Abstract
The existence and maintenance of biological rhythms linked to the 24-h light-dark cycle are essential to the health and functioning of an organism. Although much is known concerning central clock mechanisms, much less is known about control in peripheral tissues. In this study, circadian regulation of gene expression was examined in rat skeletal muscle. A rich time series involving 54 animals euthanized at 18 distinct time points within the 24-h cycle was performed, and mRNA expression in gastrocnemius muscles was examined using Affymetrix gene arrays. Data mining identified 109 genes that were expressed rhythmically, which could be grouped into eight distinct temporal clusters within the 24-h cycle. These genes were placed into 11 functional categories, which were examined within the context of temporal expression. Transcription factors involved in the regulation of central rhythms were examined, and eight were found to be rhythmically expressed in muscle. Because endogenous glucocorticoids are a major effector of circadian rhythms, genes identified here were compared with those identified in previous studies as glucocorticoid regulated. Of the 109 genes identified here as circadian rhythm regulated, only 55 were also glucocorticoid regulated. Examination of transcription factors involved in circadian control suggests that corticosterone may be the initiator of their rhythmic expression patterns in skeletal muscle.
Keywords: corticosteroids, clock genes, gene arrays, expression profiling, transcriptome
virtually all organisms have biological rhythms associated with the light-dark cycle (4, 24, 25, 34). Although a good deal is known about the central control of such rhythms by the brain, less is known about how that control is translated to peripheral tissues. The central core of the mammalian circadian clock is located in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in the anterior part of the hypothalamus, which receives direct input by way of the retinohypothalamic tract. Outputs from the SCN are directed to other parts of the hypothalamus that control both anterior and posterior pituitary hormones, as well as to the area of the hypothalamus and medulla that control the autonomic nervous system. It is these hormonal and autonomic outputs that to a large degree convey light-dark rhythmicity to the rest of the body. Besides receiving inputs from the retina, the SCN also receives inputs from forebrain areas and from the locus ceruleus that modulate the influence of the SCN. The nonretinal inputs to the SCN provide the flexibility for the existence of diurnal and nocturnal animals, as well as for animals being able, when necessary, to shift wake-sleep periods from night to day and vice versa (5, 6).
Simplistically, the central clock mechanism involves an autoregulatory negative feedback loop with a periodicity of approximately 24 h (5, 6, 34). The elements of this basic feedback loop are several transcription factors, including CLOCK and BMAL1, which heterodimerize and enhance the expression of Period (Per) and CRYPTOCHROME (CRY). These two transcription factors heterodimerize and repress the expression of CLOCK and BMAL1. The core system is entrained to the light-dark cycle with CLOCK:BMAL being high during the light period and Per:CRY being high during the dark period. However, as many as 17 transcription factors have been defined as also being involved in the central clock mechanism (10). These include within the basic mechanism several isoforms of Per and CRY, as well as neuronal PAS domain protein 2 (Npas2, Mop4), which has been reported as an alternative to CLOCK as a heterodimerizing partner with BMAL (7). The precise role of the other transcription factors in the central clock is still a subject of investigation.
The input from the SCN to the regulation of both pituitary hormones and the autonomic nervous system impart rhythmicity to peripheral tissues. However, rhythmicity in peripheral tissues is further complicated by more diffuse behavior-related factors such as sleep-wake patterns, eating, and physical activity, which alter systemic energy demands. Many of the transcription factors involved in regulating the central clock are also expressed in peripheral tissues (10). However, their regulation is complicated by variations in ancillary factors, such as hormonal patterns, autonomic output, and behavior that orchestrate peripheral rhythmicity (23). The existence of both diurnal and nocturnal mammals and the phenomena of phase shifting by food restriction illustrate both the complexity and flexibility in peripheral rhythmicity. Perhaps one of the best illustrations of the flexibility of rhythmic behavior outside the SCN is the observation that rhythmic behavior with a periodicity of ∼24 h can be induced in a variety of cells in culture (34).
The central clock anticipates the change in photoperiod and prepares the animal for the upcoming period of activity and feeding, regardless of whether that period is in the light or dark. The hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis is of particular importance to the active feeding period, as illustrated by the fact that the effector hormones, glucocorticoids, are high during the light period in diurnal animals and high during the dark period in nocturnal animals (6). The generally accepted mechanism for most glucocorticoid effects involves binding of free steroid to a cytoplasmically localized receptor, translocation of ligand-bound receptor into the nucleus, binding of a ligand receptor dimer to specific DNA sites (GREs, glucocorticoid response elements), and modulation of the amount of selective mRNA (13). Although some effects on mRNA stability have been noted, the common mechanism involves increasing or decreasing the rate of transcription of particular genes. Even though more recent evidence suggests that this mechanistic view may be overly simplistic, it is clear that changes in the amount of specific mRNAs are the basis of the vast majority of glucocorticoid actions (2, 3). By virtue of their circadian rhythmicity, glucocorticoids themselves are effectors of many but not all circadian changes in gene expression.
Skeletal muscle represents about 40% of the body mass of most mammals. From a systems point of view, the musculature is central to not only movement and posture, but also to energy metabolism. The musculature uses a very large amount of energy, most of which is in the form of lipid fuels, to maintain posture against gravity and body temperature relative to the environment. The musculature is also responsible for about 75% of the insulin-directed glucose disposal, which supports the phasic mechanical functions of type 2 fibers (15). In addition, under the influence of glucocorticoids, the musculature is shifted into net degradation of proteins, which provide amino acid carbon for gluconeogenesis in the liver and kidney (2). Energy expenditure by muscle should vary as a function of circadian rhythms with the highest expenditure during the animal's active feeding period.
Previously, we profiled the time-dependent response of skeletal muscle from adrenalectamized rats to two different dosing regimens of the synthetic glucocorticoid, methylprednisolone (MPL) (3). By using such animals, we removed not only the endogenous source of glucocorticoids, but also major aspects of the systemic influence of the sympathetic nervous system. One time series involved giving a single bolus dose of MPL (50 mg/kg) and euthanizing animals at 16 time points over a 72-h period. The second time series involved delivering MPL (0.3 mg·kg−1·h−1) via Alzet pump and euthanizing animals at 10 times over a 168-h period. In the present report, we describe the use of Affymetrix arrays to analyze skeletal muscles from intact rats maintained on a strict light-dark regimen consisting of 12:12-h light-dark cycle with three animals killed at 18 time points during the 24-h period. This rich time series allowed us to identify genes whose expression was rhythmically modulated and to group those genes into eight relatively discrete temporal circadian clusters. We grouped the genes with circadian rhythms into 11 functional categories to examine cellular activity as a function of temporal cluster. In addition, comparisons with our previous work allowed us to evaluate the response profiles of genes with circadian rhythms to the two dosing regimens of exogenous corticosteroid, providing insight into the role of glucocorticoids in regulating rhythms of gene expression in skeletal muscle.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals.
Fifty-four normal (150–175 g) male Wistar rats were purchased in two separate batches of 27 from Harlan Sprague Dawley (Indianapolis, IN), and experiments were initiated at body weights between 225 and 275 g. Animals were housed and allowed to acclimatize in a constant-temperature environment (22°C) equipped with a 12:12-h light-dark cycle. Twenty-seven rats (group 1) were acclimatized for 2 wk before study to a normal light-dark cycle, in which lights went on at 8 AM and off at 8 PM. The onset of light cycle was considered as time 0. The other 27 rats (group 2) were acclimatized for 2 wk before study to a reversed light-dark cycle, where lights went on at 8 PM and off at 8 AM. Two weeks of acclimation was sufficient time to reestablish circadian cycles, as indicated by blood corticosterone concentrations in the two groups. Rats in group 1 were killed on three successive days at 0.25, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 11, and 11.75 h after lights on to capture the light period. Rats in group 2 were killed on three successive days at 12.25, 13, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 23, and 23.75 h after lights on to capture the dark period. Animals killed at the same time on successive days were treated as triplicate measurements. Because normal rats were used, minimal animal handling with the least possible environmental disturbances was used to minimize stress. Night vision goggles were used to carry out animal procedures conducted in the dark period. At death, rats were weighed, anesthetized by ketamine:xylazine (80:10 mg/kg), and killed by aortic exsanguination. Blood was drawn from the abdominal aortic artery into syringes using EDTA (4 mM final concentration) as anticoagulant. Plasma was harvested from blood by centrifugation (2,000 g, 15 min, 4°C) and frozen at minus 80°C until analyzed for corticosterone. Gastrocnemius muscles were excised and frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately after death and stored at minus 80°C until RNA preparation. Both acute and chronic MPL dosing experiments have been previously published (26, 32). In brief, populations of adrenalectomized male Wistar rats were given doses of the synthetic glucocorticoid, MPL. In the acute experiment, the animals were given a single bolus dose (50 mg/kg) of MPL and were killed at 16 times over a 72-h period following dosing. In the chronic experiment, the animals were administered 0.3 mg·kg−1·h−1 MPL via Alzet osmotic pumps and were killed at 10 time points over a 168-h period. All rats had free access to rat chow and 0.9% saline drinking water. Our research protocol adheres to the “Principles of Laboratory Animal Care” (NIH publication 85–23, revised in 1985) and was approved by the University at Buffalo Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Plasma steroid assays.
Plasma corticosterone concentrations were determined by a sensitive normal-phase HPLC method, as previously described (11). The limit of quantitation was 10 ng/ml. The interday and intraday coefficients of variation (CV) were less than 10%.
Microarrays.
Muscle samples from each animal were ground into a fine powder in a mortar cooled by liquid nitrogen, and 100 mg was added to 1 ml of prechilled TriZOL Reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad CA). Total RNA extractions were carried out according to manufacturer's directions and were further purified by passage through RNeasy mini-columns (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) according to manufacturer's protocols for RNA cleanup. Final RNA preparations were suspended in RNase-free water and stored at minus 80°C. The RNAs were quantified spectrophotometrically, and purity and integrity were assessed by agarose gel electrophoresis. All samples exhibited 260/280 absorbance ratios of ∼2.0, and all showed intact ribosomal 28S and 18S RNA bands in an approximate ratio of 2:1, as visualized by ethidium bromide staining. Isolated RNA from each muscle sample was used to prepare target according to manufacturer's protocols. The biotinylated cRNAs were hybridized to 54 individual Affymetrix GeneChips Rat Genome 230A (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA), which contained 15,967 probe sets. The 230A chip was used in the chronic infusion experiment as well, allowing direct comparison between the two experiments. The 230A gene chips contain over 7,000 more probe sets more than the ones used (U34A) in our earlier muscle bolus dose MPL study. The high reproducibility of in situ synthesis of oligonucleotide chips allows accurate comparison of signals generated by samples hybridized to separate arrays. This data set has been submitted to GEO (GSE8989).
