Abstract
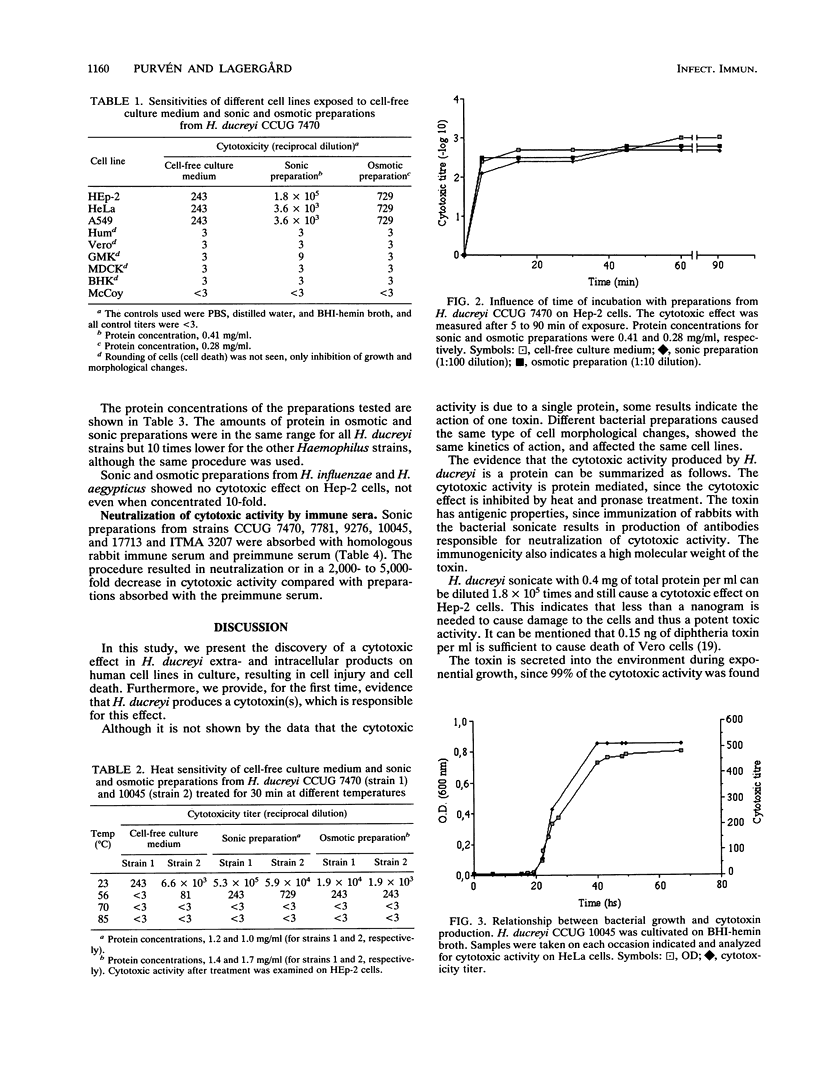
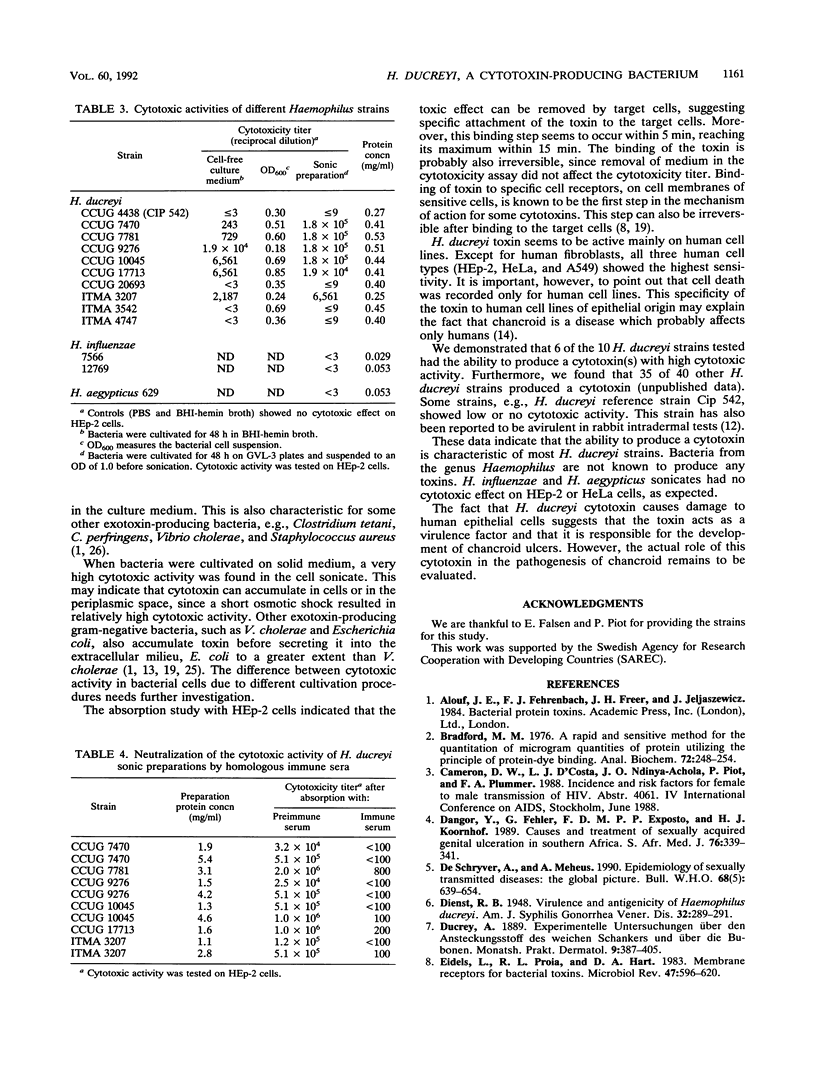
An extra- and an intracellular product from the bacterium Haemophilus ducreyi were shown to have a cytotoxic effect on cell lines of epithelial origin, e.g., HEp-2 and HeLa cells. The cytotoxic effect appeared on cells within 24 h and resulted in cell death and morphologically changed cells. The cytotoxic activity was heat and pronase sensitive. The activity could be removed by incubation with the target cells, suggesting attachment of the agent to the cells. The cytotoxic products were secreted into the environment during exponential growth of bacteria and produced by most of the H. ducreyi strains tested. The activity was neutralized by homologous rabbit immune serum but not by the corresponding preimmune serum. The results indicate that strains of H. ducreyi produce a cytotoxin which may be of importance to the pathogenesis of chancroid.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dangor Y., Fehler G., Exposto F. D., Koornhof H. J. Causes and treatment of sexually acquired genital ulceration in southern Africa. S Afr Med J. 1989 Oct 7;76(7):339–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Schryver A., Meheus A. Epidemiology of sexually transmitted diseases: the global picture. Bull World Health Organ. 1990;68(5):639–654. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidels L., Proia R. L., Hart D. A. Membrane receptors for bacterial toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):596–620. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.596-620.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillenius P., Jätmaa E., Askelöf P., Granström M., Tiru M. The standardization of an assay for pertussis toxin and antitoxin in microplate culture of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Stand. 1985 Jan;13(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(85)80034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt R. M., Lukehart S. A., Plummer F. A., Quinn T. C., Critchlow C. W., Ashley R. L., D'Costa L. J., Ndinya-Achola J. O., Corey L., Ronald A. R. Genital ulceration as a risk factor for human immunodeficiency virus infection. AIDS. 1988 Feb;2(1):47–50. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198802000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. W., Lian C. J., Wilt J. C., Ronald A. R. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Haemophilus ducreyi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):608–612. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. W., Lian C. J., Wilt J. C., Ronald A. R. Comparison of specimen collection and laboratory techniques for isolation of Haemophilus ducreyi. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jan;7(1):39–43. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.1.39-43.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiss J. K., Koech D., Plummer F. A., Holmes K. K., Lightfoote M., Piot P., Ronald A. R., Ndinya-Achola J. O., D'Costa L. J., Roberts P. AIDS virus infection in Nairobi prostitutes. Spread of the epidemic to East Africa. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 13;314(7):414–418. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602133140704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabey D. C., Wall R. A., Bello C. S. Aetiology of genital ulceration in the Gambia. Genitourin Med. 1987 Oct;63(5):312–315. doi: 10.1136/sti.63.5.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meheus A., Van Dyck E., Ursi J. P., Ballard R. C., Piot P. Etiology of genital ulcerations in Swaziland. Sex Transm Dis. 1983 Jan-Mar;10(1):33–35. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198301000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Bacterial toxins: cellular mechanisms of action. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Sep;48(3):199–221. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.3.199-221.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamura K., Nishio S., Ito A., Murata R., Kono R. Micro cell culture method for determination of diphtheria toxin and antitoxin titres using VERO cells. I. Studies on factors affecting the toxin and antitoxin titration. J Biol Stand. 1974 Jul;2(3):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-1157(74)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A. Chancroid and Haemophilus ducreyi. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2(2):137–157. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nsanze H., Fast M. V., D'Costa L. J., Tukei P., Curran J., Ronald A. Genital ulcers in Kenya. Clinical and laboratory study. Br J Vener Dis. 1981 Dec;57(6):378–381. doi: 10.1136/sti.57.6.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odumeru J. A., Wiseman G. M., Ronald A. R. Relationship between lipopolysaccharide composition and virulence of Haemophilus ducreyi. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Mar;23(2):155–162. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-2-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Export of protein in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):290–298. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.290-298.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Duangmani C., Suvongse C., O'Connor R., Pitarangsi C., Panikabutra K., Echeverria P. The role of Haemophilus ducreyi in penile ulcers in Bangkok, Thailand. Sex Transm Dis. 1984 Jul-Sep;11(3):148–151. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198407000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




