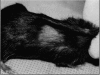
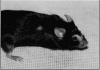
Abstract
The objective of this study was to examine the effects of polyphenolic compounds, present in noncommercially available green tea, on hair loss among rodentts. In an experimental study, we randomly assigned 60female Balb/black mice, which had developed spontaneous hair loss on the head, neck and dorsal areas into two equal groups; A (experimental) and B (control). Group A received 50% fraction of polyphenol extract from dehydrated green tea in their drinking water for six months. Group B received regular drinking water. Both groups were fed regular rodent diets (Purina Rodent Chow 5001) and housed individually in polycarbonate cages. The results showed that 33% of the mice in experimental Group A, who received polyphenol extract in their drinking water, had significant hair regrowth during six months of treatment (p = 0.014). No hair growth was observed among mice in the control group, which received regular water.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arck P. C., Handjiski B., Hagen E., Joachim R., Klapp B. F., Paus R. Indications for a 'brain-hair follicle axis (BHA)': inhibition of keratinocyte proliferation and up-regulation of keratinocyte apoptosis in telogen hair follicles by stress and substance P. FASEB J. 2001 Sep 17;15(13):2536–2538. doi: 10.1096/fj.00-0699fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arck Petra Clara, Handjiski Bori, Peters Eva Milena J., Peter Anita S., Hagen Evelin, Fischer Axel, Klapp Burghard F., Paus Ralf. Stress inhibits hair growth in mice by induction of premature catagen development and deleterious perifollicular inflammatory events via neuropeptide substance P-dependent pathways. Am J Pathol. 2003 Mar;162(3):803–814. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63877-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benencia F., Courrèges M. C., Coulombié F. C. In vivo and in vitro immunomodulatory activities of Trichilia glabra aqueous leaf extracts. J Ethnopharmacol. 2000 Mar;69(3):199–205. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(99)00010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katiyar S. K., Agarwal R., Ekker S., Wood G. S., Mukhtar H. Protection against 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-caused inflammation in SENCAR mouse ear skin by polyphenolic fraction isolated from green tea. Carcinogenesis. 1993 Mar;14(3):361–365. doi: 10.1093/carcin/14.3.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litterst C. L. Mechanically self-induced muzzle alopecia in mice. Lab Anim Sci. 1974 Oct;24(5):806–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. Y. Hair-nibbling and whisker-trimming as indicators of social hierarchy in mice. Anim Behav. 1972 Feb;20(1):10–12. doi: 10.1016/s0003-3472(72)80167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElwee K. J., Boggess D., Olivry T., Oliver R. F., Whiting D., Tobin D. J., Bystryn J. C., King L. E., Jr, Sundberg J. P. Comparison of alopecia areata in human and nonhuman mammalian species. Pathobiology. 1998;66(2):90–107. doi: 10.1159/000028002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhtar H., Katiyar S. K., Agarwal R. Green tea and skin--anticarcinogenic effects. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Jan;102(1):3–7. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12371720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strozik E., Festing M. F. Whisker trimming in mice. Lab Anim. 1981 Oct;15(4):309–312. doi: 10.1258/002367781780953040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg J. P., Cordy W. R., King L. E., Jr Alopecia areata in aging C3H/HeJ mice. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Jun;102(6):847–856. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12382416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg John P., Boggess Dawnalyn, Silva Kathleen A., McElwee Kevin J., King Lloyd E., Li Renhua, Churchill Gary, Cox Gregory A. Major locus on mouse chromosome 17 and minor locus on chromosome 9 are linked with alopecia areata in C3H/HeJ mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2003 May;120(5):771–775. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. S., Wang Z. Y. Tea and cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 Jul 7;85(13):1038–1049. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.13.1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]