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR.
The quantity of muscle glutamine synthetase along with gene-specific in vitro transcribed cRNA standards were determined by quantitative real-time RT-PCR using TaqMan probes. Briefly, primer and probe sequences were designed using PrimerExpress software (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) and custom synthesized by Biosearch Technologies, (Novato, CA) The RT-PCR was performed using Brilliant QRT-PCR Core Reagent Kit, 1-Step (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) in a Stratagene MX3005P thermocycler, according to manufacturer instructions. A standard curve was generated using the in vitro transcribed sense cRNA standards. Primer and probe sequences are as follows: forward primer (5′-CGCCCGCCGTCTGA-3′), reverse primer (5′-TCTCCTGGCCGACAATCC-3′), and probe (5-FAM-TCCACGAAACCTCCAACATCAAACGACTTT-BHQ-3′). Intraday and interday CVs were 18% and 10%, respectively.
Data set construction.
As discussed above, animals were killed at precise times on three successive days to obtain data points for the light period and three successive days to obtain data points for the dark period. Animals killed at the same time on different days were treated as three replicates for that time to construct a 24-h light-dark cycle. To obtain a clear picture of an entire cycle, two 24-h periods were concatenated to obtain a 48-h period, which allowed visualization of rhythms that spanned the dark-light and light-dark transitions.
Data mining.
A nonlinear curve fit using MATLAB was conducted, which fitted a sinusoid function [A·sin(Bt + c)] to the data, including the replicates. Genes that could be curve fitted with a R2 correlation of greater than 0.8 were kept. This curve-fitting approach enabled use of replicate information instead of depending on the ensemble average necessary with Fourier transforms or Lombs-Scargle methods. This approach is viable due to our relatively large number of time samples. This data set was then loaded into a data mining program, GeneSpring 7.0 (Silicon Genetics, Redwood City, CA), and we normalized the value of each probe set on each chip to the average of that probe set on all chips. To identify genes with similar patterns of oscillation within the daily cycle, we applied Quality Threshold Clustering (QT) in GeneSpring using Pearson's correlation as the similarity measurement.
RESULTS
Data mining.
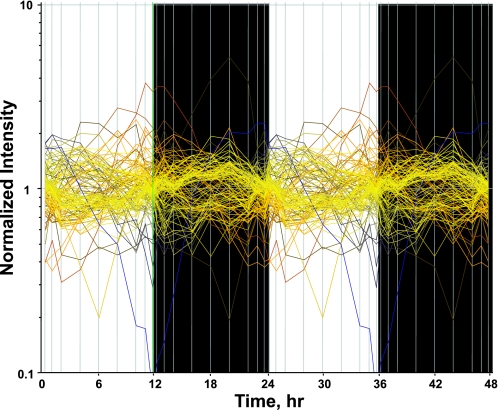
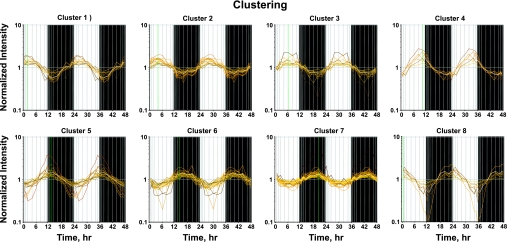
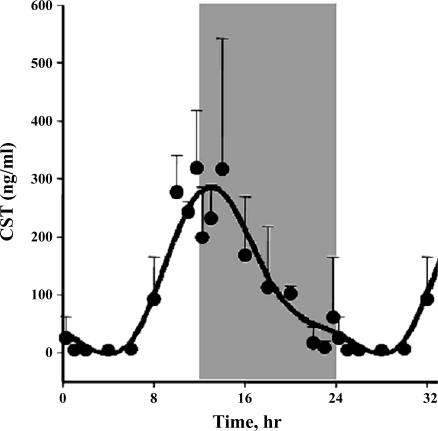
The assumption used to process this data set is that genes whose expression levels are part of the circadian rhythm will show one full oscillation every 24 h. To exploit this assumption, a nonlinear curve fit was conducted, which fitted a sinusoid to the data, including the replicates. We identified 122 probe sets which fit the model [A·sin(Bt + c)] with a R2 correlation greater than 0.8. Because of probe set redundancy (more than one probe set for a single gene), the 122 probe sets represent 109 genes. Using GeneSpring, we normalized the value of each probe set on each chip to the average of that probe set on all chips, such that the expression pattern of all probe sets oscillated approximately around 1. There appear to be two major patterns, as illustrated in Figure 1, which presents the expression pattern of all 122 probe sets. Some probe sets (represented by individual lines in Fig. 1) show expression patterns greater than one during the light period but less than one during the dark period, reflecting maximum expression during the animal's light-inactive period. Conversely, other probe sets reach a maximum (values greater than one) during the dark/active period. However, because of the richness of the data set, we were able to identify more discrete relationships between oscillations in expression and the light-dark periods. To group genes with similar patterns within the daily cycle, we applied Quality Threshold Clustering (QT clustering), yielding eight clusters. Figure 2 shows these eight clusters with the centroid (average of all of the genes in that cluster) highlighted by a white line. Fifty-seven percent of the genes (62 of 109) are in clusters 6, 7, or 8 with maximum expression during the dark/active period. Thirty-one percent of the genes (34 of 109) are in clusters 1, 2, 3, or 4, with maximum expression during the light/inactive period, and the remaining 12% (13 genes) are in cluster 5 with a maximum at hour 12, the transition between light and dark. Corticosterone reaches its maximum plasma concentration at hour 13.3 (Fig. 3). Table 1 provides a detailed list of all genes in each cluster, including probe set ID, accession number, Pearson's correlation coefficient with the centroid, gene symbol, gene name, and gene function.
Fig. 1.
A nonlinear curve fit using MATLAB was conducted which fitted a sinusoid function [A·sin(Bt + c)] to the data, including the replicates. Genes that could be curve fitted with a R2 correlation of greater than 0.8 were kept.
Fig. 2.
QT clustering of genes in muscle measured over 24 h. Each probe set has greater than a 0.75 Pearson's correlation with the centroid of the cluster.
Fig. 3.
Plasma corticosterone (CST) as a function of circadian time as measured by HPLC. Unshaded areas indicate light period and shaded areas indicate dark period.
Table 1.
Circadian-regulated genes arranged by cluster
| Probe ID | Accession No. | Correlation No. | Ontology | Symbol | Gene Name | Gene Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster 1 | ||||||
| 1398767_at | NM_017314 | 0.996 | protein degradation | Ubb, ubc | Ubiquitin B, C | protein catabolism |
| 1372280_at | BI295982 | 0.985 | protein degradation | Asb2 | Ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing protein 2 | E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes |
| 1370510_a_at | AB012600 | 0.963 | transcription | Arntl, BMAL1 | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like | circadian rhythm, transcription regulation |
| 1388426_at | BF398848 | 0.936 | lipid metabolism | srebf1 | sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1 | regulation of transcription, sterol metabolism |
| 1370847_at | AA801238 | 0.927 | immune | Spon2 | Spondin 2 | innate immune response |
| 1374204_at | BM388946 | 0.902 | protein degradation | Wsb1 | WD repeat and SOCS box-containing 1 | E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes |
| 1376963_at | BM388710 | 0.899 | transcription | Dyrk2 | Dual-specificity tyrosine-(Y)-phosphorylation regulated kinase 2 | chromatin remodeling |
| 1376944_at | AI407163 | 0.794 | signaling | Prlr | Prolactin receptor | signaling, JANUS KINASE 2, GHR and SOCS |
| Cluster 2 | ||||||
| 1387294_at | NM_054011 | 0.977 | mitochondrial | Sh3bp5 | SH3-domain binding protein 5 | mitochondrial JNK cascade |
| 1385243_at | AI180340 | 0.972 | transcription | Maf | V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene | transcription factor, DNA binding |
| 1390028_at | BE096356 | 0.971 | transcription | Dyrk2 | Dual-specificity tyrosine-(Y)-phosphorylation regulated kinase 2 | also in cluster 1; see function |
| 1399005_at | BG673380 | 0.965 | signaling | ppp2r5a | Protein phosphatase 2, regulatory subunit B (B56), alpha | signal transduction |
| 1392939_at | BM388933 | 0.962 | transport | Slc41a3 | Solute carrier family 41, member 3 | inorganic cation transport (Mg) |
| 1372624_at | BF551377 | 0.955 | EST | Unknown | unknown function | |
| 1371602_at | BI274110 | 0.933 | signaling | Tspan9 NET-5 | Tetraspanin 9 | signal transduction |
| 1367979_s_at | NM_012941 | 0.931 | lipid metabolism | Cyp51 | Cytochrome P-450, subfamily 51 | sterol 14-alpha-demethylase cholesterol synthesis |
| 1378423_at | AI639060 | 0.901 | signaling | Atcay | Caytaxin | associated with Cayman ataxia |
| 1379550_a_at | BF290483 | 0.889 | transcription | Gtf2ird1 | GTF2I repeat domain-containing protein 1 | regulates muscle fiber-type-specific promoters |
| 1370166_at | AI169682 | 0.848 | cytoskeleton | Sdc2 | Syndecan 2 | transmembrane proteoglycan, cytoskeletal binding protein |
| 1375378_at | BE108882 | 0.827 | transcription | Qki | Quaking homolog, KH domain RNA binding | Transcription, RNA-binding protein |
| 1370835_at | AF267197 | 0.755 | transcription | Tox4 | Epidermal Langerhans cell protein LCP1 | transcription regulation, DNA-dependent |
| 1387321_at | NM_053381 | 0.753 | transport | Atp1b4 | ATPase, (Na+)/K+ transporting, beta 4 polypeptide | sodium:potassium -exchanging ATPase activity, Na+-K+ transport |
| Cluster 3 | ||||||
| 1368277_at | NM_017041 | 0.961 | cell cycle | Ppp3ca | Protein phosphatase 3, catalytic subunit alpha isoform, calcineurin A | G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle |
| 1374636_at | BI298596 | 0.951 | cell cycle | Phf17 | PHD finger protein 17 | proapoptotic barrier to proliferation |
