Abstract
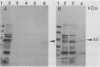
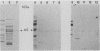
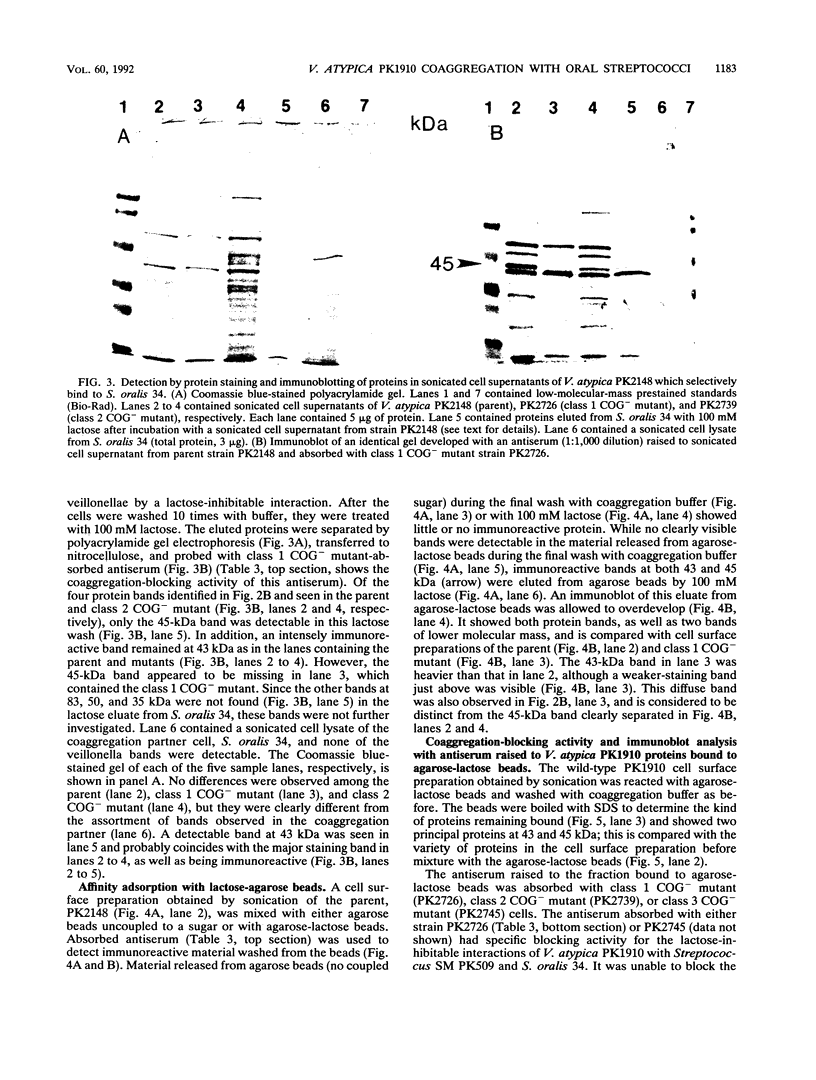
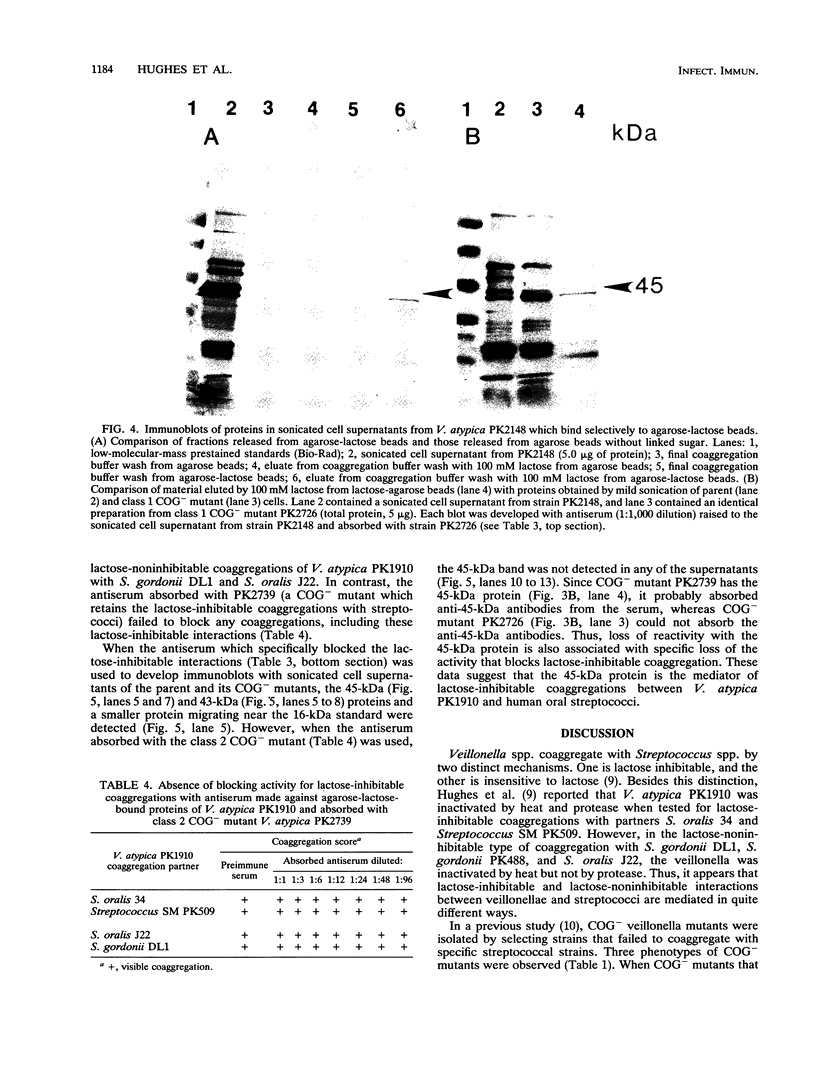
The gram-negative human oral bacterium Veillonella atypica PK1910 exhibits both lactose-inhibitable and lactose-noninhibitable coaggregations with certain human oral streptococci. A mild sonication procedure was used to obtain a veillonella surface protein preparation against which antisera were prepared. To characterize the lactose-inhibitable coaggregation, coaggregation-defective (COG-) mutants unable to exhibit this kind of coaggregation (class 1 mutants) were used to absorb the antisera. Only the lactose-inhibitable coaggregations were blocked by these absorbed antisera. The absorbed antiserum also reacted with a 45-kDa protein found in the parent and in class 2 COG- mutants that exhibited lactose-inhibitable coaggregation. This protein was not detected in surface protein preparations of class 1 COG- mutants. Two affinity protocols, involving agarose-lactose beads and the streptococcal coaggregation partner cells, were used to bind surface proteins from V. atypica PK1910. In each protocol, the 45-kDa protein was eluted by a solution containing 100 mM lactose. Antiserum was prepared against agarose-lactose beads with bound 45-kDa protein. When absorbed with class 1 COG- mutants, the antiserum blocked lactose-inhibitable coaggregation and reacted with the 45-kDa protein in immunoblots. When the same antiserum was absorbed with class 2 COG- mutant cells, it lost both properties, suggesting that the 45-kDa protein is an adhesin that mediates coaggregation with streptococci. The proposed adhesin does not seem to be the structural subunit of veillonella fimbriae, since no differences in fimbriae were observed by electron microscopy of the parent and all three classes of mutants.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batteiger B., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. The use of Tween 20 as a blocking agent in the immunological detection of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celesk R. A., London J. Attachment of oral Cytophaga species to hydroxyapatite-containing surfaces. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):768–777. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.768-777.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J. O., Kolenbrander P. E., McIntire F. C. Specificity of coaggregation reactions between human oral streptococci and strains of Actinomyces viscosus or Actinomyces naeslundii. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):742–752. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.742-752.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg S., Gerlach G. F. Enterobacterial fimbriae. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):934–938. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.934-938.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distler W., Kröncke A. Acid formation by mixed cultures of cariogenic strains of Streptococcus mutans and Veillonella alcalescens. Arch Oral Biol. 1980;25(10):655–658. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(80)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. V., Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N., Moore L. V. Coaggregation properties of human oral Veillonella spp.: relationship to colonization site and oral ecology. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):1957–1963. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.1957-1963.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. V., Roseberry C. A., Kolenbrander P. E. Isolation and characterization of coaggregation-defective mutants of Veillonella atypica. Arch Oral Biol. 1990;35 (Suppl):123S–125S. