Abstract
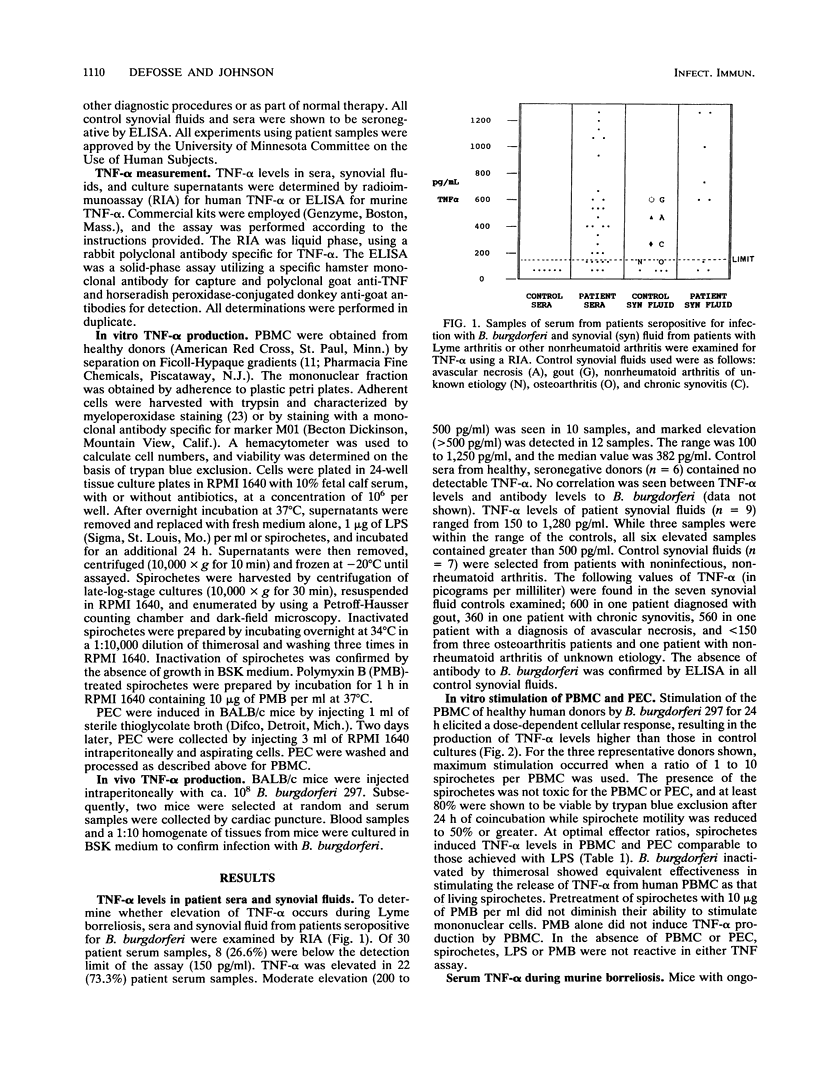
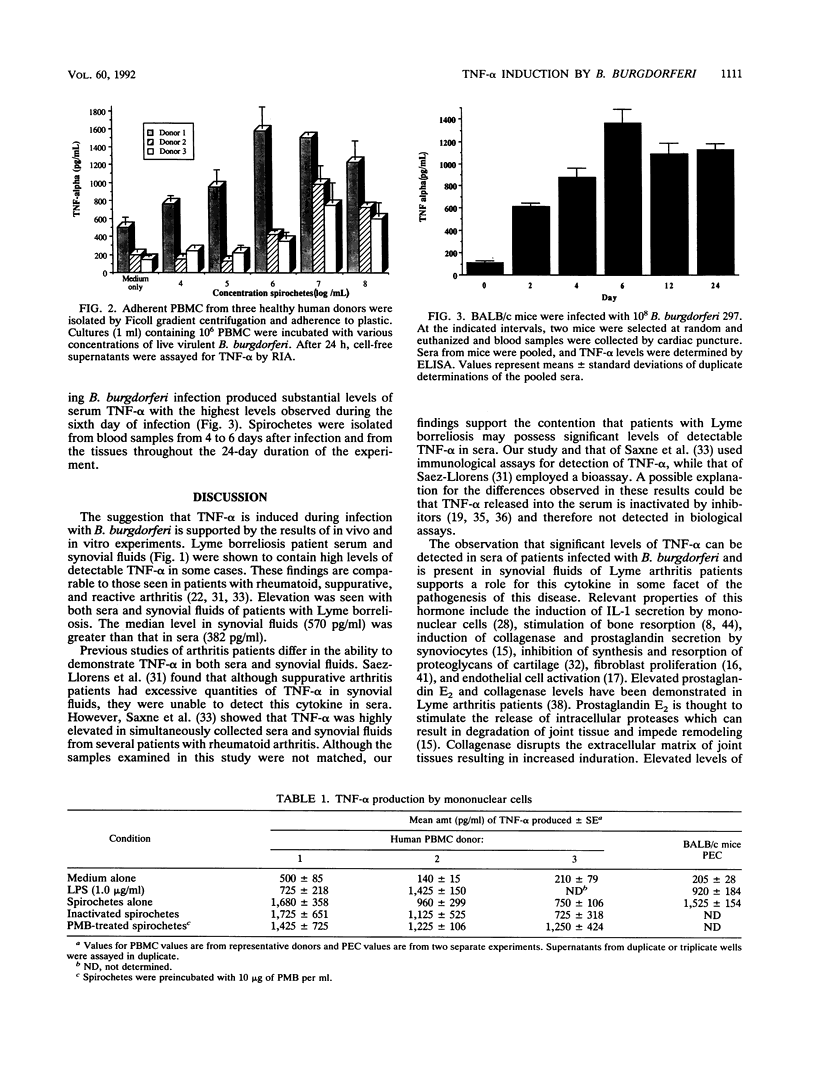
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) is an immunoregulatory cytokine with many biological activities including the mediation of inflammation. We examined sera and synovial fluids from patients seropositive for infection with Borrelia burgdorferi using a radioimmunoassay specific for TNF-alpha. Significant elevation of TNF-alpha was found in the sera and synovial fluids of patients examined, while controls showed no elevation. Sera of mice infected with B. burgdorferi contained elevated levels of TNF-alpha which varied during the course of a 24-day infection. To determine whether B. burgdorferi is capable of inducing TNF-alpha production, spirochetes were added to adherent human peripheral blood mononuclear cells or mouse peritoneal exudate cells and 24 h later supernatants were assayed. TNF-alpha induction occurred in a dose-dependent manner. The maximum stimulation occurred when a ratio of 1 to 10 spirochetes per mononuclear cell was used. At optimal concentrations, induction was not diminished by inactivation of spirochetes or pretreatment with polymyxin B. These results suggest that an increase in TNF-alpha production may occur as a result of infection with B. burgdorferi.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammann A. J., Palladino M. A., Volberding P., Abrams D., Martin N. L., Conant M. Tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and aids-related complex. J Clin Immunol. 1987 Nov;7(6):481–485. doi: 10.1007/BF00915059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Hovmark A. Early and late cutaneous manifestations in Ixodes-borne borreliosis (erythema migrans borreliosis, Lyme borreliosis). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:4–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachwich P. R., Chensue S. W., Larrick J. W., Kunkel S. L. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates interleukin-1 and prostaglandin E2 production in resting macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):94–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90881-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck G., Benach J. L., Habicht G. S. Isolation of interleukin 1 from joint fluids of patients with Lyme disease. J Rheumatol. 1989 Jun;16(6):800–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck G., Habicht G. S., Benach J. L., Coleman J. L. Chemical and biologic characterization of a lipopolysaccharide extracted from the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi). J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):108–117. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Bosler E. M., Hanrahan J. P., Coleman J. L., Habicht G. S., Bast T. F., Cameron D. J., Ziegler J. L., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W. Spirochetes isolated from the blood of two patients with Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):740–742. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolini D. R., Nedwin G. E., Bringman T. S., Smith D. D., Mundy G. R. Stimulation of bone resorption and inhibition of bone formation in vitro by human tumour necrosis factors. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):516–518. doi: 10.1038/319516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Mahoney J., Le Trang N., Pekala P., Cerami A. Purification of cachectin, a lipoprotein lipase-suppressing hormone secreted by endotoxin-induced RAW 264.7 cells. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):984–995. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Chaudhri G. Tumor necrosis factor in malaria-induced abortion. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Sep;39(3):246–249. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.39.246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):2163–2168. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransen L., Van der Heyden J., Ruysschaert R., Fiers W. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor: its effect and its synergism with interferon-gamma on a variety of normal and transformed human cell lines. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1986 Apr;22(4):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(86)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fràter-Schröder M., Risau W., Hallmann R., Gautschi P., Böhlen P. Tumor necrosis factor type alpha, a potent inhibitor of endothelial cell growth in vitro, is angiogenic in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5277–5281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fumarola D., Munno I., Miragliotta G. "Endotoxicity" of the Lyme disease spirochete. Infection. 1983 Nov-Dec;11(6):345–345. doi: 10.1007/BF01641362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatanaga T., Lentz R., Masunaka I., Tomich J., Jeffes E. W., 3rd, Baird M., Granger G. A. Identification of TNF-LT blocking factor(s) in the serum and ultrafiltrates of human cancer patients. Lymphokine Res. 1990 Summer;9(2):225–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habicht G. S., Beck G., Benach J. L., Coleman J. L., Leichtling K. D. Lyme disease spirochetes induce human and murine interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3147–3154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haranaka K., Satomi N., Sakurai A. Antitumor activity of murine tumor necrosis factor (TNF) against transplanted murine tumors and heterotransplanted human tumors in nude mice. Int J Cancer. 1984 Aug 15;34(2):263–267. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910340219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins S. J., Meager A. Cytokines in synovial fluid: II. The presence of tumour necrosis factor and interferon. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jul;73(1):88–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLOW L. S. SIMPLIFIED MYELOPEROXIDASE STAIN USING BENZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE. Blood. 1965 Aug;26:215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Nishihara T., Fujiwara T., Nisizawa T., Okahashi N., Noguchi T., Hamada S. Biochemical and immunobiological properties of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from Bacteroides gingivalis and comparison with LPS from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):638–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.638-647.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lähdevirta J., Maury C. P., Teppo A. M., Repo H. Elevated levels of circulating cachectin/tumor necrosis factor in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):289–291. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Meegan J. M., Anderson J. F., Chappell W. A. Comparison of an indirect fluorescent-antibody test with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serological studies of Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):181–184. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.181-184.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansheim B. J., Onderdonk A. B., Kasper D. L. Immunochemical and biologic studies of the lipopolysaccharide of Bacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies asaccharolyticus. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):72–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Bank I., Handley D., Cassimeris J., Chess L., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin interacts with endothelial cell receptors to induce release of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1363–1375. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opal S. M., Cross A. S., Kelly N. M., Sadoff J. C., Bodmer M. W., Palardy J. E., Victor G. H. Efficacy of a monoclonal antibody directed against tumor necrosis factor in protecting neutropenic rats from lethal infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1148–1152. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisa P., Gennene M., Söder O., Ottenhoff T., Hansson M., Kiessling R. Serum tumor necrosis factor levels and disease dissemination in leprosy and leishmaniasis. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):988–991. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J. Tumour necrosis factor alpha stimulates resorption and inhibits synthesis of proteoglycan in cartilage. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):547–549. doi: 10.1038/322547a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxne T., Palladino M. A., Jr, Heinegård D., Talal N., Wollheim F. A. Detection of tumor necrosis factor alpha but not tumor necrosis factor beta in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid and serum. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Aug;31(8):1041–1045. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scuderi P., Sterling K. E., Lam K. S., Finley P. R., Ryan K. J., Ray C. G., Petersen E., Slymen D. J., Salmon S. E. Raised serum levels of tumour necrosis factor in parasitic infections. Lancet. 1986 Dec 13;2(8520):1364–1365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Vey E., Turcatti G., Wingfield P., Dayer J. M. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitor: purification, NH2-terminal amino acid sequence and evidence for anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities. Eur J Immunol. 1990 May;20(5):1167–1174. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Zhang J. H., Hauptmann B., Dayer J. M. Characterization of a tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) inhibitor: evidence of immunological cross-reactivity with the TNF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5188–5192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor exerts endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine control of inflammatory responses. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1269–1277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Duray P. H., Butcher E. C. Spirochetal antigens and lymphoid cell surface markers in Lyme synovitis. Comparison with rheumatoid synovium and tonsillar lymphoid tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Apr;31(4):487–495. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Hardin J. A., Ruddy S., Askenase W., Andiman W. A. Erythema chronicum migrans and Lyme arthritis. The enlarging clinical spectrum. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):685–698. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sáez-Llorens X., Mustafa M. M., Ramilo O., Fink C., Beutler B., Nelson J. D. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 beta in synovial fluid of infants and children with suppurative arthritis. Am J Dis Child. 1990 Mar;144(3):353–356. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1990.02150270103035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Rothenberg R. J., Barbour A. G. Absence of lipopolysaccharide in the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2311–2313. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2311-2313.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson B. M., Mundy G. R., Chambers T. J. Tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta induce osteoblastic cells to stimulate osteoclastic bone resorption. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):775–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Halstensen A., Espevik T. Association between tumour necrosis factor in serum and fatal outcome in patients with meningococcal disease. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. J. Reaction following treatment of murine borreliosis and Shwartzman type reacion with borrelial sonicates. Parasite Immunol. 1980 Autumn;2(3):201–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1980.tb00054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