| 1376089_at | BI294974 | 0.947 | lipid metabolism | Ldlr | Low-density lipoprotein receptor | cholesterol homeostasis |
| 1375534_at | BE118698 | 0.923 | signaling | Pum2 | Pumilio homolog 2 | proliferation and self-renewal of stem cells |
| 1388924_at | AA818262 | 0.921 | lipid metabolism | angptl4 | Anigopoietin-like 4 | negative regulation of lipoprotein lipase |
| 1389618_at | BI285035 | 0.890 | EST | Unknown | unknown function | |
| 1398913_at | AI599394 | 0.886 | cell cycle | numa1 | Nuclear mitotic apparatus protein 1 | cycle-related protein |
| 1387172_a_at | NM_031131 | 0.870 | signaling | Tgfb2 | Transforming growth factor, beta-2 | negative regulation of apoptosis, regulation of cell proliferation |
| 1375984_at | BE103689 | 0.842 | transcription | Zfhx4 | Zinc finger homeodomain 4 | DNA-dependent transcription, muscle differentiation |
| 1367894_at | NM_022392 | 0.831 | lipid metabolism | insig1 | Insulin induced gene 1 | retention of the SCAP/SREBP complex in the ER |
| 1374166_at | AW252076 | 0.798 | EST | Unknown | unknown function | |
| Cluster 4 | ||||||
| 1370816_at | M25804 | 0.988 | transcription | nr1d1 | Nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group D, Member 1 | steroid hormone receptor-circadian rhythm |
| 1367602_at | AI013390 | 0.984 | transcription | Cited2 | Cbp/p300-interacting transactivator Glu/Asp-rich carboxy-term Dom 2 | positive transcription regulation |
| 1367601_at | NM_053698 | 0.965 | transcription | Cited2 | Cbp/p300-interacting transactivator Glu/Asp-rich carboxy-term Dom 2 | positive transcription regulation |
| 1388471_at | AA800197 | 0.954 | signaling | tcp11l2 | T-Complex 11 (mouse) like 2 | cell communication |
| 1369150_at | NM_053551 | 0.953 | mitochondrial | Pdk4 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isoenzyme 4 | acetyl-CoA biosynthesis from pyruvate |
| 1386946_at | NM_031559 | 0.922 | mitochondrial | cpt1a | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I | transfer long chain fatty acids across mitochondrial inner membrane |
| 1368511_at | NM_133303 | 0.900 | transcription | Bhlhb3 | Basic helix-loop-helix domain containing, class B, 3 | transcription regulation |
| Cluster 5 | ||||||
| 1390430_at | BF284190 | 0.971 | transcription | nr1d2, RVR | Nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group D, member 2 | DNA-dependent transcription regulation |
| 1387874_at | AI230048 | 0.963 | transcription | Dbp | D site of albumin promoter-binding protein | transcription regulation, circadian rhythm |
| 1370541_at | U20796 | 0.959 | transcription | nr1d2, RVR | Nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group D, member 2 | DNA-dependent transcription regulation |
| 1388525_at | BE112999 | 0.944 | signaling | PIK3IP1 | Phosphoinositide-3-kinase interacting protein 1 | binds to the p110 catalytic down modulates PI3K |
| 1371864_at | AW524563 | 0.943 | transcription | Klf9 | Kruppel-like factor 9 | mediates expression of growth-associated genes |
| 1372452_at | BG666882 | 0.938 | mitochondrial | Gpam | Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase | fatty acid metabolism |
| 1373866_at | AI228596 | 0.930 | mitochondrial | Coq10b | Coenzyme Q10 homolog B | oligonucleotide cyclase/lipid transport protein |
| 1371583_at | AI598399 | 0.927 | transcription | Rbm3 | RNA binding motif protein 3 | RNA processing, miRNA-mediated gene silencing |
| 1374574_at | AI547611 | 0.915 | EST | Unknown | unknown function | |
| 1369050_at | NM_053923 | 0.907 | signaling | Pik3c2 g | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, C2 domain containing, gamma polypeptide | Ras pathway, vesicle trafficking, secretion, and apoptosis |
| 1387669_a_at | NM_012844 | 0.904 | small molecule metabolism | ephx1 | Epoxide hydrolase 1, microsomal | small molecule metabolism |
| 1389632_at | AA799294 | 0.878 | signaling | Rhobtb1 | Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 1 | small GTPase-mediated signal transduction |
| 1368249_at | NM_053536 | 0.868 | carbohydrate metabolism | Klf15 | Krueppel-like factor 15 | regulates GLUT4 expression |
| 1388384_at | AI407618 | 0.866 | cytoskeleton | Dynll1 | Dynein light chain LC8-type 1 | molecular motor |
| 1374855_at | BI279017 | 0.856 | transcription | Per1 | Period 1 | transcription regulation, circadian rhythm |
| 1368283_at | NM_133606 | 0.823 | mitochondrial | Ehhadh | Enoyl-coenzyme A, hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase | acyl-CoA metabolism, fatty acid beta-oxidation |
| Cluster 6 | ||||||
| 1387703_a_at | AF106659 | 0.964 | protein degradation | usp2, ubp69 | Ubiquitin specific peptidase 2 | deubiquitinating enzyme, muscle cell differentiation |
| 1386935_at | NM_024388 | 0.927 | carbohydrate metabolism | nr4a1 | Nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 1 | modulates regulators of skeletal muscle energy homeostasis |
| 1372011_at | BI292028 | 0.925 | small molecule metabolism | Gda | Guanine deaminase | purine metabolism |
| 1389251_at | AA944380 | 0.923 | small molecule metab. | Nudt7 | Nucleoside diphosphate-linked moiety X Motif 7 | peroxisomal, regulates CoA and acyl-CoA levels |
| 1370019_at | AF394783 | 0.916 | small molecule metab. | Sult1a1 | Sulfotransferase family 1A, phenol-preferring, member 1 | transfer sulfate group 3¢-phosphoadenosine 5¢-phosphosulfate |
| 1387053_at | NM_012792 | 0.916 | small molecule metab. | Fmo1 | Flavin-containing monooxygenase 1 | NADPH-dependent oxidative metabolism of many drugs |
| 1371615_at | BI279069 | 0.911 | lipid metabolism | Dgat2 | Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase homolog 2 | triglyceride synthesis, glycerol, lipid metabolism |
| 1368375_a_at | AF015718 | 0.908 | immune | Il15 | Interleukin 15 | positive regulation of T cell proliferation |
| 1388804_at | BI300986 | 0.901 | cell cycle | Mn1 | Meningioma 1 | negative regulation of progression through cell cycle |
| 1390171_at | AA924717 | 0.901 | transcription | FAM76A | Family with sequence similarity 76, member A | nuclear inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1 |
| 1370663_at | D31838 | 0.899 | cell cycle | wee1 | Wee 1 homolog | DNA replication checkpoint, G2/M transition |
| 1369625_at | AA891661 | 0.877 | transport | Aqp1 | Aquaporin 1 | major water transport molecule I vascular |
| 1372178_at | BM385981 | 0.875 | transport | Abcc1 | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 1 | transporter of glutathione-linked compounds from cells |
| 1373092_at | BE109587 | 0.874 | signaling | Tgfbr3, BETA-GLYCAN | Transforming growth factor, beta receptor III | modulates several tissue development and repair processes |
| 1368182_at | NM_130739 | 0.849 | lipid metabolism | acsl6, facl6 | Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 6 | ligation of long-chain fatty acids with coenzyme A |
| 1371479_at | AA946026 | 0.847 | transcription | Mettl7a | Methyltransferase like 7A | methyltransferase activity, metabolic activity |
| 1373818_at | AI408351 | 0.847 | transport | kctd12 | Potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 12 | voltage-gated potassium channel |
| 1368303_at | NM_031678 | 0.844 | transcription | Per2 | Period homolog 2 | circadian rhythm, protein binding, signal transduction |
| 1386987_at | NM_017020 | 0.840 | immune | Il6r, Il6ra, IL6R1 | Interleukin 6 receptor | energy metabolism |
| 1373282_at | AI406494 | 0.824 | mitochondrial | slc25a33 | Solute carrier family 25, member 33 | mitochondrial carrier proteins, transport |
| 1368431_at | NM_017112 | 0.762 | cytoskeleton | Hpn | Hepsin | membrane bound serine protease |
| Cluster 7 | ||||||
| 1388113_at | BG673321 | 0.969 | mitochondrial | cox8a | Cytochrome c oxidase, subunit VIIIa | electron transport chain |
| 1368004_at | NM_022529 | 0.969 | mitochondrial | mrpl23 | Mitochondrial ribosomal protein L23 | protein biosynthesis, translation |
| 1386887_at | NM_053586 | 0.966 | mitochondrial | Cox5b | Cytochromecoxidase, subunit Vb | electron transport chain |
| 1367609_at | NM_031051 | 0.965 | immune | Mif | Macrophage migration inhibitory factor | regulation of macrophage activation |
| 1375197_at | BG665384 | 0.954 | mitochondrial | LOC686442 | Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase subunit | electron transport chain |
| 1371912_at | AI231358 | 0.952 | mitochondrial | Ndufs7 | NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) Fe-S protein 7 | electron transport chain |
| 1369590_a_at | NM_024134 | 0.951 | transcription | Ddit3, GADD153 | DNA-damage inducible transcript 3 | dominant-negative inhibitor of the transcription factors C/EBP |
| 1387015_at | NM_030873 | 0.950 | cytoskeleton | Pfn2 | Profilin 2 | regulation of actin polymerization and/or depolymerization |
