Abstract
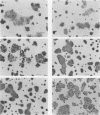
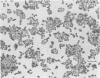
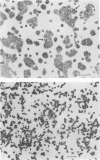
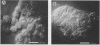
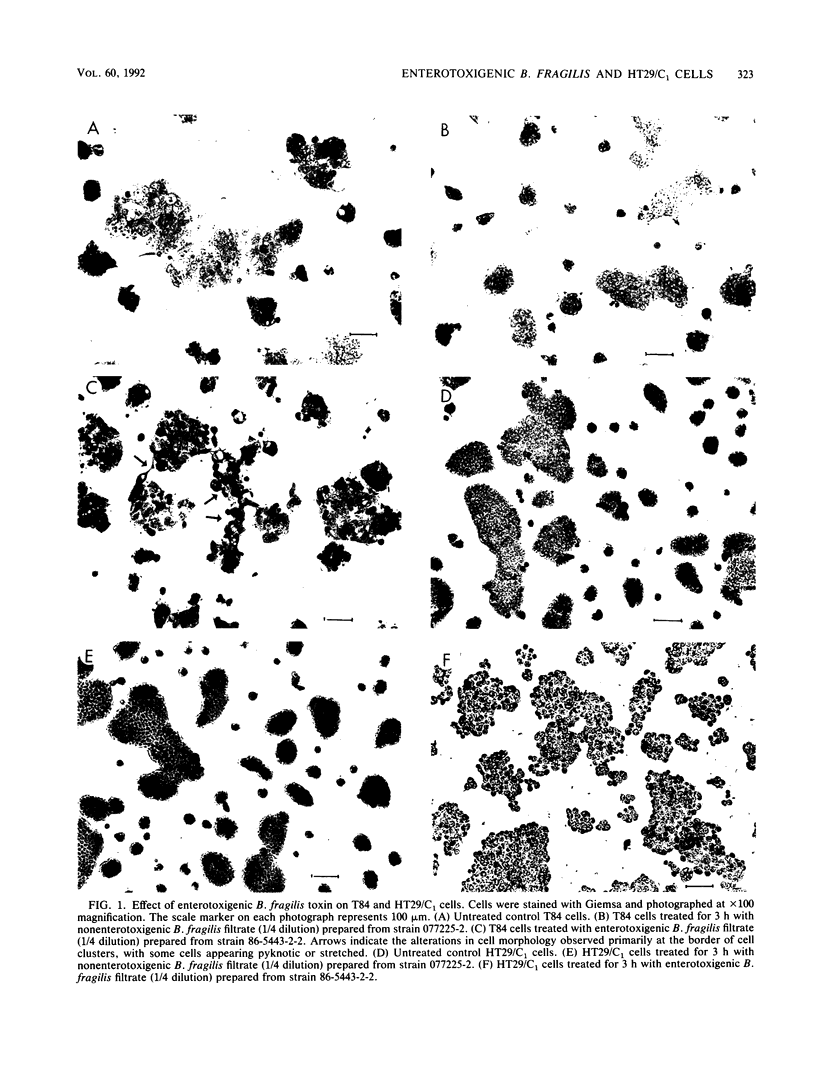
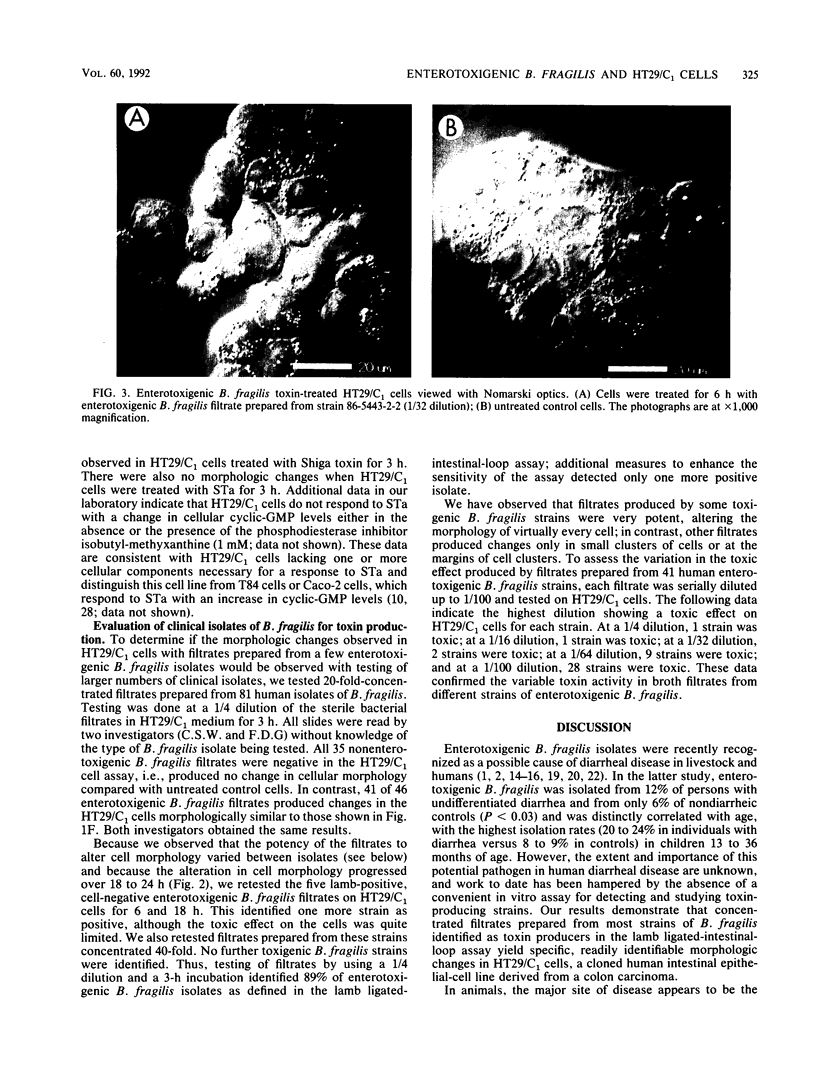
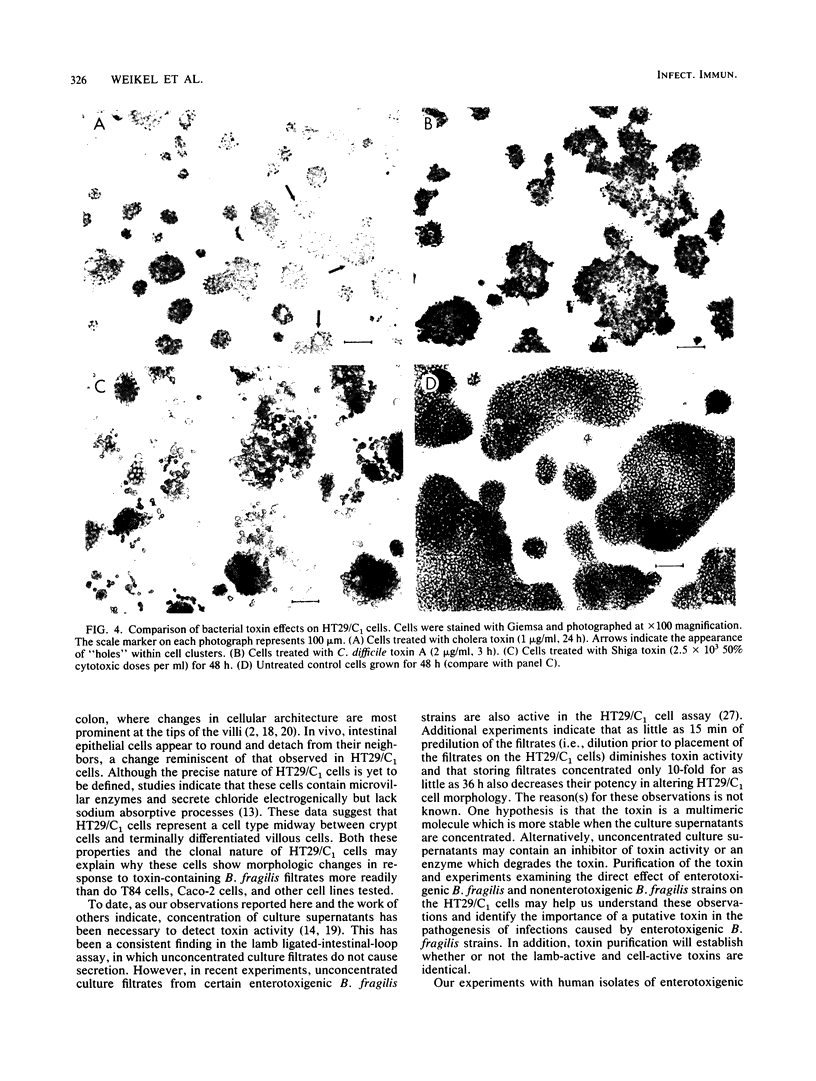
Bacteroides fragilis has been associated with causation of diarrheal disease in livestock and humans. To date, conventional tissue culture and animal assays used to detect the biologic activity of bacterial enterotoxins have failed with enterotoxigenic B. fragilis. Although enterotoxigenic B. fragilis stimulates intestinal secretion in lamb and calf ligated intestinal loops, infant rabbits, and adult rabbits with ligated ceca, these animal systems are costly and complicated, which limits their usefulness for identification of enterotoxigenic B. fragilis strains. Using the cloned human colonic-epithelial-cell line HT29/C1, we have developed an in vitro assay that is 89% sensitive and 100% specific in detecting enterotoxigenic B. fragilis strains as defined by the lamb ligated-intestinal-loop assay. Subconfluent HT29/C1 cells treated with concentrated bacterium-free culture supernatants of enterotoxigenic B. fragilis strains develop specific and striking morphologic changes including loss of cell-to-cell attachments, rounding, swelling, and, in some cases, pyknosis. These morphologic changes are initially visible at 1 h after treatment and progress over at least the first 24 h. This tissue culture assay should prove useful in epidemiologic studies of enterotoxigenic B. fragilis and may facilitate basic studies to identify the B. fragilis toxin(s) and its mechanism of action.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Border M., Firehammer B. D., Shoop D. S., Myers L. L. Isolation of Bacteroides fragilis from the feces of diarrheic calves and lambs. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):472–473. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.472-473.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. E., Bergeland M. E., Myers L. L., Shoop D. S. Exfoliating colitis associated with enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis in a piglet. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1989 Oct;1(4):349–351. doi: 10.1177/104063878900100413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Frantz J. C., Robertson D. C. Chemical properties of heat-stable enterotoxins produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of different host origins. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):539–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.539-548.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Kirchhoff L. V., Shields D. S., Nations M. K., Leslie J., de Sousa M. A., Araujo J. G., Correia L. L., Sauer K. T., McClelland K. E. Prospective study of diarrheal illnesses in northeastern Brazil: patterns of disease, nutritional impact, etiologies, and risk factors. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):986–997. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet C., Sahuquillo-Merino C., Coudrier E., Louvard D. Absorptive and mucus-secreting subclones isolated from a multipotent intestinal cell line (HT-29) provide new models for cell polarity and terminal differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):345–357. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huott P. A., Liu W., McRoberts J. A., Giannella R. A., Dharmsathaphorn K. Mechanism of action of Escherichia coli heat stable enterotoxin in a human colonic cell line. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):514–523. doi: 10.1172/JCI113626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Donohue-Rolfe A., Jacewicz M. Shigella toxin(s): description and role in diarrhea and dysentery. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;15(3):403–438. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S. A., Donowitz M., Watson A. J., Sharp G. W., Crane J. K., Weikel C. S. Characterization of the synergistic interaction of Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin and carbachol. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Pt 1):G592–G601. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.4.G592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loosli J., Gyr K., Stalder H., Stalder G. A., Vischer W., Voegtlin J., Gasser M., Reichlin B. Etiology of acute infectious diarrhea in a highly industrialized area of Switzerland. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jan;88(1 Pt 1):75–79. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montrose-Rafizadeh C., Guggino W. B., Montrose M. H. Cellular differentiation regulates expression of Cl- transport and cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator mRNA in human intestinal cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4495–4499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Firehammer B. D., Shoop D. S., Border M. M. Bacteroides fragilis: a possible cause of acute diarrheal disease in newborn lambs. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):241–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.241-244.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Shoop D. S. Association of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis with diarrheal disease in young pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1987 May;48(5):774–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Shoop D. S., Byars T. D. Diarrhea associated with enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis in foals. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Nov;48(11):1565–1567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Shoop D. S., Collins J. E., Bradbury W. C. Diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis in infant rabbits. