Abstract
The results of this study show that lipoarabinomannans (LAM) isolated from a virulent strain and from an avirulent strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which have recently been shown to differ markedly in terms of the structures of their nonreducing termini, also differ markedly in the capacity to induce the secretion of tumor necrosis factor from murine macrophages. It was found that LAM from the avirulent H37Ra strain was 100-fold more potent at inducing tumor necrosis factor secretion than LAM from the virulent Erdman strain, thus leading us to hypothesize that the structure of LAM from a given mycobacterial isolate may directly influence its ability to elicit, or avoid, cytokine-mediated mechanisms of host resistance.
Full text
PDF
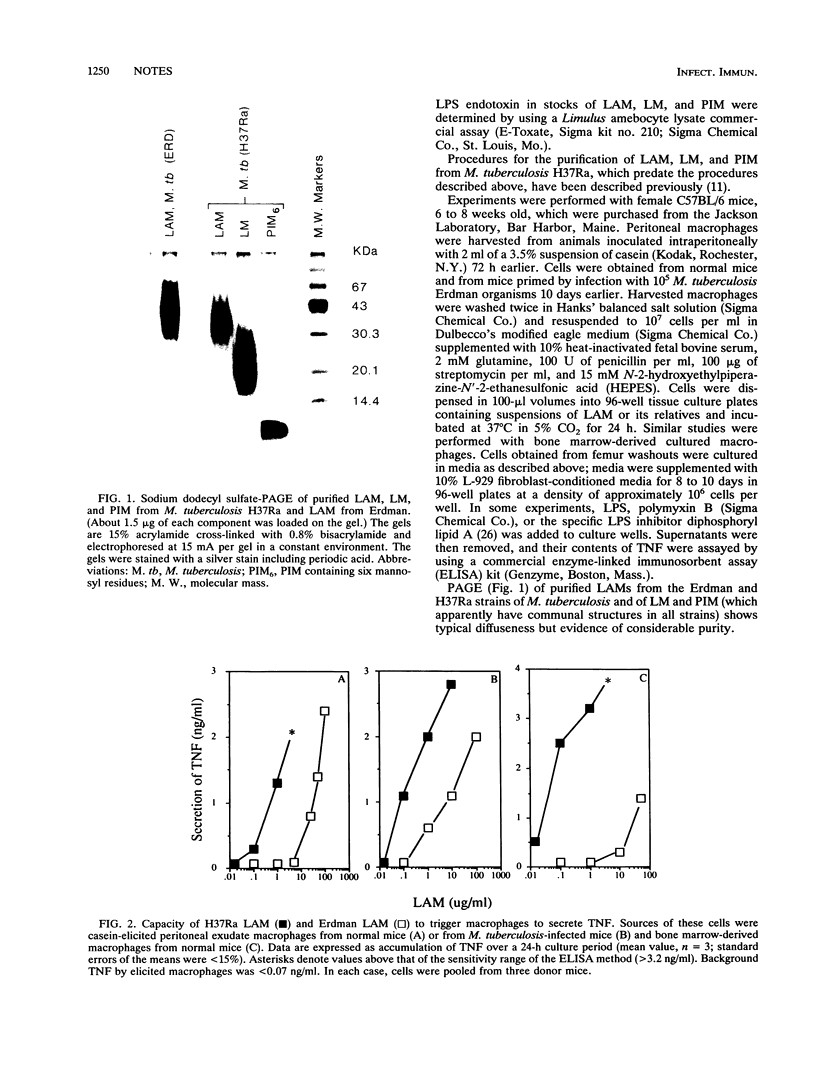
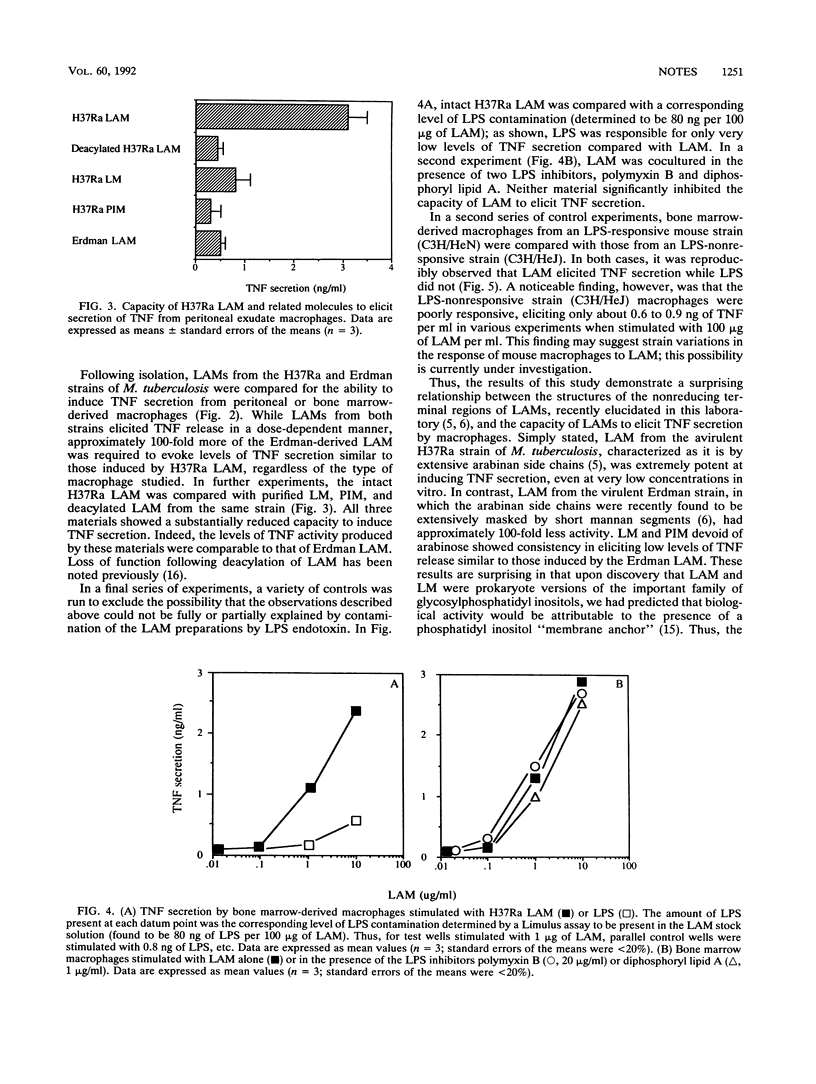
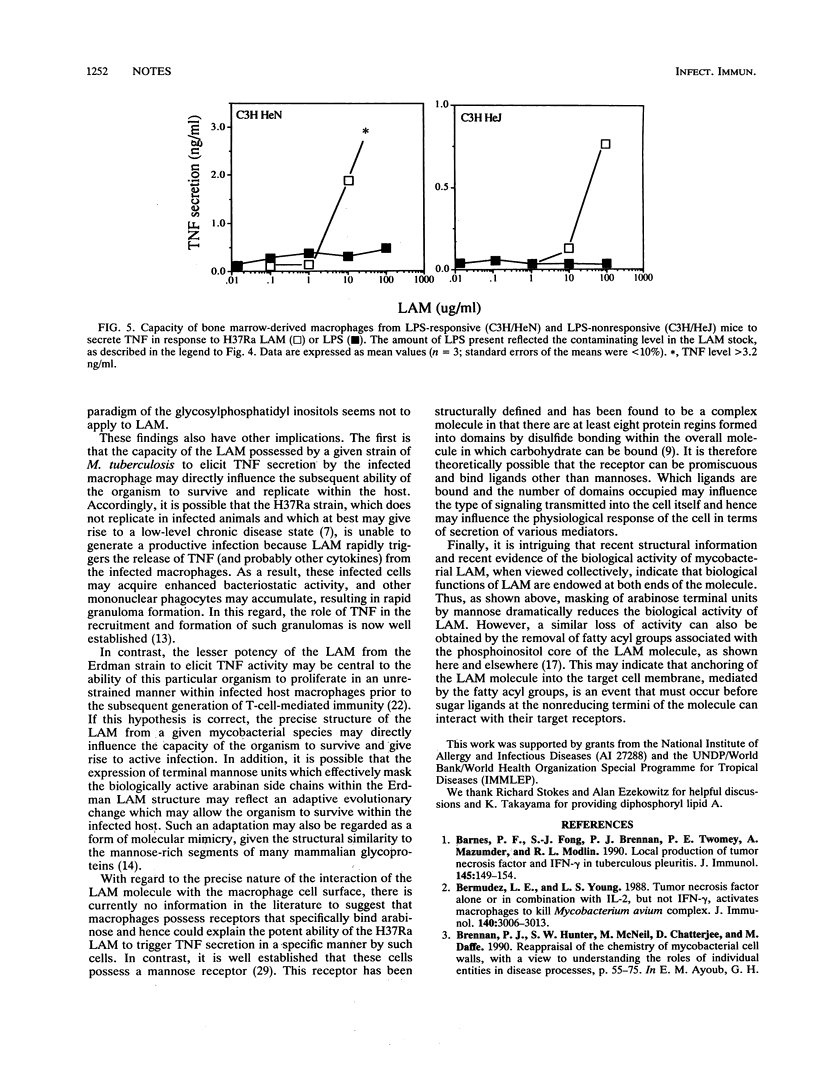

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. F., Fong S. J., Brennan P. J., Twomey P. E., Mazumder A., Modlin R. L. Local production of tumor necrosis factor and IFN-gamma in tuberculous pleuritis. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Young L. S. Tumor necrosis factor, alone or in combination with IL-2, but not IFN-gamma, is associated with macrophage killing of Mycobacterium avium complex. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3006–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J., Fan X. D., Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J., Bloom B. R. Lipoarabinomannan, a possible virulence factor involved in persistence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis within macrophages. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1755–1761. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1755-1761.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D., Bozic C. M., McNeil M., Brennan P. J. Structural features of the arabinan component of the lipoarabinomannan of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9652–9660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Morrison N. E., Montalbine V. Immune response to persistent mycobacterial infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):430–438. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.430-438.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Titto E. H., Catterall J. R., Remington J. S. Activity of recombinant tumor necrosis factor on Toxoplasma gondii and Trypanosoma cruzi. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1342–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Sastry K., Bailly P., Warner A. Molecular characterization of the human macrophage mannose receptor: demonstration of multiple carbohydrate recognition-like domains and phagocytosis of yeasts in Cos-1 cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1785–1794. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha potentiates neutrophil antimicrobial activity: increased fungicidal activity against Torulopsis glabrata and Candida albicans and associated increases in oxygen radical production and lysosomal enzyme release. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2115–2122. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2115-2122.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J. Evidence for the presence of a phosphatidylinositol anchor on the lipoarabinomannan and lipomannan of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9272–9279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Gandhi R. R., Weinstein D. E., Levis W. R., Patarroyo M. E., Brennan P. J., Cohn Z. A. Mycobacterium leprae antigen-induced suppression of T cell proliferation in vitro. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):3028–3034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. C., Ballou C. E. Complete structures of the glycophospholipids of mycobacteria. Biochemistry. 1965 Jul;4(7):1395–1404. doi: 10.1021/bi00883a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno C., Mehlert A., Lamb J. The inhibitory effects of mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan and polysaccharides upon polyclonal and monoclonal human T cell proliferation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Nov;74(2):206–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno C., Taverne J., Mehlert A., Bate C. A., Brealey R. J., Meager A., Rook G. A., Playfair J. H. Lipoarabinomannan from Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces the production of tumour necrosis factor from human and murine macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 May;76(2):240–245. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Interferon-gamma, the activated macrophage, and host defense against microbial challenge. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Apr;108(4):595–608. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-4-595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kato K. Endogenous tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is essential to host resistance against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2563–2569. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2563-2569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano Y., Onozuka K., Terada Y., Shinomiya H., Nakano M. Protective effect of recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha in murine salmonellosis. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1935–1941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M. The kinetics of emergence and loss of mediator T lymphocytes acquired in response to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):293–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., McGroarty E. J. High-molecular-weight components in lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella typhimurium, Salmonella minnesota, and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):738–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.738-745.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio E. P., Sarno E. N., Galilly R., Cohn Z. A., Kaplan G. Thalidomide selectively inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha production by stimulated human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):699–703. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J., Krahenbuhl J. L. Mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan inhibits gamma interferon-mediated activation of macrophages. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1232–1236. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1232-1236.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Qureshi N., Beutler B., Kirkland T. N. Diphosphoryl lipid A from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides ATCC 17023 blocks induction of cachectin in macrophages by lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1336–1338. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1336-1338.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Wei H., Manogue K. R., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Nguyen H. T., Kuo G. C., Beutler B., Cotran R. S., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces cachexia, anemia, and inflammation. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1211–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis R. S., Amir-Tahmasseb M., Ellner J. J. Induction of interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor by mycobacterial proteins: the monocyte western blot. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3348–3352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wileman T. E., Lennartz M. R., Stahl P. D. Identification of the macrophage mannose receptor as a 175-kDa membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2501–2505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]