| 1388364_at | BG381650 | 0.949 | mitochondrial | Ndufs3 | NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase Fe-S protein 3 | electron transport chain |
| 1388361_at | BI303856 | 0.940 | mitochondrial | PDSW | NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 beta subcomplex, 10 | electron transport chain |
| 1371351_at | AI233192 | 0.938 | transcription | Rpo 1-3 | RNA polymerase 1-3 | transcription regulation |
| 1367568_a_at | NM_012862 | 0.928 | cytoskeleton | Mgp | Matrix gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein | inhibitor of soft-tissue mineralization |
| 1398868_at | AI408157 | 0.927 | mitochondrial | timm13, sirt6 | Translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane 13 | protein folding and targeting |
| 1388683_at | AI411174 | 0.924 | transcription | Lsmd1 | LSM domain containing 1 | RNA processing |
| 1367481_at | BI278301 | 0.920 | protein degradation | vps28 | Vacuolar protein sorting 28 | ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolism |
| 1389288_at | BI279838 | 0.917 | mitochondrial | Ndufa2 | NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 1 Alpha subcomplex, 2 | electron transport chain |
| 1379243_at | AA819547 | 0.917 | mitochondrial | Ndufa6 | NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 1 Alpha subcomplex, 6 | electron transport chain |
| 1367735_at | NM_012819 | 0.897 | mitochondrial | Acadl | Acetyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase, long-chain | lipid, fatty acid metabolism, electron transport |
| 1373850_at | AW251315 | 0.894 | extracellular | Smpdl3b | Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase, acid-like 3B | hydrolase activity, acting on glycosyl bonds, secreted |
| 1388767_at | BI296393 | 0.892 | cell cycle | Pdcd6 | Programmed cell death 6-interacting protein | caspase activation, induction of apoptosis by extracellular signals |
| 1367632_at | NM_017073 | 0.892 | protein degradation | Glul, Glns | Glutamate-ammonia ligase glutamine synthetase | glutamine synthesis, muscle atrophy |
| 1372091_at | BI275959 | 0.889 | cytoskeleton | Mig12 | MID1 interacting G12-like protein | inhibition of microtubule depolymerization, microtubule stabilization |
| 1389230_at | AA818910 | 0.886 | signaling | arrdc3 | Arrestin domain containing 3 | thioredoxin interacting protein |
| 1370428_x_at | AJ249701 | 0.885 | immune | RT1-Aw2, RT1-A2, RT1-A2q | RT1 class Ib, locus Aw2 | antigen processing of peptide antigen via MHC class I |
| 1367506_at | BF283488 | 0.879 | mitochondrial | mrpl11 | Mitochondrial ribosomal protein L11 | protein biosynthesis, translation |
| 1371324_at | BG673668 | 0.876 | transcription | SF3B5 | Splicing factor 3B subunit 5 | RNA splicing, mRNA processing |
| 1367670_at | NM_017005 | 0.867 | mitochondrial | Fh1, Fh | Fumarate hydratase 1 | conversion of fumarate to malate |
| 1375971_at | BM386028 | 0.861 | protein degradation | Cln5 | Ceroid-lipofuscinosis, neuronal 5 | lysosome organization and biogenesis |
| 1369973_at | NM_017154 | 0.858 | immune | Xdh | Xanthine dehydrogenase | inflammation, vascular, muscle damage |
| 1371397_at | AI104068 | 0.858 | signaling | Nosip | Nitric oxide synthase interacting protein | negative regulation of nitric oxide synthase activity |
| 1375211_at | BM391506 | 0.846 | extracellular | Rnaset2 | Ribonuclease T2 | secreted RNases |
| 1371649_at | BI289411 | 0.846 | mitochondrial | mrps24 | Mitochondrial ribosomal protein S24 | protein biosynthesis, translation |
| 1386857_at | NM_017166 | 0.842 | signaling | Stmn1 | Stathmin 1 | signaling relay, phosphoprotein |
| 1369467_a_at | NM_012621 | 0.800 | carbohydrate metabolism | Pfkfb1 | 6-Phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 1 | glycolysis |
| 1369545_at | NM_017086 | 0.782 | transcription | Egr3 | Early growth response 3 | regulation of myotube fate |
| Cluster 8 | ||||||
| 1373108_at | BM390827 | 0.989 | carbohydrate metabolism | ppp1r3c | Protein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 3C | glycogen metabolic process |
| 1388395_at | AI406939 | 0.973 | cell cycle | G0 s2 | G0/G1 switch gene 2 | regulation of progression through cell cycle |
| 1398246_s_at | NM_053843 | 0.957 | immune | Fcgr3 | Fc receptor, IgG, low affinity III | antigen processing and presentation |
| 1372964_at | BI294751 | 0.954 | transcription | arid5b | AT rich interactive domain 5B | negative regulation of transcription |
| 1368136_at | NM_012887 | 0.923 | transcription | Tmpo, Slc25a3 | Thymopoietin | nuclear membrane protein |
| 1367850_at | NM_053843 | 0.922 | immune | Fcgr3 | Fc receptor, IgG, low affinity III | antigen processing and presentation |
| 1368488_at | NM_053727 | 0.899 | immune | Nfil3 | Nuclear factor, interleukin 3 regulated | DNA-dependent transcription regulation |
| 1374029_at | AI229596 | 0.869 | EST | Unknown | unknown function |
Probe sets exhibiting a circadian pattern in rat skeletal muscle arranged by cluster. Probe ID refers to identification number used by Affymetrix, which is distinct from GenBank accession numbers. Correlation no. represents the Pearson's correlation following QT clustering. Probe sets highlighted in bold are genes that are also MPL responsive.
Regulation.
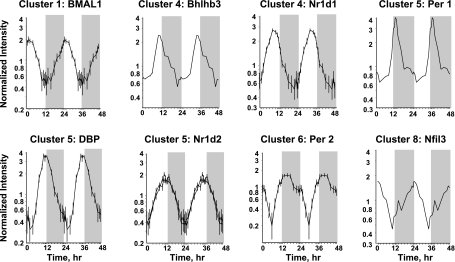
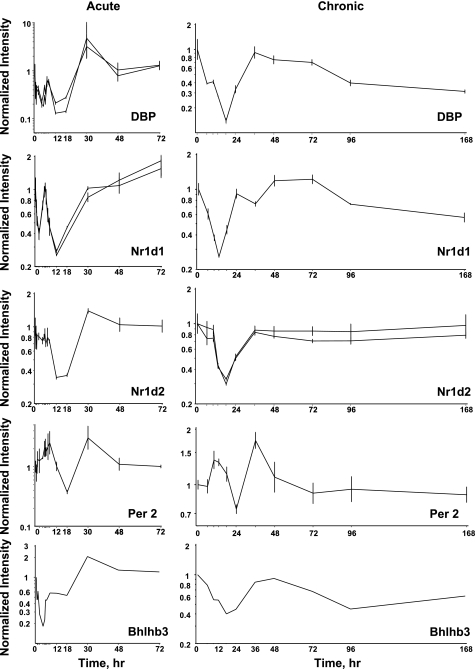
We examined the chip for probe sets for genes previously identified as involved in regulation of circadian patterns (34). The 230A chip contained probe sets for 17 of these transcription factors. However, only eight (Per1, Per2, BMAL1b, Bhlhb3, DBP, Nfil3, Nr1d1, and Nr1d2) showed distinct circadian oscillation. Figure 4 provides profiles for these eight transcription factors with circadian rhythms and their respective clusters. The chip did contain probe sets for Per3, Bhlhb2, RORB, RORC, CRY2, and CLOCK. On visual inspection, the signals for Per 3, RORB, and CRY2 were very low, which may prevent identification of rhythmicity. However, the signals for Bhlhb2, RORC, and CLOCK were reasonably intense but did not show any indication of oscillation.
Fig. 4.
Expression patterns of 8 clock-related transcription factors in skeletal muscle as a function of circadian time. Unshaded areas indicate light periods, and shaded areas indicate dark periods.
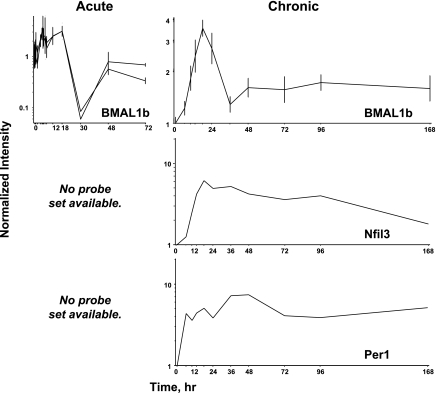
Previously, we conducted two time series experiments in which cohorts of adrenalectamized rats were given MPL either as a single bolus dose or chronic infusion, and the muscles were analyzed by gene arrays. Because a major regulator of circadian rhythms is the HPA axis, these arrays were examined for clock genes. Figure 5 shows the acute and chronic profiles for Per2, Bhlhb3, DBP, Nr1d1, and Nr1d2. In the acute profile, all five genes respond to the single-dose with a transient oscillation. Per2 began the oscillation with increased expression while DBP, Nr1d1, Bhlhb3, and Nr1d2 begin the oscillation with down-regulation. With chronic infusion, Per2 appears to oscillate throughout the 168-h infusion period beginning with enhanced expression. Consistent with the response to acute dosing DBP, Bhlhb3, Nr1d1, and Nr1d2 all show initial downregulation in response to infusion. DBP recovers baseline by 36 h and starts a slow decline throughout the remainder of the infusion. Nr1d1 recovers baseline by 24 h, shows a period of dampened oscillation for an additional 36 to 48 h, then begins a period of slow decline similar to DBP. Bhlhb3 looks almost like an inverse of Per2, in that it recovers baseline by about 48 h, after which it goes down again, and then shallowly starts back up again. Nr1d2 almost recovers baseline by 36 h, then maintains a new expression level slightly lower than baseline throughout the remainder of the infusion period. Because of their fluctuating behavior, for the most part, these five genes did not meet our criteria for corticosteroid regulation when the acute and chronic treatment data sets were initially mined (3). With acute dosing, BMAL1b oscillated with a pattern similar to Per2. However, with chronic infusion BMAL1b showed a strong peak of enhanced expression followed by a lower level of enhanced expression (Fig. 6). This figure also shows just the chronic profiles of Per1 and Nfil3 as the U34A chip did not contain probe sets for these genes. Both showed enhanced expression throughout the infusion period.
Fig. 5.
Expression patterns of 5 clock-related transcription factors in skeletal muscle as a function of time after methylprednisolone (MPL) administration to adrenalectomized animals. Left: data from acute (bolus 50 mg/kg) MPL dosing. Right: data from chronic (0.3 mg·kg−1·h−1) MPL infusion.
Fig. 6.
Expression patterns of 3 clock-related transcription factors in skeletal muscle as a function of time after MPL administration to adrenalectomized animals. Left: data from acute (bolus 50 mg/kg) MPL dosing. Right: data from chronic (0.3 mg·kg−1·h−1) MPL infusion.