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2025–2030. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2025-2030.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Shoop D. S., Collins J. E. Rabbit model to evaluate enterovirulence of Bacteroides fragilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1658–1660. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1658-1660.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Shoop D. S., Firehammer B. D., Border M. M. Association of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis with diarrheal disease in calves. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1344–1347. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Shoop D. S., Stackhouse L. L., Newman F. S., Flaherty R. J., Letson G. W., Sack R. B. Isolation of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis from humans with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2330–2333. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2330-2333.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Shiga and Shiga-like toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):206–220. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.206-220.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. D., Merson M. H. The magnitude of the global problem of acute diarrhoeal disease: a review of active surveillance data. Bull World Health Organ. 1982;60(4):605–613. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor N. S., Thorne G. M., Bartlett J. G. Comparison of two toxins produced by Clostridium difficile. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):1036–1043. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.1036-1043.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A., Warren K. S. Selective primary health care: an interim strategy for disease control in developing countries. N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 1;301(18):967–974. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911013011804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson A. J., Levine S., Donowitz M., Montrose M. H. Kinetics and regulation of a polarized Na(+)-H+ exchanger from Caco-2 cells, a human intestinal cell line. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 1):G229–G238. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.2.G229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weikel C. S., Spann C. L., Chambers C. P., Crane J. K., Linden J., Hewlett E. L. Phorbol esters enhance the cyclic GMP response of T84 cells to the heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli (STa). Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1402–1407. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1402-1407.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]