks M., LaPolla R., Bohart C., Van Hook P., Rosen J. I., Warner J., Hoey K., Wegemer D., Naso R. B. Cloning of the amino terminal nucleotides of the antigen I/II of Streptococcus sobrinus and the immune responses to the corresponding synthetic peptides. Arch Oral Biol. 1990;35 (Suppl):47S–52S. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(90)90130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Levine M. J., Cavese J. M., Prakobphol A., Murray P. A., Tabak L. A., Reddy M. S. Adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to salivary mucin bound to glass. J Dent Res. 1982 Dec;61(12):1390–1393. doi: 10.1177/00220345820610120101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi I., Okahashi N., Sasakawa C., Yoshikawa M., Hamada S., Koga T. Homology between surface protein antigen genes of Streptococcus sobrinus and Streptococcus mutans. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 5;249(2):383–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80664-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Soet J. J., van Loveren C., Lammens A. J., Pavicić M. J., Homburg C. H., ten Cate J. M., de Graaff J. Differences in cariogenicity between fresh isolates of Streptococcus sobrinus and Streptococcus mutans. Caries Res. 1991;25(2):116–122. doi: 10.1159/000261353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