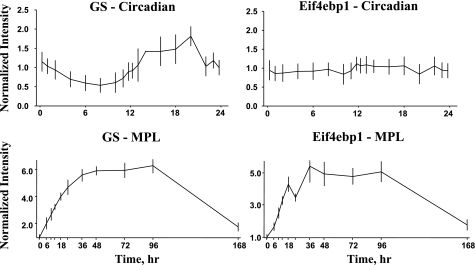
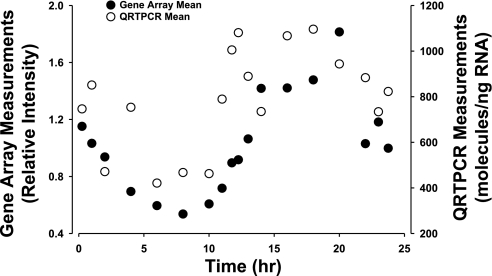
The Affymetrix 230A chip was used for chronic infusion experiments, while the acute dosing experiment used the older U34A chip, which contained fewer probe sets. Because both this circadian experiment and the chronic infusion experiment used the same chip, we were able to make a direct comparison between corticosteroid-responsive genes and those with circadian rhythms. Data mining identified over 2,000 genes in the chronic infusion data set that were responsive to the infusion of 0.3 mg·kg−1·h−1 MPL via Alzet osmotic pumps (3). Of the 109 genes with circadian rhythms, only 55 were responsive to MPL infusion, while 67 were not. The circadian rhythm-regulated probe sets that are also responsive to MPL infusion are highlighted in bold in Table 1. Just as the 109 genes are not equally distributed among the eight clusters, the percentage of genes in each cluster that respond to MPL is not the same. For example, only 25% of the genes in cluster 1 are responsive, while 71% of the genes in cluster 6 are responsive. Cluster 6 is the first cluster to reach a maximum after plasma corticosterone reaches its maximum. The reverse is also true; not all genes that are responsive to MPL infusion have circadian rhythms. For example, Fig. 7 shows the response profiles of two genes to MPL infusion (bottom) together with their response profiles over the 24-h circadian time series (top). Both of these genes are likely involved in the atrophy caused by MPL infusion. The first is glutamine synthetase (GS), which is involved in the export of amino acid carbon from the musculature (22). The second is eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4e binding protein (Eif4ebp), which binds to the initiation factor and prevents the initiation of translation (33). Both genes are responsive to MPL. GS has a strong circadian rhythm, which has also been verified by quantitative RT PCR (Fig. 8). In contrast, Eif4ebp does not exhibit a circadian rhythm.
Fig. 7.
Expression patterns of GS (left) and Eif4ebp1 (right) following chronic infusion of MPL (0.3 mg·kg−1·h−1) over 168 h (top), and within the 24 h circadian cycle (bottom).
Fig. 8.
Circadian pattern of expression of glutamine synthetase measured by gene arrays (•) and by kinetic-based quantitative RT PCR (○).
Functional groupings.
The accession numbers for all 122 probe sets were analyzed using the National Center for Biotechnology Information Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) to both definitively identify the gene and to obtain alternative names and symbols. Using this information, we extensively researched each gene to identify and categorize its function. The genes were then separated into the following 11 functional groupings: carbohydrate metabolism, cell cycle, cytoskeleton/extracellular, immune, lipid metabolism, mitochondrial, protein degradation, signaling, small molecule metabolism, transcription, and transport. In several cases, we needed to decide on the most appropriate category because some genes could fit into more than one group. For example, the transcription factor, sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1 (SREBP1), was placed in the category of lipid metabolism because it is critical to this function, while alternative placement in transcription would also have been valid (8). Similarly, two genes, WD repeat and suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) box-containing 1 and ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing protein 2, were placed in the immune functional category rather than signaling. Both of these genes are adaptor/regulatory modules that contain a SOCS box that is essential for the physiological inhibition of interferon signaling (28). Table 2 provides the grouping of genes into functional categories.
Table 2.
Functional categorization of circadian regulated genes
| Probe ID | Cluster | Symbol | Gene Name | Gene Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrate Metabolism | ||||
| 1369467_a_at | 7 | Pfkfb1 | 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 1 | glycolysis |
| 1373108_at | 8 | ppp1r3c | Protein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 3C | glycogen metabolic process |
| 1368249_at | 5 | Klf15 | Krueppel-like factor 15 | regulates GLUT4 expression |
| 1386935_at | 6 | nr4a1 | Nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 1 | regulator of muscle energy homeostasis |
| Cell Cycle | ||||
| 1398913_at | 3 | numa1 | Nuclear mitotic apparatus protein 1 | cycle-related protein |
| 1374636_at | 3 | Phf17 | PHD finger protein 17 | proapoptotic barrier to proliferation |
| 1368277_at | 3 | Ppp3ca | Protein phosphatase 3, catalytic subunit, alpha isoform, calcineurin A | G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle |
| 1388804_at | 6 | Mn1 | Meningioma 1 | negative regulation of progression through cell cycle |
| 1370663_at | 6 | wee1 | Wee 1 homolog | DNA replication checkpoint, G2/M transition |
| 1388767_at | 7 | Pdcd6 | Programmed cell death 6-interacting protein | caspase activation, induction of apoptosis by extracellular signals |
| 1388395_at | 8 | G0 s2 | G0/G1 switch gene 2 | regulation of progression through cell cycle |
| Cytoskeleton-Extracellular | ||||
| 1370166_at | 2 | Sdc2 | Syndecan 2 | transmembrane proteoglycan, cytoskeletal binding protein |
| 1388384_at | 5 | Dynll1 | Dynein light chain LC8-type 1 | molecular motor |
| 1368431_at | 6 | Hpn | Hepsin | Membrane-bound serine protease |
| 1367568_a_at | 7 | Mgp | Matrix gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein | inhibitor of soft-tissue mineralization |
| 1372091_at | 7 | Mig12 | MID1 interacting G12-like protein | inhibition of microtubule depolymerization, microtubule stabilization |
| 1387015_at | 7 | Pfn2 | Profilin 2 | regulation of actin polymerization and/or depolymerization |
| 1373850_at | 7 | Smpdl3b | Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase, acid-like 3B | hydrolase activity, acting on glycosyl bonds, secreted |
| 1375211_at | 7 | Rnaset2 | Ribonuclease T2 | secreted RNase |
| Immune | ||||
| 1370847_at | 1 | Spon2 | Spondin 2 | innate immune response |
| 1368375_a_at | 6 | Il15 | Interleukin 15 | positive regulation of T cell proliferation |
| 1386987_at | 6 | Il6r, Il6ra, IL6R1 | Interleukin 6 receptor | energy metabolism |
| 1367609_at | 7 | Mif | Macrophage migration inhibitory factor | regulation of macrophage activation |
| 1370428_x_at | 7 | RT1-Aw2, RT1-A2, RT1-A2q | RT1 class Ib, locus Aw2 | antigen processing and presentation via MHC class I |
| 1369973_at | 7 | Xdh | Xanthine dehydrogenase | inflammation, vascular, muscle damage |
| 1398246_s_at | 8 | Fcgr3 | Fc receptor, IgG, low-affinity III | antigen processing and presentation |
| 1367850_at | 8 | Fcgr3, | Fc receptor, IgG, low-affinity III | antigen processing and presentation |
| 1368488_at | 8 | Nfil3 | Nuclear factor, interleukin 3 regulated | DNA-dependent transcription regulation |
| Lipid Metabolism | ||||
| 1388426_at | 1 | srebf1 | Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1 | regulation of transcription, sterol metabolism |
| 1367979_s_at | 2 | Cyp51 | Cytochrome P-450, subfamily 51 | sterol 14-alpha-demethylase cholesterol synthesis |
| 1376089_at | 3 | Ldlr | Low-density lipoprotein receptor | cholesterol homeostasis |
| 1388924_at | 3 | angptl4 | Anigopoietin-like 4 | negative regulation of lipoprotein lipase |
| 1367894_at | 3 | insig1 | Insulin-induced gene 1 | retention of the SCAP/SREBP complex in the ER |
| 1368182_at | 6 | acsl6, facl6 | Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 6 | ligation of long-chain fatty acids with coenzyme A |
| 1371615_at | 6 | Dgat2 | Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase homolog 2 | triglyceride synthesis, glycerol, lipid metabolism |
| Mitochondrial | ||||
| 1387294_at | 2 | Sh3bp5 | SH3-domain binding protein 5 | mitochondrial JNK cascade |
| 1369150_at | 4 | Pdk4 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isoenzyme 4 | acetyl-CoA biosynthesis from pyruvate |
| 1386946_at | 4 | cpt1a | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I | transfer long-chain fatty acids across the mitochondrial inner membrane |
| 1368283_at | 5 | Ehhadh | Enoyl-coenzyme A, hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase | acyl-CoA metabolism, fatty acid beta-oxidation |
| 1373866_at | 5 | Coq10b | Coenzyme Q10 homolog B | oligonucleoxide cyclase/lipid transport protein |
| 1372452_at | 5 | Gpam | Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase | fatty acid metabolism |
| 1373282_at | 6 | slc25a33 | Solute carrier family 25, member 33 | mitochondrial carrier proteins, transport |
| 1367735_at | 7 | Acadl | Acetyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase, long-chain | lipid, fatty acid metabolism, electron transport |
| 1386887_at | 7 | Cox5b | Cytochrome c oxidase, subunit Vb | electron transport chain |
| 1388113_at | 7 | cox8a | Cytochrome c oxidase, subunit VIIIa | electron transport chain |
| 1388361_at | 7 | PDSW | NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 beta subcomplex, 10 | electron transport chain |
| 1389288_at | 7 | Ndufa2 | NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 1 Alpha subcomplex, 2 | electron transport chain |
| 1379243_at | 7 | Ndufa6 | NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 1 Alpha subcomplex, 6 | electron transport chain |
| 1388364_at | 7 | Ndufs3 | NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase Fe-S protein 3 | electron transport chain |
| 1371912_at | 7 | Ndufs7 | NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) Fe-S protein 7 | electron transport chain |
| 1375197_at | 7 | LOC686442 | Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase subunit | electron transport chain |
