Abstract
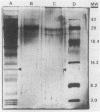
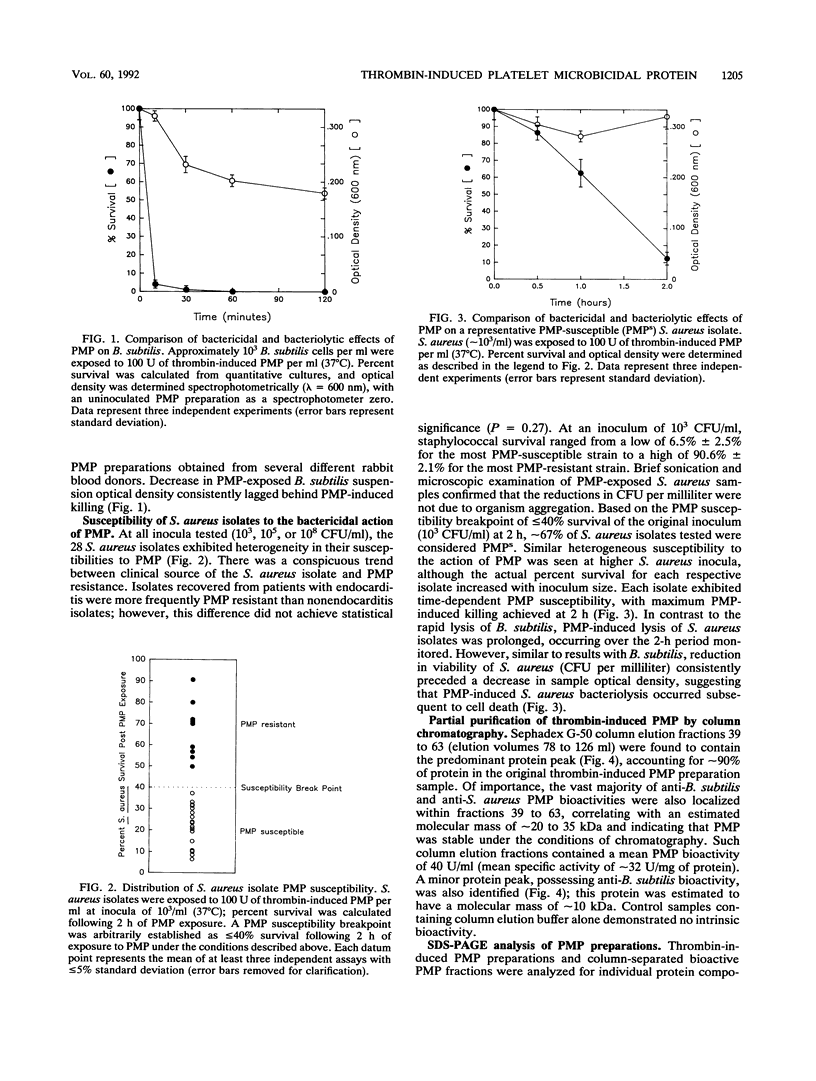
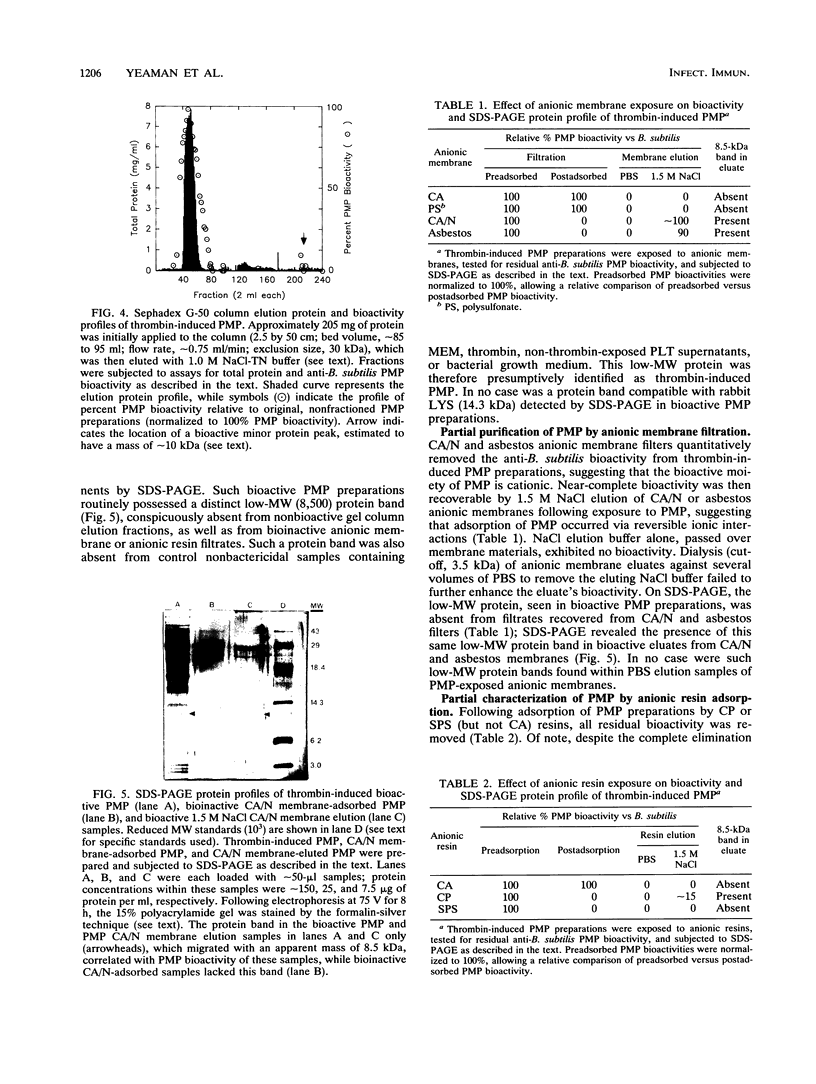
Thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein (PMP) is considered to play an important role in preventing an important role in preventing streptococcal endocarditis. However, the structural features and functions of PMPs have not been well characterized, and their antibacterial spectra against other common endocarditis pathogens, such as the staphylococci, are not known. Thrombin stimulation of washed rabbit platelets (10(8)/ml) yielded a PMP-rich preparation with a specific activity of approximately 25 U/mg of protein as determined by Bacillus subtilis bioassay. Twenty-eight clinical and laboratory Staphylococcus aureus isolates, exposed to a standardized PMP preparation (100 U/ml for 2 h at 37 degrees C), exhibited a Poisson-distributed heterogeneity to the bactericidal action of PMP, with approximately one-third designated as PMP resistant. Gel filtration chromatography (Sephadex G-50) identified the bioactive moiety within PMP preparations to be in the major protein elution peak; sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) presumptively identified PMP as a low-molecular-weight (MW) (8,500) protein present only in such bioactive protein peaks. Both the bioactivity of PMP preparations and the low-MW protein band were removable by specific anionic membranes (e.g., cellulose-acetate/nitrate), as well as by a variety of anionic resins, further corroborating the suspected cationic charge of PMP. In addition, both PMP bioactivity and the low-MW protein band were recoverable by 1.5 M NaCl elution of the anionic membrane filters post-PMP adsorptive removal. Adsorption of bioactive PMP preparations by highly PMP-susceptible B. subtilis (10(8) CFU/ml, 30 min) resulted in a near-complete loss of residual bioactivity; in contrast, adsorption of bioactive PMP preparations with less PMP-susceptible S. aureus strains failed to reduce bioactivity. Significant lysozyme contamination of PMP-rich preparations was ruled out by determination of differences between bioactive PMP preparations and exogenous lysozyme as regards (i) relative heat stabilities; (ii) differential bactericidal activity versus B. subtilis and Micrococcus luteus; and (iii) SDS-PAGE protein profiles. These data show that the bioactive PMP protein moiety is of low MW, is heat stable, is probably cationic (similar to leukocyte-derived defensins), and possesses potent bactericidal activity against a significant percentage of S. aureus isolates.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G., Fekety F. R. Experimental endocarditis due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Description of a model. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jul;134(1):1–7. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buiting A. G., Thompson J., van der Keur D., Schmal-Bauer W. C., Bertina R. M. Procoagulant activity of endocardial vegetations and blood monocytes in rabbits with Streptococcus sanguis endocarditis. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Nov 24;62(3):1029–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. F., Martinez R. J. Antibacterial peptide from normal rabbit serum. 3. Inhibition of microbial electron transport. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):5988–5994. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson C. C., White J. G. Platelet interaction with bacteria. II. Fate of the bacteria. Am J Pathol. 1971 Nov;65(2):381–397. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson D. M., Tew J. G. beta-Lysin of platelet origin. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):501–513. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.501-513.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake T. A., Pang M. Effects of interleukin-1, lipopolysaccharide, and streptococci on procoagulant activity of cultured human cardiac valve endothelial and stromal cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):507–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.507-512.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake T. A., Pang M. Staphylococcus aureus induces tissue factor expression in cultured human cardiac valve endothelium. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):749–756. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Beeson P. B. Experimental bacterial endocarditis. I. Colonization of a sterile vegetation. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Feb;53(1):44–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Beeson P. B. Experimental bacterial endocarditis. II. Survival of a bacteria in endocardial vegetations. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Feb;53(1):50–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T. Experimental bacterial endocarditis. IV. Structure and evolution of very early lesions. J Pathol. 1975 Feb;115(2):81–89. doi: 10.1002/path.1711150204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. Defensins. Eur J Haematol. 1990 Jan;44(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1990.tb00339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G. Comparative bactericidal activities of blood serum and plasma serum. J Exp Med. 1960 Jul 1;112:15–22. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann M., Suchard S. J., Boxer L. A., Waldvogel F. A., Lew P. D. Thrombospondin binds to Staphylococcus aureus and promotes staphylococcal adherence to surfaces. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):279–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.279-288.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Bayer A. S., Karchmer A. W., Theofilopoulos A. N., Swartz M. N. Circulating immune complexes in prosthetic valve endocarditis. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Nov;143(11):2081–2084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Valone J. A., Sande M. A. Bacterial adherence in the pathogenesis of endocarditis. Interaction of bacterial dextran, platelets, and fibrin. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1394–1404. doi: 10.1172/JCI109057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Zak O., Vosbeck K., Sande M. A. Bacterial adhesion in the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis. Effect of subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations on streptococcal adhesion in vitro and the development of endocarditis in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1381–1384. doi: 10.1172/JCI110388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Lehrer R. I. Purification and antibacterial activity of antimicrobial peptides of rabbit granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):150–154. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.150-154.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler B. B., Nachman R. L. Rabbit platelet bactericidal protein. J Exp Med. 1971 Nov 1;134(5):1114–1130. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.5.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]