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(90)90141-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N. Characterization of Streptococcus gordonii (S. sanguis) PK488 adhesin-mediated coaggregation with Actinomyces naeslundii PK606. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):3064–3072. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.3064-3072.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N., Moore L. V. Intrageneric coaggregation among strains of human oral bacteria: potential role in primary colonization of the tooth surface. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Dec;56(12):3890–3894. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.12.3890-3894.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Inouye Y., Holdeman L. V. New Actinomyces and Streptococcus coaggregation groups among human oral isolates from the same site. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):501–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.501-506.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E. Intergeneric coaggregation among human oral bacteria and ecology of dental plaque. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:627–656. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.003211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E. Isolation and characterization of coaggregation-defective mutants of Actinomyces viscosus, Actinomyces naeslundii, and Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1200–1208. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1200-1208.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E. Surface recognition among oral bacteria: multigeneric coaggregations and their mediators. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1989;17(2):137–159. doi: 10.3109/10408418909105746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Williams B. L. Lactose-reversible coaggregation between oral actinomycetes and Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):95–102. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.95-102.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Williams B. L. Prevalence of viridans streptococci exhibiting lactose-inhibitable coaggregation with oral actinomycetes. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):449–452. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.449-452.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogfelt K. A., Bergmans H., Klemm P. Direct evidence that the FimH protein is the mannose-specific adhesin of Escherichia coli type 1 fimbriae. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1995–1998. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1995-1998.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Gibbons R. J. Ability of Veillonella and Neisseria species to attach to oral surfaces and their proportions present indigenously. Infect Immun. 1971 Sep;4(3):264–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.3.264-268.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London J., Allen J. Purification and characterization of a Bacteroides loeschei adhesin that interacts with procaryotic and eucaryotic cells. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2527–2534. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2527-2534.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTHY C., SNYDER M. L., PARKER R. B. THE INDIGENOUS ORAL FLORA OF MAN. I. THE NEWBORN TO THE 1-YEAR-OLD INFANT. Arch Oral Biol. 1965 Jan-Feb;10:61–70. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(65)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryanski J. H., Wittenberger C. L. Mannitol transport in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1475–1481. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1475-1481.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Van der Hoeven J. S. Role of interbacterial adherence in colonization of the oral cavities of gnotobiotic rats infected with Streptococcus mutans and Veillonella alcalescens. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):467–472. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.467-472.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikx F. H., Van der Hoeven J. S. Symbiosis of Streptococcus mutans and Veillonella alcalescens in mixed continuous cultures. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Jul;20(7):407–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikx F. H., van der Hoeven J. S., König K. G., Plasschaert A. J., Guggenheim B. Establishment of defined microbial ecosystems in germ-free rats. I. The effect of the interactions of streptococcus mutans or Streptococcus sanguis with Veillonella alcalescens on plaque formation and caries activity. Caries Res. 1972;6(3):211–223. doi: 10.1159/000259801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Cato E. P., Smibert R. M., Burmeister J. A., Palcanis K. G., Ranney R. R. Comparative bacteriology of juvenile periodontitis. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):507–519. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.507-519.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Smibert R. M., Good I. J., Burmeister J. A., Palcanis K. G., Ranney R. R. Bacteriology of experimental gingivitis in young adult humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):651–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.651-667.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgren M., Normark S., Lark D., O'Hanley P., Schoolnik G., Falkow S., Svanborg-Edén C., Båga M., Uhlin B. E. Mutations in E coli cistrons affecting adhesion to human cells do not abolish Pap pili fiber formation. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1159–1165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01945.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz H. L. Microbial population shifts in developing human dental plaque. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Dec;12(12):1561–1568. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. I., Kolenbrander P. E., London J., Hand A. R., Andersen R. N. Fimbria-associated proteins of Bacteroides loescheii PK1295 mediate intergeneric coaggregations. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4215–4222. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4215-4222.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. I., London J., Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N., Fischler C., Siraganian R. P. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies to fimbria-associated adhesins of Bacteroides loescheii PK1295. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):219–224. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.219-224.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. I., London J., Kolenbrander P. E., Hand A. R., Siraganian R. Localization and enumeration of fimbria-associated adhesins of Bacteroides loescheii. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1123–1128. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1123-1128.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Hoeven J. S., Toorop A. I., Mikx R. H. Symbiotic relationship of Veillonella alcalescens and Streptococcus mutans in dental plaque in gnotobiotic rats. Caries Res. 1978;12(3):142–147. doi: 10.1159/000260324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]