| 1367506_at | 7 | mrpl11 | Mitochondrial ribosomal protein L11 | protein biosynthesis, translation |
| 1368004_at | 7 | mrpl23 | Mitochondrial ribosomal protein L23 | protein biosynthesis, translation |
| 1371649_at | 7 | mrps24 | Mitochondrial ribosomal protein S24 | protein biosynthesis, translation |
| 1398868_at | 7 | timm13, sirt6 | Translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane 13 | protein folding and targeting |
| 1367670_at | 7 | Fh1, Fh | Fumarate hydratase 1 | conversion of fumarate to malate |
| Protein Degradation | ||||
| 1398767_at | 1 | Ubb, ubc | Ubiquitin B, C | protein catabolism |
| 1374204_at | 1 | Wsb1 | WD repeat and SOCS box-containing 1 | E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes |
| 1372280_at | 1 | Asb2 | Ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing protein 2 | E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes |
| 1387703_a_at | 6 | usp2, ubp69 | Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2 | deubiquitinating enzyme, muscle cell differentiation |
| 1375971_at | 7 | Cln5 | Ceroid-lipofuscinosis, neuronal 5 | lysosome organization and biogenesis |
| 1367632_at | 7 | Glul, Glns | Glutamine synthetase | glutamine synthesis, muscle atrophy |
| 1367481_at | 7 | vps28 | Vacuolar protein sorting 28 | ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolism |
| Signaling | ||||
| 1376944_at | 1 | Prlr | Prolactin receptor | signaling, JANUS KINASE 2, GHR and SOCS |
| 1378423_at | 2 | Atcay | Caytaxin | associated with Cayman ataxia |
| 1399005_at | 2 | ppp2r5a | Protein phosphatase 2, regulatory subunit B (B56), alpha | signal transduction |
| 1371602_at | 2 | Tspan9 NET-5 | Tetraspanin 9 | signal transduction |
| 1387172_a_at | 3 | tgfb2 | Transforming growth factor, beta-2 | negative regulation of apoptosis, regulation of cell proliferation |
| 1388471_at | 4 | tcp11l2 | T-complex 11 like 2 | cell communication |
| 1369050_at | 5 | Pik3c2 g | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, C2 domain containing, gamma | Ras pathway, vesicle trafficking, secretion, and apoptosis |
| 1388525_at | 5 | PIK3IP1 | Phosphoinositide-3-kinase interacting protein 1 | binds to the p110 catalytic down modulates PI3K |
| 1389632_at | 5 | Rhobtb1 | Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 1 | small GTPase-mediated signal transduction |
| 1373092_at | 6 | Tgfbr3, BETA-GLYCAN | Transforming growth factor, Beta receptor III | modulates several tissue development and repair processes |
| 1386857_at | 7 | Stmn1 | Stathmin 1 | signaling relay phosphoprotein |
| 1371397_at | 7 | Nosip | Nitric oxide synthase interacting protein | negative regulation of nitric oxide synthase activity |
| 1389230_at | 7 | arrdc3 | Arrestin domain containing 3 | thioredoxin interacting protein |
| Small Molecule Metabolism | ||||
| 1387669_a_at | 5 | ephx1 | Epoxide hydrolase 1, microsomal | small molecule metabolism |
| 1389251_at | 6 | Nudt7 | Nucleoside diphosphate-linked moiety X motif 7 | peroxisomal, regulates CoA and acyl-CoA levels |
| 1370019_at | 6 | Sult1a1 | Sulfotransferase family 1A, phenol-preferring, member 1 | transfer of a sulfate group from 3¢-phosphoadenosine 5¢-phosphosulfate |
| 1387053_at | 6 | Fmo1 | Flavin-containing monooxygenase 1 | NADPH-dependent oxidative metabolism of many drugs |
| 1372011_at | 6 | Gda | Guanine deaminase | purine metabolism |
| Transcription | ||||
| 1375378_at | 2 | Qki | Quaking homolog, KH domain RNA binding | transcription, RNA-binding protein |
| 1375984_at | 3 | Zfhx4 | Zinc finger homeodomain 4 | DNA-dependent transcription, muscle differentiation |
| 1367602_at | 4 | Cited2 | Cbp/p300-interacting transactivator, Glu/Asp-rich carboxy-terminal domain, 2 | positive transcription regulation |
| 1367601_at | 4 | Cited2 | Cbp/p300-interacting transactivator, Glu/Asp-rich carboxy-terminal domain, 2 | positive transcription regulation |
| 1370816_at | 4 | nr1d1 | Nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group D, member 1 | steroid hormone receptor-circadian rhythm |
| 1368511_at | 4 | Bhlhb3 | Basic helix-loop-helix domain containing, class B, 3 | transcription regulation |
| 1387874_at | 5 | Dbp | D site of albumin promoter-binding protein | transcription regulation, circadian rhythm |
| 1371864_at | 5 | Klf9 | Kruppel-like factor 9 | mediates expression of growth-associated genes |
| 1390430_at | 5 | nr1d2, RVR | Nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group D, member 2 | DNA-dependent transcription regulation |
| 1370541_at | 5 | nr1d2, RVR | Nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group D, member 2 | DNA-dependent transcription regulation |
| 1371583_at | 5 | Rbm3 | RNA binding motif protein 3 | RNA processing, miRNA-mediated gene silencing |
| 1368303_at | 6 | Per2 | Period homolog 2 | circadian rhythm, protein binding, signal transduction |
| 1390171_at | 6 | FAM76A | Family with sequence similarity 76, member A | nuclear inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1 |
| 1371479_at | 6 | Mettl7a | Methyltransferase like 7A | methyltransferase activity, metabolic activity |
| 1369545_at | 7 | Egr3 | Early growth response 3 | regulation of myotube fate |
| 1371351_at | 7 | Rpo1-3 | RNA polymerase 1-3 | transcription regulation |
| 1369590_a_at | 7 | Ddit3, GADD153 | DNA-damage-inducible transcript 3 | dominant-negative inhibitor of the transcription factors C/EBP |
| 1388683_at | 7 | Lsmd1 | LSM domain containing 1 | RNA processing |
| 1371324_at | 7 | SF3B5 | Splicing factor 3B subunit 5 | RNA splicing; mRNA processing |
| 1368136_at | 8 | Tmpo, Slc25a3 | Thymopoietin | nuclear membrane protein |
| 1372964_at | 8 | arid5b | AT rich interactive domain 5B | negative regulation of transcription |
| Transport | ||||
| 1392939_at | 2 | Slc41a3 | Solute carrier family 41, member 3 | inorganic cation transport (Mg) |
| 1372178_at | 6 | Abcc1 | ATP-binding cassette, subfamily C (CFTR/MRP), member 1 | transporter of glutathione-linked compounds from cells |
| 1369625_at | 6 | Aqp1 | Aquaporin 1 | major water transport molecule I vascular |
| 1373818_at | 6 | kctd12 | Potassium channel tetramerization domain containing 12 | voltage-gated potassium channel |
Probe sets exhibiting a circadian pattern in rat skeletal muscle arranged by gene function. Probe ID refers to identification number used by Affymetrix, which is distinct from GenBank accession numbers. Cluster number refers to circadian expression patterns identified by QT clustering, as presented in Table 1.
DISCUSSION
This report describes a gene array analysis of circadian oscillation of mRNA expression in the skeletal muscle of adult male Wistar rats. Animals were killed at nine time points during a 12-h light period and nine corresponding time points during a 12-h dark period (n = 3 per time point). Muscle RNAs from each of the 54 animals were applied to individual Affymetrix GeneChips Rat Genome 230A, which contained 15,967 probe sets. Analysis yielded 122 probe sets (representing 109 genes) with a 24-h periodicity. Because of the richness of this data set, we were able to apply QT clustering and identified eight clusters with maxima at different times during the cycle. Four clusters peaked during the light period and contained 31% of the genes, three clusters peaked during the dark period and contained 57% of the genes, and one peaked very close to the light to dark transition (12% of the genes). In 13 cases, there were two probe sets on the chip for a gene. In 12 of these cases, both probe sets were in the same cluster with similar correlations to the centroid. However, in one case, dual-specificity tyrosine-(Y)-phosphorylation regulated kinase 2 (Dyrk2), one probe set was in cluster 1 with a maximum at 2 h, and the other was in cluster 2 with a maximum at 4 h. Both probe sets BLAST to the consensus sequence for this gene (NM_001108100.1). Both have similar scores around 1,000, indicating a very good match with the consensus sequence. Visual inspection of the expression patterns confirms that they are different in both time and intensity.
Regulation of the central SCN clock involves as many as 17 genes (34). The 230A array contained probe sets for 14 of these. Eight (Per1, Per2, BMAL1b, Bhlhb3, DBP, Nfil3, Nr1d1, and Nr1d2) showed distinct circadian oscillations in skeletal muscle. However, six (Per3, Bhlhb2, RORB, RORC, CRY2, and CLOCK) did not demonstrate oscillations in our study. In the cases of Per3, RORB, and CRY2, this may be due to very low signal intensities. However, the signal intensities of CLOCK, Bhlhb2, and RORC were reasonable. Zambon et al. (40), using a much sparser data set and statistical analysis, did report a circadian rhythm for CRY1 in human skeletal muscle (40). However, visual inspection of their data does not suggest an oscillation with a 24 h periodicity, which was the criterion that we applied here. While the 230A chip used here did not contain a probe set for CRY1, it did contain a probe set for CRY2. McCarthy et al. (20) reported circadian oscillation of CRY2 in mouse skeletal muscle using RTPCR. This suggests that our result may be due to the inability of the CRY2 probe set on the 230A array to measure the signal. In contrast, CLOCK exhibited a strong signal but no circadian pattern in our studies. It has been reported by others that at least in some tissues, CLOCK is expressed at tonic levels and that cycling is due to the rhymicity of its heterodimeric partner BMAL (27). Steeves et al. (30), using Northern blot hybridization, did report the expression of CLOCK in skeletal muscle (30). However, they only measured one time point, so oscillation was not measured. Our result confirms their observation that CLOCK is expressed in skeletal muscle and indicates that it does not have circadian rhythmicity. In addition, in our chronic infusion studies CLOCK does not respond significantly to MPL.
Because skeletal muscle represents about 40% of the mass of a normal healthy mammal, it is a major target of endogenous glucocorticoids. The large protein mass of the musculature provides a major underpinning for systemic glucose homeostasis. Glucocorticoids shift muscle into a net negative nitrogen balance, and much of the resultant amino acid carbon is used to synthesize glutamine. Glucocorticoids also enhance the expression of enzymes in the liver and kidney that use the amino acid carbon released from the musculature for gluconeogenesis. We also used kinetic-based RT PCR to measure the expression of mRNA for glutamine synthesis in the same muscle used for this array experiment. As expected, RT PCR and array data exhibit virtually identical circadian patterns (Fig. 8). The array results presented here put that observation within the broader context of all gene expression changes and demonstrates that this enzyme is in cluster 7, which reaches a maximum about 5 h after the maximum of the corticosterone rhythm. Synthetic glucocorticoids, corticosteroids, are widely used therapeutic agents for modulation of immune/inflammatory responses. Previously, we measured the time course of the responses of skeletal muscle to both a single bolus dose and continuous infusion of the corticosteroid methylprednisolone (3). Because those experiments were conducted with adrenalectamized animals, corticosterone circadian rhythmicity was absent. Although corticosteroids are widely used agents to modulate immune/inflammatory responses, they have a low therapeutic index. The effect of these agents on the musculature contributes substantially to the side effects of corticosteroids. Not only does the musculature atrophy to provide amino acid carbon for increased gluconeogenesis by the liver and kidney but also the musculature becomes insulin resistant. The result is a condition known as steroid diabetes.
The effects of glucocorticoids/corticosteroids on skeletal muscle are quite complex. Some, like the enhanced expression of glutamine synthetase, appear to be due to the interaction of the hormone receptor complex with a GRE 5′ to the coding region. Others are less direct and more complex due to the effects of corticosteroids on, among other things, the expression of other transcription factors. For example, corticosteroids enhance the expression of myostatin, a muscle-specific transcription factor (18). We examined our previously obtained acute and chronic data sets to ascertain the effect of chronic MPL infusion and where possible acute dosing on the eight transcription factors identified in the current data set as having circadian rhythms. In the six cases for which acute profiles were available, the response was that the drug caused the expression to begin oscillation, which dampened with time. The first phase of this oscillation was up for BMAL1b and Per2, while the first phase of the oscillation was down for Bhlhb3, DBP, Nr1d1, and Nr1d2. With chronic infusion, the initial effect was in the same direction as the acute dosing. Per2, Bhlhb3, DBP, and Nr1d1 continued oscillating with different periodicities throughout the infusion period, while Nr1d2 made a significant initial decline and almost recovered baseline. However, three genes BMAL1b, Nfil3, and Per1 showed very significant prolonged changes in expression. BMAL1b showed a very sharp increase in expression that dropped by about 50% by 36 h to a state of continuous enhanced expression over baseline throughout the infusion period. Per1 quickly went up 5- to 6-fold and remained at this level throughout the infusion period. Nfil3 also quickly went up about 5- to 6-fold and slowly began to decline over the infusion period but was still about twice the baseline at the end (168 h). Taken together, the results suggest that the expression of some of these transcription factors, BMAL1b, Nfil3, and Per1, are more closely linked to the corticosterone circadian rhythm than others (Per2, Bhlhb3, DBP, Nr1d1, and Nr1d2). However, the fact that all of the measurable transcripts in our acute bolus dosing study begin to oscillate suggest that the corticosterone rhythm may be the initiator of their rhythmic pattern of gene expression. This is consistent with the observation by McCarthy that some genes in muscle maintain rhythmic expression in CLOCK mutant mice and that diurnal and nocturnal animals can phase shift not only their glucocorticoid rhythm but also the rhythms of gene expression in peripheral tissues (20).
We also compared circadian-regulated genes with those identified as regulated by the chronic infusion of MPL. Of the more than 2,000 probe sets identified as responsive to MPL infusion, only 57 probe sets (55 genes) with circadian rhythms were among the glucocorticoid-regulated group. However, these data sets together allowed us to address two basic but related questions. The first is: do all genes that respond to corticosteroids have circadian rhythms? The second is: do all genes with circadian rhythms respond to corticosteroid? The answer to both questions is “No.” Only 55 of the genes identified were both circadian and MPL-responsive. The facts that all genes that respond to MPL are not circadian and that all genes with circadian rhythms do not respond to MPL suggest that there is some diversity in mediating mechanisms. This result is consistent with both the previously described observations comparing our acute and chronic profiles and the current observation that the genes can be separated into eight clusters (3).
If an animal is diurnal, increased mRNA expression near the end of the dark period begins to prepare the animal for activity and feeding. Similarly, downward changes during the end of the light period prepare the diurnal animal for inactivity and rest. For example nocturin, a deadenylase that has peak expression in the early dark period in rodents, has been implicated in the regulation of genes important to feeding and energy metabolism (9). Rats are nocturnal, and cycling of gene expression in peripheral tissues like the muscle is reversed relative to humans who are essentially diurnal. On the basis of extensive literature searching, we placed each of the 109 genes into functional groupings as follows: carbohydrate metabolism, cell cycle, cytoskeleton/extracellular, immune, lipid metabolism, mitochondrial, protein degradation, signaling, small molecule metabolism, transcription, and transport. The objective of this analysis was to ascertain which functions are most influenced by circadian patterns and when they are occurring. The most populated functional group is transcription (Table 2). In addition to the 25 genes that appear on this table, Nfil3 (which we placed in the immune grouping), Klf15 and nr4a1 (in the carbohydrate grouping), and srebpf1 (in the lipid grouping) are also transcription factors. Thus about one-fourth of the genes with circadian rhythms are involved in the regulation of transcription/translation. It is also important to note that genes in this grouping occur in all eight clusters, which illustrate the complex nature of circadian rhythms on gene expression. Almost all of the genes in this grouping are involved in transcription. However, a notable exception is Pumilio homolog 2 (Pum2), which is in cluster 3. Cluster 3 also contains zinc finger homeodomain 4 (Zfhx4). Pum2 is involved in mRNA degradation and has been shown to promote stem cell proliferation (37). Kostich and Sanes (16) observed that Zfhx4 was high during proliferation but decreased with differentiation. These observations, together with the observation that transforming growth factor, beta-2 (tgfb2) in the signaling group, which is an inhibitor of differentiation (29), is also in cluster 3 suggests that muscle stem cell proliferation may be initiated during the middle of the light/inactive period. Reinforcing this conclusion is the presence of nuclear mitotic apparatus protein 1 (numa1), PHD finger protein 17 (Phf17), and protein phosphatase 3, catalytic subunit, alpha isoform (Ppp3ca) from the cell cycle group in cluster 3 as well.
The second most populated group is mitochondrial with 21 genes. In stark contrast to the transcription grouping, 14 of these genes are in cluster 7, which reached its maximum in the middle of the dark/active period of the animal. The gastrocnemius muscle is a mixed-fiber muscle, but because the animals are awake but relatively sedentary, the musculature in general is using primarily lipid fuels that require mitochondria. This grouping also illustrates quite well that genes that work together are expressed together.
The third most populated group is signaling, with 14 genes. In addition to the cluster 3 gene, tgfb2, the signaling group also contains two probe sets for protein phosphatase 2, regulatory subunit B56 alpha (ppp2r5a), a cluster 2 gene that would be consistent with cell proliferation occurring during the light period (21). In contrast, the expression of genes such as Stathmin 1 (35), along with the mitochondrial genes in cluster 7, suggests that the circadian expression is by differentiated cells. All genes in the functional immune group, except Spondin 2 (Spon2), which is involved in innate immune responses (12), are expressed in clusters 6, 7, and 8, which reach maxima during the dark/active period.
Although there are only seven genes in the lipid group, several are central to the regulation of lipid metabolism in skeletal muscle. The first is SREBP1 which is a master transcription factor that plays a role in the expression of many lipogenic genes (8). SREBP1 is in cluster 1 that reaches a maximum early in the light period. Cluster 2 contains lanosterol 14-demethylase (CYP51), an enzyme important for cholesterol biosynthesis (31). Cluster 3 contains three genes that are central to muscle lipid metabolism. The first is low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR). The second is anigopoietin-like 4 (angptl4), which inhibits lipoprotein lipase (39), and the last is insulin-induced gene 1 (insig1), which facilitates the retention of the SREBP cleavage-activated protein/SREBP complex in the endoplasmic reticulum (1). Cluster 6, which has a maximum during the dark period, contains two genes important for the synthesis of triglycerides. The first is acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 6 (acsl6), which catalyzes the ligation of long-chain fatty acids with coenzyme A (19). The second is diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase homolog 2 (Dgat2), which catalyzes the covalent linking of diacylglycerol to long-chain fatty acyl-CoAs (17).
The functional group that we labeled cytoskeleton/extracellular contains eight genes. Only one of these, syndecan 2 (Sdc2) is in a cluster that has a maximum during the light period. For the most part, these genes seem to reflect muscle mechanical activity during the dark period. In contrast, the distribution of genes in the cell cycle group spans many clusters, which illustrates the progression of stem cells through the cell cycle with cell division beginning during the light period.
Surprisingly few genes with circadian rhythms are associated with protein degradation. Enhanced expression of GS, which is glucocorticoid responsive and is associated with several atrophy conditions is found in cluster 7, along with a few other relevant genes. In the case of GS, data suggest that the maximum expression of this gene is directly associated with the maximum of the corticosterone rhythm, which occurs several hours earlier (38). However, no such data are available for other cluster 7 genes associated with protein degradation. What is surprising is that ubiquitin B, C (Ubb, Ubc) is in cluster 1. Enhanced expression of this gene is associated with several muscle atrophy conditions, including atrophy induced by glucocorticoids (14). The genes in the small molecule metabolism group concentrate in cluster 6, which probably reflects the increased activity of the animal during the dark period. Likewise, surprisingly few genes associated with carbohydrate metabolism have circadian rhythms. The fact that 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 1 (Pfkfb1), along with most of the mitochondrial genes are in cluster 7, suggest that this is the period of highest energy demand by the musculature. However, these animals were housed in single cages and were relatively sedentary, which may influence energy demands by muscle fibers.
The last grouping was transport. Three of the four genes in this group were in cluster 6, which is rational, given the activity of the animals. The last, Slc41a3, is a Mg+ transporter found in cluster 2 (36). Very little data are available on the function of this gene in skeletal muscle.
These microarray experiments only reflect changes in the amount of expressed message for a gene. Although we only identified 109 genes whose message had a rhythm with a 24-h periodicity, the nature of some of these genes will magnify the effect of the rhythmicity. For example, rhythmicity in Pum2, which mediates mRNA degradation, will likely change the amount of many other messages. However, these changes may not have a strict 24-h periodicity. Similarly, the fact that many phosphatases and kinases have rhyhmicity will magnify oscillations at the functional level. Similar to secondary changes in the amount of message, rhythmic changes in function may not necessarily have a 24-h periodicity.
Perspectives and Significance
Although much progress has been made in understanding the control of circadian rhythms in the SCN, translation of control to peripheral tissues, which ultimately mediate systemic biological rhythms, is much less well understood. The present study identifies patterns of circadian gene expression changes in one peripheral tissue: skeletal muscle. It also identifies eight transcription factors that have been implicated in central clock mechanisms as having oscillating patterns in muscle as well. Extensions of such studies to other peripheral tissues such as liver and adipose tissue will address the question of what genes are regulated in a circadian pattern in multiple tissues of an organism and will allow a better understanding of how changes in multiple peripheral tissues can be integrated into systemic biological effects, such as rhythmic changes in energy metabolism. This study also demonstrates that although glucocorticoids serve as important signals for translating rhythms from central control centers in the brain to the periphery, factors other than glucocorticoids likely also play a role in this translation.
GRANTS
This work was supported by Grants GM 24211 and GM 67650 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD, and by a grant from NASA. This data set was developed under the auspices of a grant from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/NIH Programs in Genomic Applications HL-66614. E. Yang and I. P. Androulakis also acknowledge support from NSF Grant 0519563 and EPA Grant GAD R 832721-010.
The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. The article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
REFERENCES
- 1.Adams CM, Reitz J, De Brabander JK, Fermamisco JD, Li L, Brown MS, Goldstein JL. Cholesterol and 25-hydroxycholesterol inhibit activation of SREBPs by different mechanisms, both involving SCAP and Insigs. J Biol Chem 279: 52772–52780, 2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Almon RR, DuBois DC, Jin JY, Jusko WJ. Temporal profiling of the transcriptional basis for the development of corticosteroid-induced insulin resistance in rat muscle. J Endocrinol 184: 219–232, 2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Almon RR, DuBois DC, Yao Z, Hoffman EP, Ghimbovschi S, Jusko WJ. Microarray analysis of the temporal response of skeletal muscle to methylprednisolone: comparative analysis of two dosing regimens. Physiol Genomics 30: 282–299, 2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Badiu C Genetic clock of biologic rhythms. J Cell Molec Med 7: 408–416, 2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Challet E, Caldelas I, Graff C, Pevet P. Synchronization of the molecular clockwork by light- and food-related cues in mammals. Biol Chem 384: 711–719, 2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dardente H, Klosen P, Caldelas I, Pevet P, Masson-Pevet M. Phenotype of Per1- and Per2-expressing neurons in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of a diurnal rodent (Arvicanthis ansorgei): comparison with a nocturnal species, the rat. Cell Tissue Res 310: 85–92, 2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.DeBruyne JP, Noton E, Lambert CM, Maywood ES, Weaver DR, Reppert SM. A clock shock: mouse CLOCK is not required for circadian oscillator function. Neuron 50: 465–477, 2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Eberle D, Hegarty B, Bossard P, Ferre P, Foufelle F. SREBP transcription factors: master regulators of lipid homeostasis. Biochimie 86: 839–848, 2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Green CB, Douris N, Kojima S, Strayer CA, Fogerty J, Lourim D, Keller SR, Besharse JC. Loss of nocturnin, a circadian deadenylase, confers resistance to hepatic steatosis and diet-induced obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 9888–9893, 2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hastings M, O'Neill JS, Maywood ES. Circadian clocks: regulators of endocrine and metabolic rhythms. J Endocrinol 195: 187–198, 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Haughey DB, Jusko WJ. Analysis of methylprednisolone, methylprednisone and corticosterone for assessment of methylprednisolone disposition in the rat. J Chromatogr A 430: 241–248, 1988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.He YW, Li H, Zhang J, Hsu CL, Lin E, Zhang N, Guo J, Forbush KA, Bevan MJ. The extracellular matrix protein mindin is a pattern-recognition molecule for microbial pathogens. Nat Immunol 5: 88–97, 2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Herbert J, Goodyer IM, Grossman AB, Hastings MH, de Kloet ER, Lightman SL, Lupien SJ, Roozendaal B, Seckl JR. Do corticosteroids damage the brain? J Neuroendocrinol 18: 393–411, 2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jagoe RT, Lecker SH, Gomes M, Goldberg AL. Patterns of gene expression in atrophying skeletal muscles: response to food deprivation. FASEB J 16: 1697–1712, 2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Koistinen HA, Zierath JR. Regulation of glucose transport in human skeletal muscle. Ann Med 34: 410–418, 2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kostich WA, Sanes JR. Expression of zfh-4, a new member of the zinc finger-homeodomain family, in developing brain and muscle. Dev Dyn 202: 145–152, 1995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Levin MC, Monetti M, Watt MJ, Sajan MP, Stevens RD, Bain JR, Newgard CB, Farese RVS, Farese RVJ. Increased lipid accumulation and insulin resistance in transgenic mice expressing DGAT2 in glycolytic (type II) muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293: E1772–E1781, 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ma K, Mallidis C, Artaza J, Taylor W, Gonzalez-Cadavid N, Bhasin S. Characterization of 5′-regulatory region of human myostatin gene: regulation by dexamethasone in vitro. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 281: E1128–E1136, 2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mashek DG, Li LO, Coleman RA. Rat long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase mRNA, protein, and activity vary in tissue distribution and in response to diet. J Lipid Res 47: 2004–2010, 2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.McCarthy JJ, Andrews JL, McDearmon EL, Campbell KS, Barber BK, Miller BH, Walker JR, Hogenesch JB, Takahashi JS, Esser KA. Identification of the circadian transcriptome in adult mouse skeletal muscle. Physiol Genomics 31: 86–95, 2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.McCright B, Rivers AM, Audlin S, Virshup DM. The B56 family of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) regulatory subunits encodes differentiation-induced phosphoproteins that target PP2A to both nucleus and cytoplasm. J Biol Chem 271: 22081–22089, 1996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.McKay LI, DuBois DC, Sun YN, Almon RR, Jusko WJ. Corticosteroid effects in skeletal muscle: gene induction/receptor autoregulation. Muscle Nerve 20: 1318–1320, 1997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Minh NL, Damiola F, Tronche F, Schutz G, Schibler U. Glucocorticoid hormones inhibit food-induced phase-shifting of peripheral circadian oscillators. EMBO J 20: 7128–7136, 2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Murphy PJM Regulation of glucocorticoid receptor steroid binding and trafficking by the hsp90/hsp70-based chaperone machinery: implications for clinical intervention. Leukemia 19: 710–712, 2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Oishi K, Miyazaki K, Kadota K, Kikuno R, Nagase T, Atsumi Gi Ohkura N, Azama T, Mesaki M, Yukimasa S, Kobayashi H, Iitaka C, Umehara T, Horikoshi M, Kudo T, Shimizu Y, Yano M, Monden M, Machida K, Matsuda J, Horie S, Todo T, Ishida N. Genome-wide expression analysis of mouse liver reveals CLOCK-regulated circadian output genes. J Biol Chem 278: 41519–41527, 2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ramakrishnan R, DuBois DC, Almon RR, Pyszczynski NA, Jusko WJ. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacogenomics of methylprednisolone during 7-day infusions in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 300: 245–256, 2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Reddy AB, Wong GKY, O'Neill J, Maywood ES, Hastings MH. Circadian clocks: neural and peripheral pacemakers that impact upon the cell division cycle. Mutat Res 574: 76–91, 2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ronn SG, Billestrup N, Mandrup-Poulsen T. Diabetes and suppressors of cytokine signaling proteins. Diabetes 56: 541–548, 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sanoudou D, Haslett JN, Kho AT, Guo S, Gazda HT, Greenberg SA, Lidov HGW, Kohane IS, Kunkel LM, Beggs AH. Expression profiling reveals altered satellite cell numbers and glycolytic enzyme transcription in nemaline myopathy muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 4666–4671, 2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Steeves TDL, King DP, Zhao Y, Sangorum AM, Du F, Bowcock AM, Moore RY, Takahashi JS. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human CLOCK gene: expression in the superchiasmatic nuclei. Genomics 57: 189–200, 1999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Stromstedt M, Waterman MR, Haugen TB, Tasken K, Parvinen M, Rozman D. Elevated expression of lanosterol 14a-demethylase (CYP51) and the synthesis of oocyte meiosis-activating sterols in postmeiotic germ cells of male rats. Endocrinology 139: 2314–2321, 1998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sun YN, McKay LI, DuBois DC, Jusko WJ, Almon RR. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic models for corticosteroid receptor down-regulation and glutamine synthetase induction in rat skeletal muscle by a receptor/gene-mediated mechanism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288: 720–728, 1999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tsukiyama-Kohara K, Vidal SM, Gingras AC, Glover TW, Hanash SM, Heng H, Sonenberg N. Tissue distribution, genomic structure, and chromosome mapping of mouse and human eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding proteins 1 and 2. Genomics 38: 353–363, 1996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ueda HR, Hayashi S, Chen W, Sano M, Machida M, Shigeyoshi Y, Iino M, Hashimoto S. System-level identification of transcriptional circuits underlying mammalian circadian clocks. Nat Genet 37: 187–192, 2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Vanlandingham JW, Tassabehji NM, Somers RC, Levenson CW. Expression profiling of p53-target genes in copper-mediated neuronal apoptosis. Neuromolecar Med 7: 311–324, 2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wabakken T, Rain E, Kveine M, Aasheim HC. The human solute carrier SLC41A1 belongs to a novel eukaryotic subfamily with homology to prokaryotic MgtE Mg2+ transporters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 306: 718–724, 2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wang X, McLachlan J, Zamore PD, and Tanaka-Hall TM. Modular recognition of RNA by a human pumilio-homology domain. Cell 110: 501–512, 2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yao Z, DuBois DC, Almon RR, Jusko WJ. Modeling circadian rhythms of glucocorticoid receptor and glutamine synthetase expression in rat skeletal muscle. Pharm Res 23: 670–679, 2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yu X, Burgess SC, Ge H, Wong KK, Nassem RH, Garry DJ, Sherry AD, Malloy CR, Berger JP, Li C. Inhibition of cardiac lipoprotein utilization by transgenic overexpression of Angptl4 in the heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 1767–1772, 2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zambon AC, McDearmon EL, Salomonis N, Vranizan KM, Johansen KL, Adey D, Takahashi JS, Schambelan M, Conklin BR. Time- and exercise-dependent gene regulation in human skeletal muscle. Genome Biol 4: R61, 2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]